Abstract
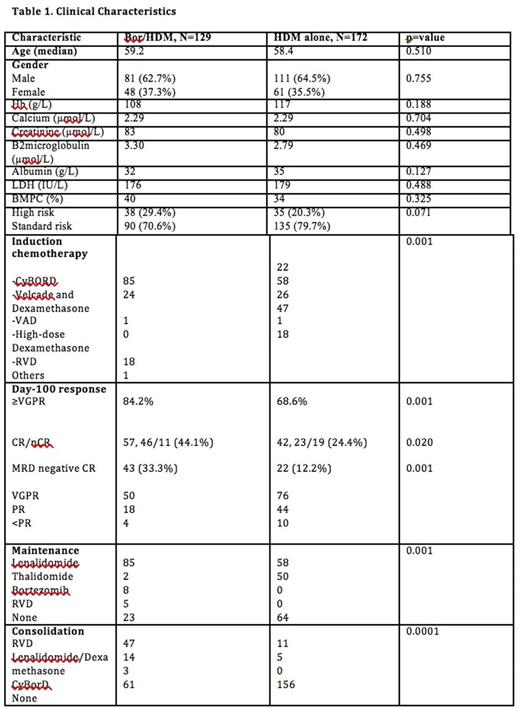
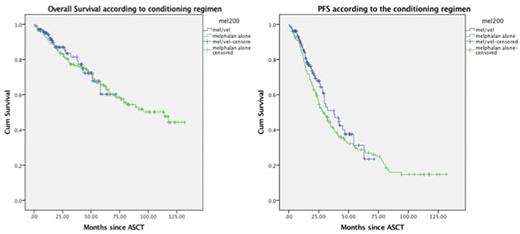
Introduction Recent data suggests that bortezomib, a proteasome inhibitor, in combination with high-dose melphalan (Bor-HDM) provides with a synergistic effect able to improve the level of response for MM patients undergoing auto-SCT. In the present study, patients receiving induction followed by ASCT with Bor-HDM and HDM alone were evaluated. Methods All consecutive patients undergoing ASCT from 01/2004 to 03/2016 were evaluated. All patients received induction chemotherapy before undergoing auto-SCT. Patients received conditioning with either HDM at 200 mg/m2 (or adjusted as per renal failure) or HDM with Bortezomib (Bor-HDM). Most of patients received Bortezomib conditioning at 1.3 mg/m2. As per physician discretion, the dose of 1 mg/m2 was also employed in 30% of cases. Definitions of response and progression were used according to the EBMT modified criteria. MRD negativity was assessed by flow cytometry at day-100 post-ASCT. Results Clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1. Among 301 cases, 129 were treated with Bor-HDM while 172 patients went onto receive HDM alone as part of the conditioning regimen. Induction regimens are shown in Table 1. At the time of analysis, 83% and 58% of patients in the Bor-HDM and HDM group are still alive and 34% and 69.1% of patients have already progressed, respectively. At day-100 post ASCT, ORR of 97%, with CR/VGPR rate of 84.2% was seen in the Bor-HDM group compared to 94.2% and 68.6% in the HDM group (p=0.001). MRD negativity was higher in the Bor-HDM group (33.3%) compared to HDM (12.2%) (p=0.001). Median OS was similar for Bor-HDM and HDM (p=0.864) (Fig 1a). In addition, median PFS did not differ among patients receiving HDM or Bor-HDM (37.7months vs 29.3 months, p=0.2) (Fig1b) In conclusion,Bor-HDMis a conditioning regimen able to provide higher rates ofnCR/CR, as well as MRD negativity compared to HDM alone. Further studies are warranted to explore this regimen, especially when other upfront therapies are employed.
Overall Survival according to the conditioning regimen employed for patients with MM undergoing ASCT
Overall Survival according to the conditioning regimen employed for patients with MM undergoing ASCT
Progression-Free Survival according to the conditioning regimen employed for patients with MM undergoing ASCT
Progression-Free Survival according to the conditioning regimen employed for patients with MM undergoing ASCT
Jimenez-Zepeda:Takeda: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene, Janssen, Amgen, Onyx: Honoraria. Neri:Celgene and Jannsen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Bahlis:Onyx: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal