Abstract
Background.TP53 mutations were described to have a negative impact on prognosis of patients with B-chronic lymphoid leukemia and diffuse large cell lymphoma. However, a role of TP53 mutations in high-grade B-cell lymphomas (HGL) is not well defined in context of other genetic aberrations.
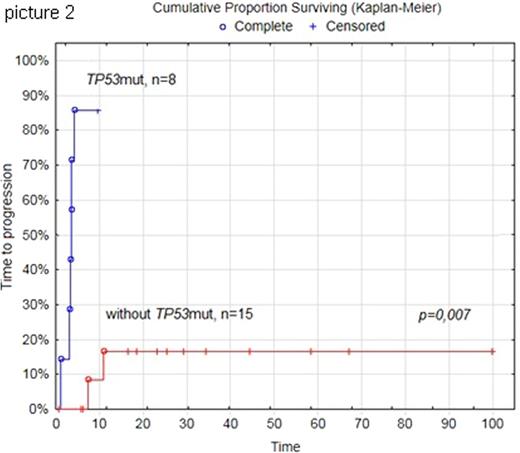
Materials and methods. 23 patients (7 males and 16 females) had diagnosis of HGL were treated in National Research Center for hematology, Moscow, Russia. Median age was 49 years old (30-76). 5 patients had HGL with c-MYC (MYC-R) and BCL2 genes rearrangements and 2 - HGB with MYC-R and BCL6 rearrangements. 17 (74%) patients had MYC-R, 11/23 (48%) had double expresser lymphoma (MYC≥40%, BCL2≥50%) (DE). Median of observation time was 29,1 months (6,3-99,8). 19 (82%) of patients had IPI score 3-5 points. 16 patients underwent LM-B-04 with rituximab (Table 1), 5 - R-(DA)-EPOCH, 2 - R-CHOP-21. In 5 cases autologous stem cell transplantation was performed. Sanger sequencing was performed to identify mutations in exons 5-8 of TP53 gene using DNA extracted from formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue («Extra-DNA» kit, «Genetechnology» LLC). Primers to TP53 gene were synthesized based on nucleotide sequences data available online on website ncbi.com by «Evrogene». To evaluate an influence of such factors as TP53 mutation (TP53mut), MYC-R, DHL, DE, gender, therapy on overall survival (OS) and time to progression (TTP) were performed multivariate dispersion analysis and Cox regression analysis (STATISTICA 10).
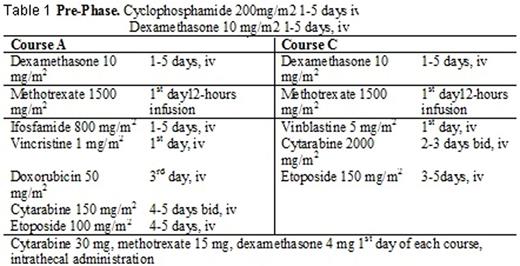
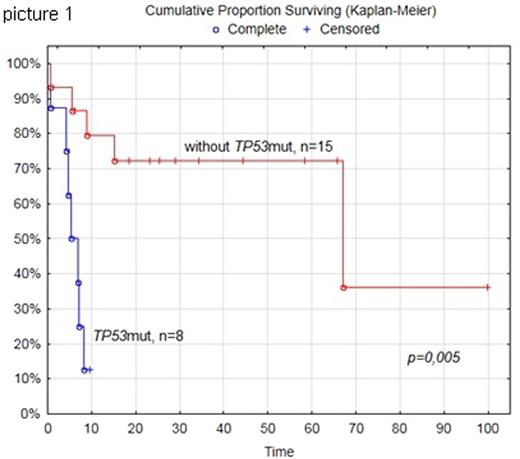
Results: 8 (35%) cases with TP53mut were identified: c.535C>T 45,6% p.H179Y, c.524G>C 15,6% p.R175P, c.743G>A 75,6% p.R247Q, c.487T>A 25,2% p.Y163N, c.824G>A 75% p.C275Y, c.713G>A 87,7% p.C238Y, c.745A>G 31,9% p.R249G, c.639A>G 41,8% p.R213R. 7/8 of them harbored MYC-R, 2/8 had DHL. In univariate (Picture 1, 2) and multivariate analysis pts harboring TP53mut had worse OS (median OS was 6,2 (0,7-9,5) vs 25,5 (0,7-99,8) months, p=0,004) and shorter TTP (median TTP 3,5 (0,7-9,5) vs 23,1 (0,7-99,8) months, p=0,027) than patients without TP53mut. DHL status had also an adverse effect on OS with lower significance than in pts with TP53mut (p=0,022). Adverse effect of TP53mut trends to play a role in combination with c-MYC gene rearrangement, thus5 pts TP53mut/MYC-R had shorter TTP than 5 DHL pts (3,4 (1,1-9,5) vs 7,3 (0,6-67,1) months, p=0,07).
Conclusion: High-grade lymphoma has a more powerful and independent prognostic factor than double-hit status - TP53 mutation that contribute inferior prognosis. This factor shouldn't be underestimated in routine diagnostics because of its frequency and requirement of a different therapeutic approach.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal