Abstract
T cell immunodeficiency is the common characteristics in patients with AML, which may play an important role in leukemia progression and promote the expansion of malignant clones. Recently, increasing data showed that the immunosuppressive microenvironment, such as overexpression of the T cell immunosuppressive receptors, including programmed death-1 (PD-1) or cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4), Tim-3 and BTLA may be related to tumor immunosuppression and poor prognosis. Our previous studies indicated that the T cell immunodeficiency in leukemia patients are characterized by peripheral T cells that are incapable of interacting with blasts, reduced the thymic output function, oligoclonally restricted T cell repertoires, and led to low activation and a low antigen response. However, little is known the alterative expression of T cell immunosuppressive receptors in T cells, as well as their role in T cell exhaustion and immunosupression in AML patients.
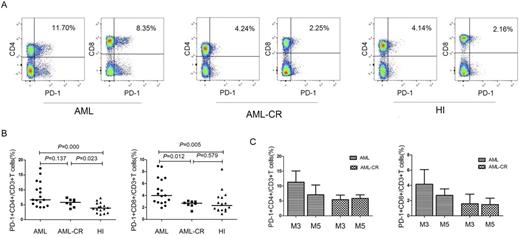
In this study, we analyzed the frequency of PD-1, CTLA-4, Tim-3 and BTLA expression in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 17 patients with de novo AML (AML-M0 2 cases, M2 2 cases, M3 4 cases, M4 1 case, M5 7 cases and M6 1 case), 8 patients with AML in complete remission (AML-CR) (M3 4 cases and M5 4 cases) and 16 healthy individuals by Flow cytometry. We also detected the frequency of CD244 and CD57 expression in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, which are the immune markers for T cell exhaustion. The results showed that significant higher percentage of PD-1+CD4+ and PD-1+CD8+ T cells was detected in AML group compared with healthy group, obvious, the percentage of PD-1+CD4+/CD8+ T cells was relative different in different cases, while similar expression pattern was found between AML-CR and healthy groups (Figure 1 A and 1B ). Interesting, high frequency of either PD-1+CD4+ and PD-1+CD8+ T cells was found in AML-M3 subgroup than that in AML-M5 subgroup, however, the frequencies became similar between M3-CR and M5-CR groups (Figure 1C). The percentages of CD244+CD4+ and CD244+CD8+ T cells, CD57+CD4+ and CD57+CD8+ T cells were relative high in AML group in comparison with healthy group, although the statistical significance was only found in CD244+CD4+ T cells group. Further investigation is needed in a large cohort to confirm the results and to explore the difference of the PD-1 expression in T cells in different AML subgroup. In conclusion, we firstly characterized the distribution of T cell immunosuppressive receptors in AML, which may be related to T cell exhaustion and immunosuppression in patients with AML.
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81570143 and 81270604), the Guangzhou Science and Technology Project of (201510010211) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (21616108).
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal