Abstract
Introduction. HIV infected individuals have an increased risk of developing lymphoma compared to sex- and age matched non-immunocompromised control population and approximately 2% of HIV infected individuals developed lymphoma (Gopal et al, J Natl cancer Inst 2013). Our group has been among the first who identified novel serum protein markers present at time of HIV diagnosis, which were predictive of subsequent lymphoma development (Vase et al, AIDS 2016). Galectins are important regulators of cell adhesion, apoptosis, cell cycle, and mRNA processing. Galectin-1 (Gal-1) is a known lectin-binding protein able to mediate Th2 skewed microenvironment in lymphomas (Juszczynski et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007; Cedeno-Laurent et al, Blood 2012), and facilitates HIV-infection (Sato et al, Ann N Y Acad Sci 2012). Increased serum Gal-1 levels were correlated to increased tumor burden and adverse clinical features in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) (Kamper et al, Blood 2011; Ouyang et al, Blood 2013) and low Gal-1 levels were associated with an increased risk of chronic graft-versus-host disease in patients with hematologic malignancies treated with non-myeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Petruskevicius et al, BMT 2016). In this study, we investigated whether the serum level of Gal-1 at the time of HIV diagnosis was predictive for subsequent lymphoma development.
Methods. We determined the serum levels of Gal-1 in serum samples from19 HIV infected patients collected at the time of HIV diagnosis. Measurements were performed using a time-resolved immunofluorometric assay, as previously described (Petruskevicius et al, BMT 2016). Patients were grouped based on clinical outcomes in (i) future HIV-associated lymphoma (HIV/lymphoma), (ii) future HIV-associated benign lymphadenopathy (HIV/adenopathy), and (iii) no future neoplasia (HIV/no neoplasia), Table 1. Furthermore, serum Gal-1 levels were compared to those of a healthy control group (n=30), as previously reported (Petruskevicius et al, BMT 2016). Gal-1 sample concentrations were calculated by regression anaysis on basis of a standard curve of recombinant Gal-1 at concentrations of 100 to 0.78 ng/mL with 1:4 sample dilutions. Gal-1 levels > 400ng/mL was included in the analyses with a value of 400ng/mL. Estimates of differences between groups were evaluated using Student's t-test or ANOVA on log transformed data. A ROC analysis was computed to establish cut-off values for serum galectin-1, with respect to development of lymphoma.
Results. Overall, the serum Gal-1 level in the HIV cohort was lower than in the healthy control group (p<0.001), Figure 1A. At HIV diagnosis, those HIV patients who would subsequently develop lymphoma had significantly lower levels of serum Gal-1 compared to the remaining cohort, Figure 1B (p=0.017). There was no gender-related difference (p=0.436) and Gal-1 serum levels did not correlate with either CD4 count (p=0.553) or viral load (p=0.600) at time of HIV diagnosis. In this size-limited study population, it was not possible to show any significant difference between HIV/lymphoma, HIV/adenopathy, and HIV/no neoplasia. ROC calculated cut-off of 2.6 ng/mL was able to separate HIV patients with future lymphoma from the remaining HIV patients and controls with a specificity of 78% and sensitivity of 100%. At this cut-off 13 (31%) patients were allocated to the low Gal-1 group, including all future lymphoma patients.
Conclusion. HIV infected patients had significant lower serum Gal-1 levels than compared to a healthy control cohort. All HIV infected patients that later developed lymphoma belonged to the subset with lowest serum Gal-1 levels. If confirmed in independent cohorts of HIV patients from the cART era, this observation will support the use of low serum levels of Gal-1 as an early predictive biomarker for subsequent lymphoma development in HIV infected individuals. This may in turn have potential implications on the clinical monitoring strategy of these patients.
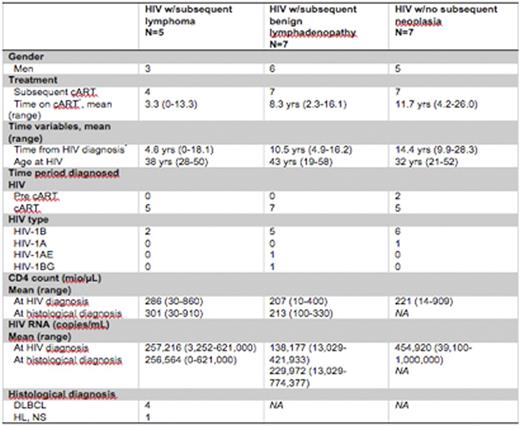
Characteristics of HIV patients in the serum galectin-1 study
*Time before lymphoma or day of follow up (death or study end)
Characteristics of HIV patients in the serum galectin-1 study
*Time before lymphoma or day of follow up (death or study end)
Serum levels of Gal-1. A: Serum Gal-1 levels in the HIV cohort (n=19) were significant lower than in the healthy control group (n=30). B: At HIV diagnosis, significant lower serum Gal-1 levels was observed in HIV-patients with future lymphoma diagnosis (n=5) compared to the remaining cohort (n=44).
Serum levels of Gal-1. A: Serum Gal-1 levels in the HIV cohort (n=19) were significant lower than in the healthy control group (n=30). B: At HIV diagnosis, significant lower serum Gal-1 levels was observed in HIV-patients with future lymphoma diagnosis (n=5) compared to the remaining cohort (n=44).
d'Amore:Servier: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Boards; CTI LIfe Sciences: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Boards.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal