Abstract
Aim: To investigate the therapeutic effect of combined treatment with the anti-CD37 antibody radionuclide conjugate (ARC) 177Lu-satetraxetan-lilotomab (177Lu-p-SCN-Bn-DOTA-HH1, tradename Betalutin®, short name 177Lu-lilotomab) and the anti-CD20 immunotherapy with rituximab in a subcutaneous (s.c.) preclinical model of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). These studies build on previously presented data that showed that treatment with 177Lu-lilotomab increased binding of rituximab in NHL cells in-vitro and in-vivo.
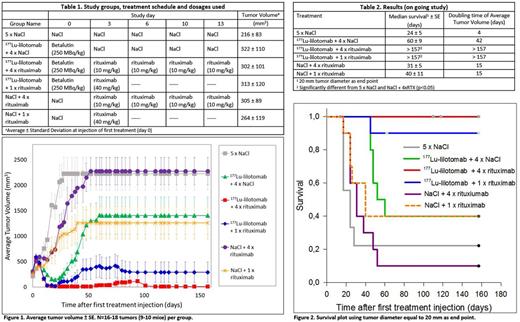
Materials and Methods:The therapeutic effect of the combination of 177Lu-lilotomab and rituximab was studied in nude mice with s.c. Burkitt's lymphoma (Daudi) xenografts using 250 MBq/kg 177Lu-lilotomab, 1 dose of 40 mg/kg rituximab, 4 doses of 10 mg/kg rituximab orNaCl. Treatmentswere given every 3 to 4 days (Table 1). Nine to 10 mice bearinga total of 16 to 18 tumors per group were used in the study. Tumor volume was measured every 2-3 days and weekly after study day 100. The therapeutic effect of the combination treatmentswas compared with the therapeutic effect of each of the treatments alone using Log-Rank and clustered cox-proportional hazards tests.
Results:The effect of the combination treatment in mice with s.c. xenografts was better than that of each treatment alone (Figure 1 & 2). The median survival of mice given the combination treatment was longer (>157 days) than each of the treatments alone (31-60 days) and of the sum of both treatments alone (91-100 days), but the difference was not statistically significant (Table 2). The study is currently on-going and none of the mice given the combination treatment have any palpable tumors, so it is expected that the median survival of those mice eventually will double the sum of both treatments alone. Median time to quadruplicate tumor volume was 2 times longer for the combination treatments (>157 days) than in any of the treatments alone (25-49 days) and longer than the sum of both treatments alone (74-82 days) (Table 2). When using time to quadruplicate tumor volume as end-point, the 177Lu-lilotomab + 4 x rituximab combination was significantly different from either treatment alone (p < 0.01, clustered cox-proportional hazards model). Moreover, the median time to complete remission of tumors in mice given the combination treatment was 5 times shorter (13 days) than each of the treatments alone (>66 days) (p<0.05). Three mice in the combination treatment of 177Lu-lilotomab + 4 x rituximab and one mouse in the combination treatment of 177Lu-lilotomab + 1 x rituximab doses were sacrificed due to body weight loss 14, 110, 118 and 157 days after injection of 177Lu-lilotomab respectively. It is not known if this was normal age-related symptoms or random occurrences or due to treatment toxicity. Histopathology examination will be included in the next mice tobe sacrificed to study this in more detail and evaluate if there is any late toxicity due to the combination treatment.
Conclusion:Treatment of NHL in-vitro and in-vivo with 177Lu-lilotomab results in an increased binding, tumor uptake and tumor suppression of anti-CD20 immunotherapy. If the same effect is confirmed in clinical studies, it could change the way ARC and CD20 immunotherapy would be used in the future.
Repetto-Llamazares:Nordic Nanovector ASA: Employment, Equity Ownership. Larsen:Nordic Nanovector ASA: Equity Ownership. O'Shea:Nordic Nanovector ASA: Employment, Equity Ownership. Dahle:Nordic Nanovector ASA: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal