Abstract
Background: Histone deacetylase inhibitors increase acetylation of proteins involved in multiple oncogenic pathways, including the aggresome protein degradation pathway (Blood 2006; 108:3441-9). Preclinical and clinical studies have shown synergism with the combination of proteasome inhibitors (PIs) and histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) such as panobinostat.(PAN) (Cancer Lett 2009; 280:233-41; J Clin Oncol 2011; 29:8075) PAN was approved by the FDA in combination with bortezomib (BTZ) and dexamethasone based on the efficacy demonstrated in the PANORAMA1 trial (Lancet Oncol 2014;15:1195-206). We previously reported the combination of Carfilzomib (CFZ) and PAN in patients (pts) with relapsed and relapsed/refractory MM (Haematologica 2015;100:670-6). The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of CFZ and PAN was never reached and we extended our original study to investigate higher dose levels. Here we present the final results of the second dose expansion (DL 6).
Methods: Pts with MM who relapsed after ≥ 1 prior treatments (tx) were enrolled. PAN was administered orally on days 1, 3, 5, 15, 17, 19 of each 28-day cycle. CFZ was administered IV over 30 min on days 1, 2, 8, 9, 15, and 16. The initial dose escalation portion of the study used a standard 3+3 design to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of an initial 4 planned dose levels of the combination of CFZ and PAN. MTD was not reached and the maximum planned dose DL 4 (30 mg PAN and 20/45 mg/m2 CFZ) was expanded. The study was then revised to escalate to DL 5 (30 mg PAN plus 20/56 mg/m2 CFZ). Numerous PAN dose reductions resulted in a delivered PAN dose closer to 20 mg so DL 6 (PAN 20 mg and CFZ 20/56 mg/m2) was explored and eventually expanded. Tx continued until PD or intolerable toxicity. The primary efficacy endpoint was the overall response rate (ORR) (≥ PR). Secondary end points were time to progression (TTP), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), calculated using Kaplan-Meier methods. Adverse events (AEs) were assessed according to CTCAE V4 and responses were assessed using IMWG criteria (plus minimal responses (MRs) per the EBMT criteria).
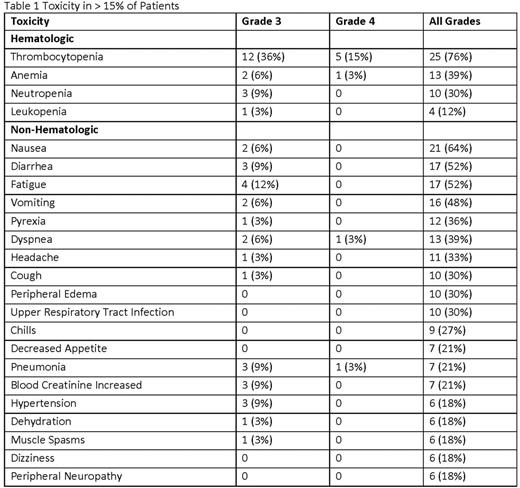
Results: Here we report the results of the second expansion cohort only (DL 6 (PAN 20 mg and CFZ 20/56 mg/m2). 33 pts were enrolled (61% male, median age 63 (range 49-91), 67% poor risk, 100% exposed to prior PIs, and a median of 2 prior therapies (range 1-7). 48% of pts were refractory to prior PI tx and 51% were refractory to prior immunomodulator (IMiD) tx. Pts completed a median of 7 tx cycles. There were CFZ dose reductions in 16 pts and PAN dose reductions in 21 pts, resulting in an average CFZ dose of 48.4 mg/m2 and average PAN dose of 14.7 mg. To date, 3 (9%) pts remain on active tx overall and 30 pts (91%) have discontinued due to disease progression (36%), toxicity (24%), stem cell transplant (15%), physician discretion or patient request (12%), and death (3%). The most common AEs are shown in Table 1. AEs of note were dyspnea (36%) and neuropathy (18%). There were 2 grade 3/4 cardiac toxicities, congestive cardiac failure and supraventricular tachycardia. There were 7 tx-related serious AEs (SAEs) in 6 pts and no tx-related deaths. 1 pt died on study of unrelated respiratory failure. The ORR was 82% and clinical benefit rate was 88% (6% complete response (CR)/near CR, 30% very good partial response, 47% partial response, 6% MR). ORR for pts refractory to prior PI was 75% and the CBR was 88%. ORR for pts refractory to prior IMiDs was 71% and the CBR was 82%. Median time to best response was 1.9 months (mos). With a median follow up (FU) of 19.6 mos (range 3.8-28 mos), median PFS was 9.69 mos, median TTP was 13.5 mos and median OS was 24.7 mos.
Conclusions: The combination of PAN/CFZ is effective with an acceptable safety profile in this refractory population. Efficacy in this cohort (ORR 82%) was similar to the previously published expanded DL4 cohort (ORR 72%). A CFZ dose of 56 mg/m2 with PAN at 20mg as given in this schedule did not appear to result in increased cardiopulmonary toxicity, but dyspnea rates were higher in this cohort than previously reported. GI toxicity was manageable. Further evaluation of this combination at this dose level is warranted.
Berdeja:Abbvie, Acetylon, Amgen, Bluebird, BMS, Calithera, Celgene, Constellation, Curis, Epizyme, Janssen, Karyopharm, Kesios, Novartis, Onyx, Takeda, Tragara: Research Funding. Gregory:Novartis: Honoraria. Faber:Cardinal Health: Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Speakers Bureau. Matous:Takeda Pharmaceuticals International Co.: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Hart:Onyx: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Onyx: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding. Flinn:Janssen: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; RainTree Oncology Services: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal