Abstract
Background : Prognosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is very varied from cure to death. So the prediction for prognosis of DLBCL is very important to make a decision regarding the treatment. Now, international prognostic index (IPI) risk model is widely known as the powerful prognostic indicator for lymphoma. However, many inflammatory factors have been demonstrated as prognostic factors in patients with DLBCL such as C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, ¥â2-microglobulin (B2MG), absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) and albumin etc. But LDH is the only inflammatory factor in those of IPI. So we find a new prognostic risk model (inflammatory factors based modified IPI risk model ; inflammatory-IPI) including other inflammatory prognostic factors for predicting more correct survival outcomes and progression free survival (PFS) in patients with DLBCL treated with rituximab combined cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine and prednisone (RCHOP).
Methods: A total of 278 patients who were newly diagnosed with DLBCL and received RCHOP at hospitals throughout South Korea between January 2007 and December 2014 were enrolled retrospectively in the current study. Baseline serum CRP, ferritin, B2MG, ALC, albumin and factors of IPI were measured within 4 weeks before beginning the first line of chemotherapy. Each inflammatory factor of serum CRP > 1.5mg/dL, ferritin > 500ng/mL, B2MG > 3.5mg/L, ALC level < 1.0x109/L, serum albumin < 3.5g/dL, LDH level > 450 IU/L was defined as an abnormal findings, and if the sum of these abnormal findings are not fewer than 2, it is given 1 point as a factor of inflammatory-IPI instead of LDH. After that, sum of this point and the number of negative prognostic factors present at the time of diagnosis (age > 60 years, ECOG performance status ¡Ã 2, extranodal site ¡Ã 2, stage III/IV disease) is named the inflammatory-IPI. The inflammatory-IPI risk model were divided into four groups seems like IPI according to the scores ; low risk were 0 or 1 score, low-intermediate risk were 2 scores, and high-intermediate risk were 3 scores, high risk were 4 scores respectively.
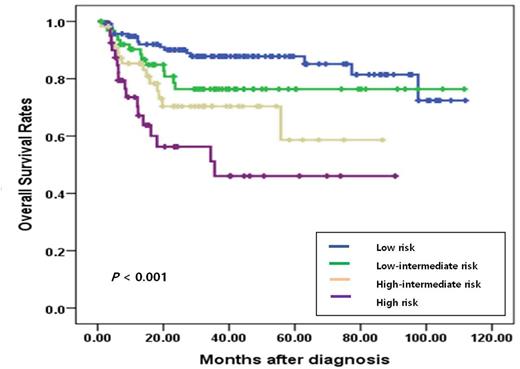
Results: In univariate analysis, the following factors showed significant higher 5 years overall survival rates (OS) : age (p=0.001), stage III/IV disease (p=0.008), LDH level (p<0.001), CRP (p=0.001), ferritin (p<0.001), B2MG (p<0.001), revised IPI (p<0.001). These factors also showed significant higher 5 years PFS. But some other factors did not showed significant OS and PFS in our data : ECOG, extranodal involvement, ALC, albumin. The studied groups were comprised of 117 patients in low risk group, 63 patients in low-intermediate group, 56 patients in high-intermediate group, 40 patients in high risk group according to inflammatory-IPI scores including sum of abnormal inflammatory findings. The OS and PFS according to the inflammatory-IPI showed significant differences (p<0.001 and p<0.001, respectively) (Figure 1).
Conclusions: The survival outcomes showed significant differences between risk groups which were categorized by inflammatory-IPI. This new inflammatory-IPI risk model could be supplemented the deficiency of standard IPI by including other prognostic inflammatory factors as well as LDH. It will be helpful to predict prognosis and make treatment planning in patients with DLBCL treated with RCHOP.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal