Abstract
Background. Aggressive lymphomas accounts for about 80% of primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin`s lymphomas (PGIAL). In adults the most common type is diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is rare and mainly affects children. R-CHOP chemotherapy can induce favorable result for localized-stage. But the presence of adverse factors (AF) and advanced stage decrease the efficacy of this therapy: 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) are about 50% and 60% respectively. The optimal treatment strategy for this pts still remains unknown.
Aim. Efficacy and safety assessment of the modified chemotherapy protocol NHL-BFM-90 (m NHL-BFM-90 and LB-M-04) in the treatment of the PGIAL with advanced stage and AF.
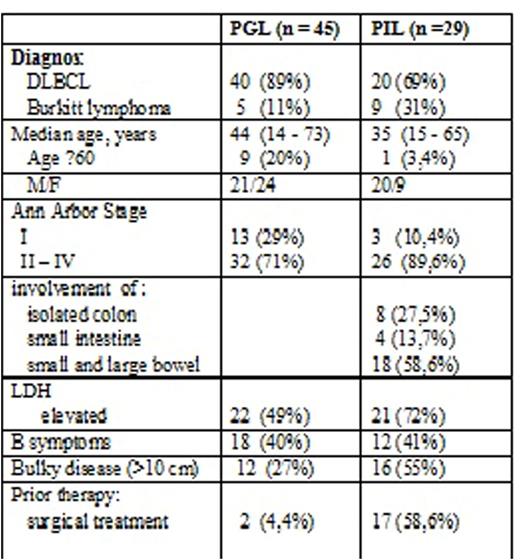
Patients. 74 previously untreated pts with PGIAL underwent mNHL-BFM-90 or LB-M-04 treatment between January 2002 and December 2015; out of them, 45 pts - primary gastric lymphoma (PGL), 29 pts - primary intestinal lymphoma (PIL); median age 39 years (range 14-72); age ≥60 years 10 pts (13,5%); M\F=44\30; stage >I 58 pts (78,3%); B-symptoms 30 pts (40,5%); Bulky disease 28 pts (37,8%). Patients characteristics in groups presented in Table 1. In the PIL group compared with the PGL was predominance of male (M\F=20\9 versus 21\24), stage II-IV (89,6% versus 71%), high level of LDH (72% versus 49%), Bulky disease (55% versus 27%). In pts with high Ki-67 (>40%) FISH test on t(8;14) was performed. Burkitt`s lymphoma diagnosed in 5 pts (11%) with PGL and 9 pts (31%) with PIL. In the PIL group more than half (58,6%) pts received surgical treatment before chemotherapy, and only 2 pts (4,4%) - in the PGL group. Of the 74 pts, 60 (81%) were diagnosed with DLBCL, 14 (19%) - BL. All pts with DLBCL received treatment according to the mNHL-BFM-90 program (2 courses A and 2 courses B) that was modified in the following way: doxorubicin (50mg\m2) was added on the third day of course A. All patients with BL received treatment according to the LB-M-04 program (2 courses A and 2 courses C) that was modified in the following way: doxorubicin (50mg\m2) was added on the third day of course A, methotrexate was administered on the 1st day of course C at a dose 1500mg/m2 for 12 hours. No one received consolidation radiotherapy from both groups.
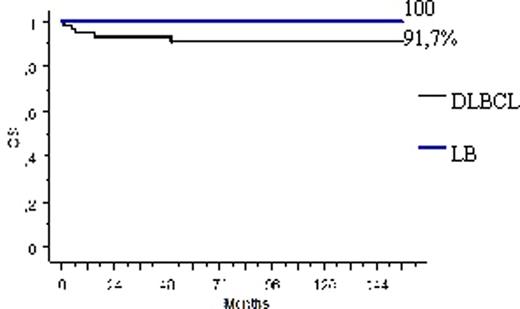
Results. In DLBCL group the overall response rate (ORR) was 95%. Complete remission (CR) was achieved in 38 from 40 pts (95%) in PGL, and 17 from 20 pts (85%) PIL. With a median follow-up of 74 months (range, 1-156) disease-free and overall survival of 60 pts with DLBCL constituted 86.7% and 91,7%, respectively. In BL group all pts achieved CR and alive with no signs of progression with a median follow-up of 110 months (range, 62-154). Hematologic toxicity of grade 3 and 4 was observed in 80% of pts. Severe complications became the reason for subsequent switch to CHOP therapy after 2 courses in 6 pts with PGL DLBCL. There was no treatment-related mortality.
Conclusions. The mNHL-BFM-90 and LB-M-04 demonstrated acceptable toxicity and high efficacy in patients with PGIAL. Burkett lymphoma is not rare in adults with PGIAL and detection of t(8;14) can improve treatment outcomes.
Characteristics of the patients with aggressive primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin`s lymphomas.
Characteristics of the patients with aggressive primary gastrointestinal non-Hodgkin`s lymphomas.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal