Abstract
Background:
Cytarabine (Ara C) is considered the most effective chemotherapeutic agent in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) treatment. Several studies suggest that single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the genes involving metabolic pathway of Ara C could influence in treatment outcomes, although their clinical relevance remains undetermined.
Methods:
The SNPs of cytarabine pathway (DCK: rs2306744, rs11544786, rs4694362; CDA: rs2072671, rs3215400, rs532545, rs602950; NT5C2: rs11598702; RRM1: rs9937; NME1: rs2302254) were evaluated in 225 adult patients at initial diagnosis from AML using a mass spectrometry-based multiplex genotyping assay (Sequenom®). All patients received induction chemotherapy consisting of idarubicin plus cytarabine (PETHEMA 99, 2007 and 2010 trials).
Efficacy of first induction cycle was evaluated comparing complete remission (CR) vs. partial remission (PR) or resistance (patients dying during induction excluded); and overall survival (OS). Induction death was defined as patients dying during induction against CR, excluding these patients with PR or resistance. Based on WHO grading scale, toxicities were grouped as binary variables (grades 0-1 vs. 2-4; or 0 vs. 1-4), assigning the maximum grade of all the specific toxicities within that group (evaluated in all patients). Genotypes were studied with co-dominant model. Association between variables was assessed using linear and logistic regression adjusting for age, gender, cytogenetic risk, ECOG, leukocyte and platelet count, hemoglobin, creatinine, bilirubin, albumin and LDH level at diagnosis (R® version 3.1.2). Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional were employed to OS estimates with the same covariates.
Results:
The median age of patients was 51.1 years (16-78 years). The variant allele of DCK SNP rs2306744, enzyme that catalyzes the limiting first phosphorylation in activation of Ara C, showed higher CR (OR:6.3; 95%CI 1.3-31.1; P=0.024), as well as higher mucositis (OR:3.3; 95%CI 1.1-10.0; P=0.038).
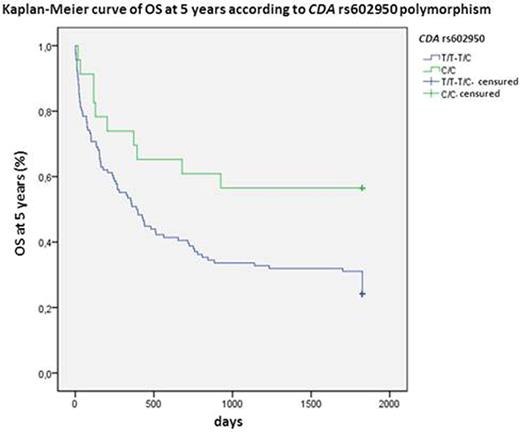
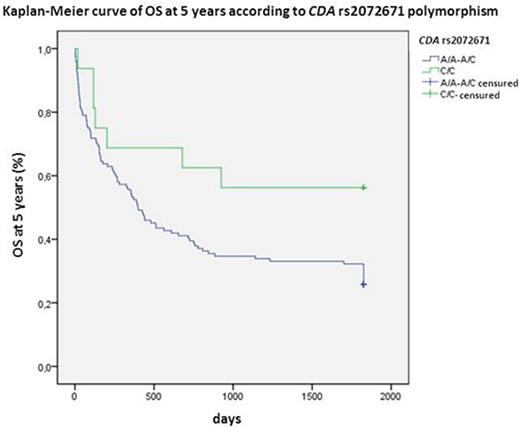
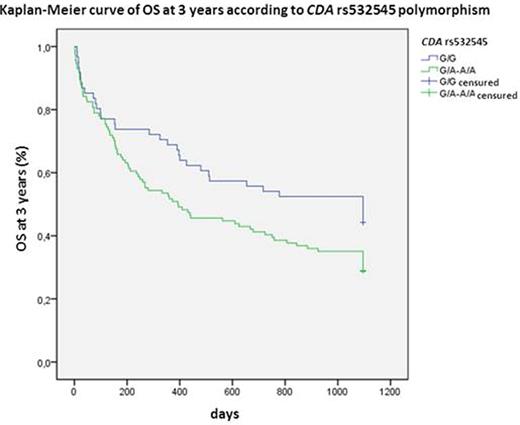
CDA is the main inactivating enzyme of Ara C. The variant allele of rs602950 was related to higher CR (OR:3.0; 95%CI 1.02-8.8; P=0.045) and OS at 5 years (HR:0.4; 95%CI 0.2-0.9; P=0.012; Figure 1) and the variant homozygous of rs2072671 to higher OS at 5 years (HR:0.3; 95%CI 0.1-0.96; P=0.018; Figure 2), whereas the wild-type allele of rs532545 was associated to higher OS at 3 years (HR:1.5; 95%CI 1.01-2.4; P=0.039; Figure 3). In addition, variant alleles of rs532545 and rs602950 were related to skin toxicity (OR:2.2; 95%IC 1.1-4.3; P=0.033; OR:2.1; 95%IC 1.01-4.5; P=0.047, respectively).
Variant allele of RRM1 (rs9937), enzyme directly associated with Ara C sensitivity, was associated to induction death (OR:0.2; 95%IC 0.03-0.9, P= 0.034). Variant allele of NT5C2 (rs11598702), responsible of nucleotide pools balance, showed higher hepatotoxicity (OR: 4.1; 95%IC 1.1-14.5; P=0.032).
Conclusions:
This study reveals the influence in Ara C efficacy of DCK and CDA polymorphisms in AML adult patients, previously suggested in other studies. In addition, novel associations between SNPs in metabolic Ara C genes and toxicities were detected. Further studies with larger population are needed to validate these associations.
Boluda:Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria La Fe: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal