Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRs), a class of 19- to 23-nucleotide non-coding RNA molecules, are involved in tumorigenesis by regulating tumor cells and microenvironment. Our study revealed serum miR21 expression in a large cohort of B-cell lymphoma patients and the biological function of miR21 both in vitro and in vivo.
Comparing with healthy volunteers, serum miR21 was significantly increased in patients with B-cell lymphoma (Figure 1A). As revealed by immunohistochemistry in 50 tumor samples of DLBCL, CD31-positive microvessels were more frequently observed in high miR21 group than in low miR21 group (Figure 1B). High miR21 expression patients displayed more peripheral blood Treg cells than low miR21 expression patients, instead of natural killer (NK) cells (Figure 1C).
We futher study the biological function of miR21, B-lymphoma cell SU-DHL-4 were transfected with miR21 mimics and treated with chemotherapeutic agents. Under the monoculture condition, as compared to the control mimics, ectopic expression of miR21 significantly diminished the cytotoxic effect of doxorubicin and cisplatin, but sensitized lymphoma cells to ABT-199. Under the direct co-culture system, mimicking lymphoma microenvironment, miR21 overexpression resulted in lymphoma cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents, but sensitivity to ABT-199 in the direct co-culture system. ABT-199 remarkably downregulated miR21 expression in both the monoculture system and the direct co-culture system, irrespective to Bcl-2 expression.
To clarify the underlying mechanism of miR21-mediated sensitization of ABT-199 on B-cell lymphoma, we studied the effect of miR21 on HUVEC sorted from the direct co-culture system. Co-culturing with miR21-overexpressing lymphoma cells significantly stimulated HUVEC growth, which was retarded by ABT-199 (Figure 2A). As detected by ELISA, VEGFA was increased by miR21 transfection and reduced by ABT-199 in both control siRNA-transfected HUVEC and Bcl-2 siRNA-transfected HUVEC (Figure 2B). Accordingly, similar changes of tube formation and endothelial cell migration towards lymphoma cells were present (Figure 2C). We hereafter studied the effect of miR21 on Treg cells sorted from the direct co-culture system. Consistent with change of VEGFA, co-culturing with miR21-overexpressing lymphoma cells significantly increased VEGFR2 expression on Treg cells, which were decreased by ABT-199 (Figure 2D). ABT-199-induced downregulation of VEGFA/VEGFR2 signaling was associated with Treg cell growth inhibition, resulting in reduction of immunosuppressive cytokine TGF-¦Â and molecule IL-2 (Figure 2E and 2F).
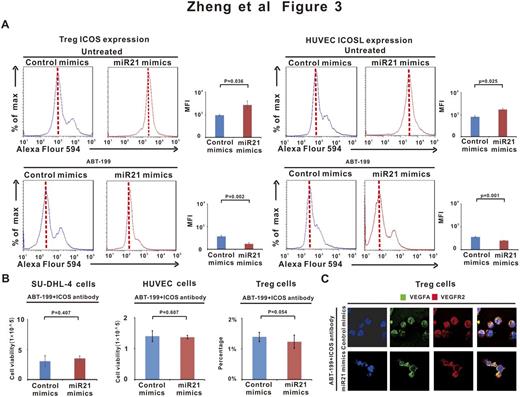
In the direct co-culture system, miR21 overexpression induced ICOS expression on Treg cells and ICOSL expression on HUVEC and, both of which were inhibited by ABT-199 (Figure 3A). To confirm the role of ICOS/ICOSL axis, antibody against ICOS was added to the direct co-culture system. Pharmacological inhibition of ICOS/ICOSL interaction significantly abrogated the sensitivity of miR21-overexpressing cells to ABT-199, as well as HUVEC and Treg cell growth (Figure 3B). Blockade of ICOS/ICOSL also interfered the action of ABT-199 on VEGFA/VEGFR2 signaling between Treg cells and endothelial cells (Figure 3C).
Murine xenograft model was established with subcutaneous injection of B-lymphoma cells, ABT-199 particularly retarded the growth of miR21-overexpressing tumors, consistent with the inhibition of ICOS/ICOSL axis, VEGFA/VEGFR2 signaling, tumor angiogenesis and Treg cell growth.
Collectively, these data demonstrated that miR21 plays an oncogenic role in B-cell lymphoma by modulating tumor microenvironment and supported clinical rationale for using miR21 as a biomarker to select chemoresistant B-lymphoma patients who may benefit from treatments containing ABT-199.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal