Abstract
Introduction
The major reasons for failure to achieve cure in the majority of AML patients (pts) are primary refractoriness of disease to initial chemotherapy or failure to maintain complete remission (CR) that has been achieved (relapse). There is no uniformly accepted standard treatment for relapsed or refractory (RR) AML, with most available therapies regarded as palliative or as a bridge to allogeneic transplantation. While the past two decades have witnessed trials of several investigational therapies in RR AML, data regarding the effectiveness of these interventions remains unclear. We studied the impact of experimental drugs in RR AML pts by undertaking a comprehensive analysis of all phase 2 and 3 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) reported in the past 3 decades.
Methods
We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Controlled Trials Register electronic databases, ClinicalTrials.gov and conference abstracts from the American Society of Hematology (ASH), American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) and European Hematology Association (EHA) websites covering a period from 1988 to 2015. Key words used during this search included "refractory" or "relapsed" or "AML" or "phase II" or "phase III" or "randomized". Only double-arm, phase II with a sample size of at least 50 pts and phase III RCTs conducted in RR AML pts were included. Two reviewers independently extracted data on study methods, participants, therapies, and outcomes from all eligible trials: differences in how to classify agents in RCTs were resolved by discussion. The primary outcomes examined in the experimental arms (EAs) and standard arms (SAs) included CR rates, disease-free survival (DFS), refractory disease rates, treatment-related mortality (TRM) rates and overall survival (OS). Odds ratios (OR) were used to summarize differences between EAs and SAs. The DerSimonian and Laird random-effects model was used to compare them and to assess the overall impact of time.
Results
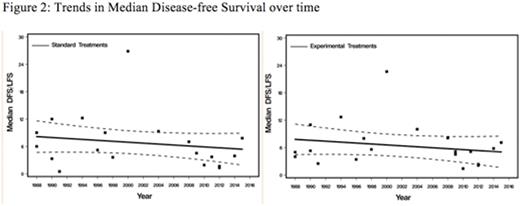
Of 5500 included pts, 40.5% were treated on 21 double-arm, phase II trials, 51% on 10 phase III trials and 6.6% analyzed through 4 retrospective studies. There was no change in CR rates in either EAs (p=.21) or SAs (p=.15) over time (Figure 1). The CR rates in EAs tended to be higher than in SAs [OR=1.24; 95% CI, 1.02-1.50, p=.03). Rates of disease refractoriness to salvage regimens in both EAs (p=.70) and CAs (p=.31) did not change over time and these rates were not significantly different between treatment arms [OR=0.82; 95% CI, 0.62-1.08, p=.16]. TRM rates tended to decrease over time but the change was not significant in either group [p=.24 for SAs and p=.33 for EAs]. TRM rates were higher in SAs compared to CAs but did not reach statistical significance [OR=1.21; 95% CI, 0.97-1.50, p=.09]. Over time, there was no significant change inDFS in either group (p=.32 for CAs and p=.58 for EAs). DFS rates did not differ between EAs and SAs [OR=1.01; 95% CI, 0.86-1.19, p=.89] (Figure 2). OS tended to remain stable over time in both groups [p=.85 for SAs and p=.66 for EAs]. While OS tended to be higher in SAs, it did not reach statistical significance [OR=0.93; 95% CI, 0.83-1.05, p=.27].
Conclusions:
These findings indicate a lack of significant or clinically meaningful improvement in disease outcomes, including OS, in RR AML pts treated within RCTs over the past 3 decades. Greater efforts need to be directed towards designing RCTs using novel statistical approaches and directed agents based on recent discoveries of targetable mutations.
Carraway:Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Baxalta: Speakers Bureau; Celgene Corporation: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Advani:Pfizer Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; Blinatumomab: Research Funding. Sekeres:Millenium/Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mukherjee:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.



This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal