Abstract
Introduction: Opportunistic infections such as Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) occur commonly in immunocompromised hosts such as patients (pts) with cancer (especially hematological malignancies such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia [CLL] and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma [iNHL]) or those receiving immunosuppressive therapies (such as steroids, chemotherapy). Recently, an increased risk of PJP infection was identified in 3 ongoing phase 3 studies evaluating idelalisib, administered in combination with the standard regimens rituximab (R) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), in front-line CLL and early-line iNHL. Subsequently, a comprehensive analysis evaluating PJP infection across the clinical development program was performed to identify possible risk factors for developing PJP infection, including age, concomitant therapy (co-therapy) administered, geographic distribution of PJP infection, and regional use of prophylaxis.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 2198 pts receiving study treatment with idelalisib alone or in combination with co-therapy (anti-CD20 antibody or BR) and pts receiving only co-therapy (anti-CD20 ± bendamustine) (n = 1391 and 807, respectively) across 8 studies (frontline/relapsed CLL and relapsed iNHL) between 2010 and 2016 was performed. PJP infection was defined based on MedDRA high-level term of pneumocystis infections. In this analysis, other parameters were included for evaluation of risk of developing PJP infection-prophylaxis for PJP, geographic region, age, and CD4 count.
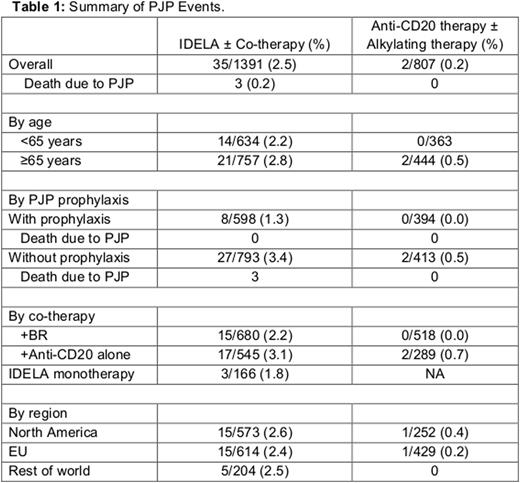
Results: The overall incidence of PJP infection was 2.5% in pts on idelalisib ± co-therapy vs 0.2% in pts receiving only anti-CD20 antibody alone or BR alone (relative risk = 12.5). The median time to PJP event was 141 days since initiation of IDELA or co-therapy. The incidence of PJP infection was similar, irrespective of pt age. In the pt population receiving IDELA ± co-therapy - prophylaxis for PJP reduced the incidence of infection to 1.3% (from 3.4% in pts not receiving prophylaxis). Additionally, analysis by type of co-therapy received - the incidence of PJP infection was 2.2% vs 3.1% with IDELA + BR and IDELA + anti-CD20 alone respectively. A correlation between CD4 count (<200 cells/mcL) and an increased risk of PJP infection was not observed. Additional data are provided in Table 1.
Conclusion: There is a small but increased risk of PJP infection during treatment with idelalisib within the clinical trial program. These data suggest that prophylaxis for PJP may reduce the risk of infection by as much as 60%. Administration of PJP prophylaxis is now recommended in all pts receiving treatment with idelalisib.
Sehn:roche/genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria; amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; seattle genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; TG therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; lundbeck: Consultancy, Honoraria; janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Hallek:Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen-Cilag: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; F. Hoffmann-LaRoche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Jurczak:Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Celltrion, Inc: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding. Brown:Infinity: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Sun BioPharma: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy. Barr:Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy. Catalano:Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead Sciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Coutre:Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Research Funding. Furman:Gilead Sciences: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Lamanna:Gilead Sciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Zelenetz:Gilead Sciences: Research Funding. Sharman:Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding. Adewoye:Gilead Sciences: Employment, Equity Ownership. Kim:Gilead Sciences: Employment, Equity Ownership. Flinn:Janssen: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; RainTree Oncology Services: Equity Ownership. Salles:Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal