Abstract
Background: While therapeutic outcomes in patients (pts) with acquired severe aplastic anemia (SAA) has greatly improved in recent years, results remain poor for pts who are refractory to first-line immunosuppressive therapy (IST) and lack a matched unrelated donor. We conducted a prospective multi-center phase II uncontrolled trial to assess the efficacy and safety of cord blood transplantation (CBT) in refractory SAA pts (NCT 01343953).
Patients and methods: Pts with SAA refractory to IST with anti-thymocyte globuline (ATG) and ciclosporin (CsA) were eligible in case of no existing matched unrelated donor but available one or two unrelated CB units containing alone or both together more than 4 x 107/Kg frozen nucleated cells/Kg (no more than 2 out of 6 HLA mismatches allowed between each CB unit and the pts). Pts with isolated bone marrow cytogenetic abnormality (absence of morphologic evidence of myelodysplastic syndrome) were also eligible. The conditioning regimen consisted of fludarabine 30mg/m2 (D-6 to D-3), cyclophosphamide 30mg/kg (D-6 to D-3), ATG (thymoglobulin) 2.5mg/kg at D-3 and D-2 (5mg/Kg total dose) and total body irradiation (2 Gray) on D-2. All pts received one injection of anti-CD20 (150 mg/m2) to prevent EBV reactivation (D+5). CsA was given alone as prophylaxis for graft versus host disease (GVHD). The trial used the Fleming's Single Stage Phase II Design, with sample size computed to demonstrate an improved overall survival (OS) rate at one year from 20% up to 50%, with type I and type II error rates set at 0.05. A minimum sample of 25 pts was required, with a minimum number of 9 pts alive at one year needed to indicate treatment efficacy. Secondary endpoints included cumulative incidences (CumI) of engraftment, acute and chronic GVHD (aGVHD and cGVHD), infections, relapse and late cause of death.
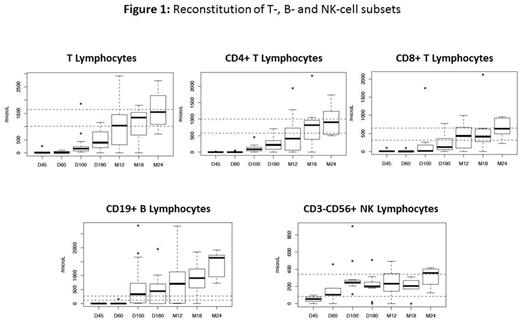
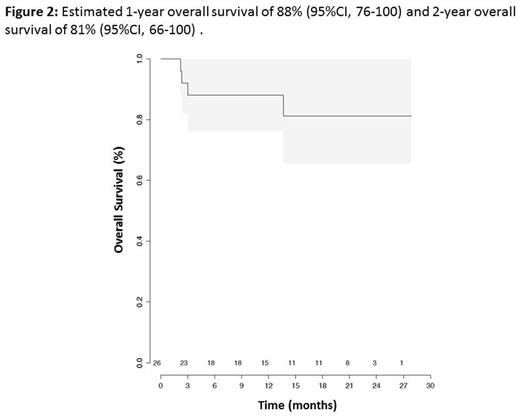
Results: 29 pts were included between June 2011 and October 2015. One pt was diagnosed with dyskeratosis congenita and a matched unrelated donor was identified for another pt between inclusion and anticipated date of CBT (exclusion criteria). One pt died before CBT due to a septic shock (D+4 after inclusion). Analyses were conducted in the remaining 26 pts. Median time between SAA diagnosis and CBT was 12 months (interquartile range (IQR) 8.7 to 17.8). All pts received at least one course of IST before CBT (2 courses, n=8). Twenty-three pts received 20 or more transfusions before CBT. BM karyotyping showed 2 pts respectively with monosomy 7 in 4 and 15 mitoses as well as one pt with trisomy 8 in 4 mitoses before CBT. Eight pts (31%) have a PNH clone (median 4.5% [IQR: 3.1-9.7]). Median age at time of CBT was 16 years (IQR 8.25 to 23) and median follow-up is 13.2 months (IQR 4.1 - 23.5). Three out of 26 pts incorrectly received twice the dose of ATG (10mg/Kg total dose) due to protocol violation. Sixteen pts received one CB and 10 received two CB units. Median number of nucleated cells infused was 3.7 x 107/Kg (IQR, 3-4.9) and CD34+ cells infused was 1.4 x 105/Kg (IQR, 1.0-1.9). Myeloid engraftment occurred in 23 pts, with a 60 day-CumI of neutrophil engraftment of 88.5% with full chimerism for all of them. Three pts did not engraft (2 deaths at D71 and D92 and one successful second HSCT). The 100 day-CumI of grade II-IV acute GVHD was 40% (95% CI, 20-60) (8 grade II; 0 grade III; 2 grade IV). Among the 23 pts alive at day 100, five developed cGVHD leading to a one-year CumI of cGVHD at 27% (95% CI, 7-47) (severe cGvHD in 2 pts). During follow-up, 8 pts experienced a total of 18 grade III infections with a 6-month CumI of 32% (95% CI, 13-51). None of the pts presented post-transplant EBV-related lymphoproliferative disorder. Immune reconstitution is shown in Figure 1. Three pts died before 1 year due to non-engraftment (n=2) and infection (n=1, one of those who received twice the dose of ATG). With 23 pts alive at 1 year, the primary objective of the study was thus reached. The one-year treatment related mortality (TRM) was 15% (95%CI, 4-35). One additional pt who had also received twice the dose of ATG died (severe cGvHD) after one year (at 13.6 months), resulting in a 14-month OS of 81% (95%CI, 66-100) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: CBT with at least 4 x 107/Kg frozen nucleated cells/Kg after a FLU-CY-TBI-ATG conditioning regimen gave rise to very encouraging results in this particular high risk SAA refractory population. Pediatric and young adult SAA pts who are refractory to first-line IST should now be considered either way for matched unrelated donor or CBT.
Peffault de Latour:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal