Abstract
Background: Three component prothrombin complex concentrates (PCCs) are currently approved to treat bleeding associated with Hemophilia B, and 4 component PCCs for warfarin reversal. They are increasingly used to treat bleeding in cardiac surgery patients. High dose PCC administration in the non-surgical setting has been associated with thrombotic complications, likely due to increased Factor II (Prothrombin) levels. We hypothesized that the use of low dose 3 factor PCCs (Profilnine, Grifols, CA) reduces bleeding following cardiopulmonary bypass without increasing the incidence of postoperative thrombotic complications.
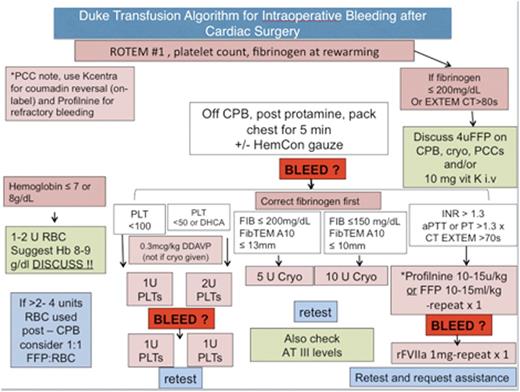
Methods: After IRB approval, a retrospective chart review of patients who underwent cardiac surgery and received Profilnine for refractory bleeding from February 2014 to February 2015. Demographic information, preoperative lab values, blood product use before and after PCC, use of rFVIIa, chest tube output and venous and arterial thromboembolic complications were collected. PCC was dosed according to an institutional perioperative bleeding algorithm (Figure 1) after approval by one of the senior authors (KG, JL or IW).
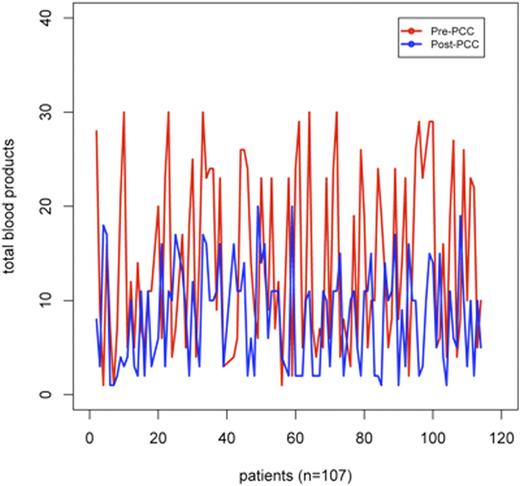
Results: 114 patients received Profilnine¨ (Grifols, CA) for postoperative bleeding following cardiac surgery. The most common procedure that required PCC administration was elective aortic reconstruction (61, 57%) followed by acute aortic dissection (13, 12.1%). The mean dose of PCC was 15.8±7.1 IU. The chest tube output for the first hour after arriving in the ICU 150.8±214.0 ml and quickly decreased to 89.5±122.1 ml in the second hour. The mean total blood product transfusion was 12.4±9.9 units prior to PCC dose and 5±6.3 units post dose. The difference is represented in Figure 2 and was found to be statistically significant on a paired t-test. (p <0.0001). Only 4 patients (3.7%) of the patients had to return to the operating room for a re-exploration.
Four patients (3.7%) had a cerebrovascular infarction in the postoperative period, of which two patients had undergone ventricular assist device (VAD) insertions, one had an aortic reconstruction and one had central ECMO cannulation performed following a STEMI. The patient with the aortic reconstruction received a higher dose of PCC (3000 Units or 33.5U/kg) and recombinant VIIa. One patient, who had a VAD inserted, had a pulmonary embolism. They received a low dose of PCC (13.8U/kg) did not receive factor VIIa. The post dose factor II activity level for this patient was 64%. Six patients (5.6%) had deep vein thrombosis diagnosed by venous doppler ultrasound. Four of these patients had received factor VIIa after PCC administration.
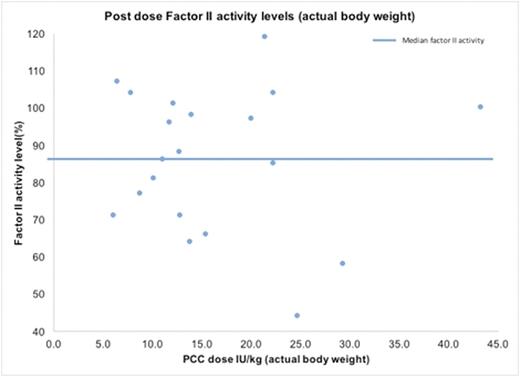
Post dose prothrombin levels were measured in 20 patients, with a mean of 85.9%(±19.3%).
The mean PCC dose in this group was 16.3 (±9.0) IU/kg per actual body weight, and 20.2 (±12.1) IU/kg per ideal body weight. Post dose factor II levels were plotted against PCC dose/kg in this group. The median factor II level was 87% (Figure 3). 12 out of these 20 patients received factor VIIa as part of the algorithm, and no postoperative thrombotic complications were reported in this subgroup.
Conclusions: Our initial findings from this ongoing study revealed a reduction of total blood products transfused after administration of PCC compared to before administration. Our series is reporting a higher rate of thrombotic events. While some of these are associated with factor VIIa administration following the PCC dose, most are likely to be multifactorial in etiology and were well tolerated. Additional randomized studies are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of PCCs in cardiac surgical patients.
Transfusion algorithm for intraoperative bleeding at Duke
PCCs = Prothrombin Complex Concentrates
Transfusion algorithm for intraoperative bleeding at Duke
PCCs = Prothrombin Complex Concentrates
This chart shows the total blood product transfusion for all patients before (red) and after(blue) PCC administration (p <0.0001)
This chart shows the total blood product transfusion for all patients before (red) and after(blue) PCC administration (p <0.0001)
This chart shows the factor II levels after PCC dose (dose/actual body weight) in a small subgroup of patients (n=20). The median factor II level was 87%.
This chart shows the factor II levels after PCC dose (dose/actual body weight) in a small subgroup of patients (n=20). The median factor II level was 87%.
Ghadimi:Portola Pharmaceuticals: Other: KG is a Co-Investigator in a prospective, open-label study of Andexanet Alfa in patients receiving factor Xa inhibitors with acute major bleeding, sponsored by Portola Pharmaceuticals . Levy:Boehringer Ingelheim: Consultancy; CSL Behring AG: Consultancy; Grifols: Consultancy; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; The Medicines Company: Consultancy. Welsby:NIH: Research Funding; Portola Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; CSL Behring: Research Funding; Terumo BCT: Research Funding; Zimmer-Biomet: Other: non financial support.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal