Abstract
Introduction: Ibrutinib (Ibr), idelalisib (Ide), andvenetoclax (Ven), are all now approved for treating CLL patients in the US. However, in the absence of head-to-head comparator trials, there is limited guidance as to the optimal sequence of these therapies and to the best choice upon failure of first selected agent. To address these gaps in current literature, 9 large US cancer centers and the Connect CLL Registry collaborated to capture the experience of 683 CLLpts treated with kinase inhibitors (KIs) - focusing on optimal sequencing and patterns of failure.
Patients and Methods: We conducted a multicenter, retrospective analysis of CLLpts treated withIbr-, Ide- orVen-based therapy. We examined demographics, discontinuation rates, reasons for discontinuation, overall response rates (ORR), survival, and post kinase inhibitor (KI) salvage strategies. Primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) (time from KI treatment to progression, death, or last follow-up) as determined by the Kaplan Meier (KM) method. Comparisons were made using the log rank (LR) test and COX regression analyses.
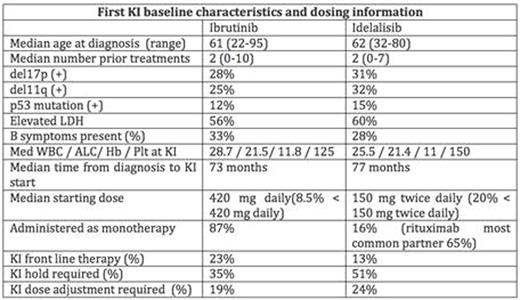
Results: A total of 683 pts treated with KI therapy (Ibr=621/Ide=62) were identified (Table 1). Baseline characteristics were similar in theIbr and Ide-based groups. ORR toIbr as first KI was 69% [complete response (CR) 11%, partial response (PR) 45%, and PR-L 13%] and Ide was 81% (CR 5%, PR 71%,PR-L 5%). With a median follow-up from start of first KI of 17 months (range 1-60), median PFS and OS for the entire cohort from first KI was 35 months (216 events) and not reached respectively (107 events). Interestingly,pts treated withIbr (vs. Ide) as first KI had a significantly better PFS in all settings; front-line (figure a, HR 2.8, CI 1.3-6.3 p=.01), relapsed-refractory (figure b, HR 2.8, CI 1.9-4.1 p<.001), clinical trials (HR 3.3, CI 1.8-5.9 p<.001), commercial use (HR 2.5, CI 1.5-4.0 p<.001), del17p (HR 2.0, CI 1.2-3.4 p=.008), or complex karyotype (HR 2.5, CI 1.2-5.2 p=.02). Moreover, at the time of initial KI failure, the use of either an alternate KI orVen was associated with superior PFS as compared tochemoimmunotherapy (CIT) combinations (figure c). When treated with an alternate KI (Ibr followed by Ide or Ide followed byIbr),pts intolerant of a KI therapy due to toxicity had a superior PFS compared with those taken off a KI therapy due to CLL progression (p=0.03, LR test). Furthermore,Ibr-failurepts had a marginally better PFS if treated withVen (ORR 79%) vs. Ide (ORR 46%) (figure d, HR .6, CI.3-1.0 p=.06).
Conclusions: In the largest experience of novel agents published to date in CLL,Ibr appears superior to Ide in all settings as first choice KI. Further, in the setting of KI failure, an alternate KI orVen therapy appear superior to CIT combinations. Alternate KI appear particularly effective in the setting of intolerance to a prior KI. The use ofVen uponIbr failure might be superior to the use of Ide. These data provide guidance for sequencing of novel agents and support the need for trials directly comparing novel agents and sequencing strategies in CLL.
Mato:Abbvie, Gilead Sciences, Pharmacyclics, TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Abbvie, Acerta Pharma, Gilead Sciences, ProNAi, TG Therapeutics, Theradex: Research Funding. Lamanna:Roche-Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; TGR Therapeutics: Research Funding. Barr:Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy. Ujjani:Genentech: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Brander:Gilead: Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding. Cheson:Acerta: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Kiselev:Celgene: Employment, Equity Ownership. Svoboda:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Schuster:Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Hoffman-LaRoche: Research Funding; Nordic Nanovector: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen Research & Development: Research Funding. Nabhan:Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy; Infinity: Consultancy; Cardinal Health: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal