Abstract
Introduction: The PK profile of carfilzomib is well characterized in patients with multiple myeloma. However, during clinical development of carfilzomib, patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (HI) were excluded from initial clinical studies. To support carfilzomib dose recommendations for patients with baseline HI, this study evaluated PK and safety of carfilzomib in patients with varying degrees of HI and relapsed or progressive advanced malignancies.
Methods: This open-label, single-arm, phase 1 study evaluated adult patients with normal (Norm) hepatic function or, mild, moderate (Mod), severe HI receiving carfilzomib infusion on days (D) 1-2, 8-9, 15 and 16 in 28-D cycles (C). Dose was escalated from 20 mg/m2 on C1 D1-D2 to 27 mg/m2 on D8 of C1 and if tolerated, further to 56 mg/m2 on D1 of C2. Norm hepatic function defined as bilirubin and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels </=upper limit of normal (ULN). HI defined as mild: bilirubin >1-1.5 x ULN, or AST >ULN but with bilirubin </=ULN; Mod: bilirubin >1.5-3 x ULN with any AST; or severe: bilirubin >3 x ULN and any AST. The primary objective was to assess the effect of HI on area under the curve (AUC) from time 0 to the last concentration measured (AUC0-last) and from time 0 extrapolated to infinity (AUC0-inf) of carfilzomib. Secondary objectives included evaluation of carfilzomib maximum plasma concentration (Cmax), time to maximum concentration (Tmax), clearance (CL), terminal half-life (T1/2), volume of distribution at steady state (Vss), mean residence time (MRT), and safety and tolerability, as well as PK parameters for carfilzomib's major metabolites. Plasma for analysis of PK parameters were collected on C1D16 for carfilzomib 27 mg/m2 and on C2D1 for the 56 mg/m2 dose. PK parameters were evaluated using a non-compartmental approach. The carfilzomib PK in HI patients was compared with Norm patients using summary statistics and analysis of variance. Due to enrollment challenges and lack of demonstrable efficacy with carfilzomib monotherapy, enrollment of severe HI patient (mostly advanced solid tumors) was discontinued.
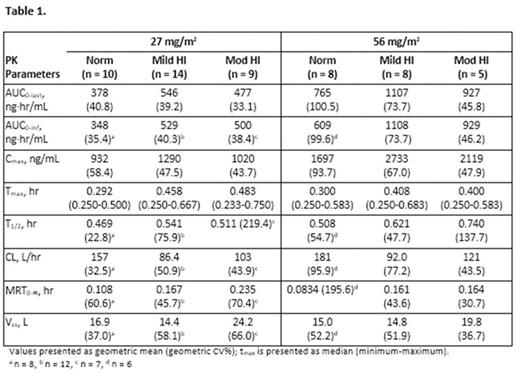
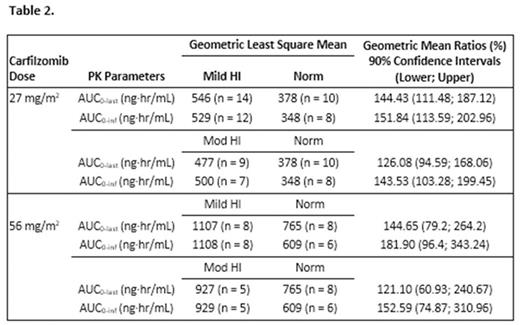
Results: 11 Norm, 17 Mild, 14 Mod, and 4 severe patients were enrolled; 61% male, mean age 62 years. Of these patients, 10 Norm, 14 Mild, 9 Mod, and 0 severe HI patients were PK evaluable. Following carfilzomib 27 and 56 mg/m2, considerable PK variability was seen within each of the treatment groups, with an overlapping exposure observed between groups (Table 1). Median Tmax ranged from 0.29 to 0.48 hour with peak concentrations of carfilzomib most often observed at 15 minutes after start or immediately before the end of infusion. Thereafter, concentrations of carfilzomib declined rapidly with a mean T1/2 of approximately 0.5 to 0.7 hour in all patient groups. A dose-dependent increase in mean AUC and Cmax of carfilzomib was observed between 27 mg/m2 and 56 mg/m2 in all 3 patient groups (Table 1); however, there was no consistent trend of increasing exposure (AUC0-last, AUC0-inf, and Cmax) with increasing severity of HI (Table 1 and 2). The mean AUC of the most abundant metabolite, PR-389/M14 was similar across all groups. A mean increase of approximately 60%-80% was observed for M15 and M16 AUC0-last, AUC0-inf and Cmax in patients with Mod HI vs Norm patients. These metabolites have no known biological activity. Median duration of exposure was 6 (Norm), 4.3 (Mild), 2.3 (Mod), and 0.8 (severe) wks. Thirty-five (76%) patients had grade >/=3 adverse events (AEs) including 15 patients with treatment-related grade >/=3 AEs. Grade >/=3 increased blood bilirubin (22%; Mod HI patients only), anemia (15%), fatigue (15%), and increased alanine aminotransferase (9%; Mod HI patients only) occurred in >3 patients.
Conclusions: No marked differences in exposures (AUC and Cmax) were observed between Norm patients and mild/Mod HI patients following carfilzomib doses of 27 and 56 mg/m2.No consistent trend in carfilzomib exposure related to HI severity was seen. With the exception of the increased frequency of AEs consistent with hepatic function abnormalities, the observed AE profile in this study was consistent with the known safety profile of carfilzomib. HI did not appear to substantially increase severity of AEs; however, the number of patients was limited. Based on the results in this study, no carfilzomib dose adjustment appears to be warranted in patients with relapsed or progressive advanced malignancies and mild or Mod HI.
Anthony:Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Speakers Bureau; Paradigm Diagnostics: Consultancy. De Vos:European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Dutch Working Group Neuro-Oncology: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; University Medical Center Utrecht: Employment. White:Amgen: Employment. Schupp:Amgen Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Ou:Amgen: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal