Abstract
The combination of intravenous (IV) methylprednisolone (IVMP) and IV immune globulin (IVIG) is often used in children with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) to rapidly increase platelet counts (PCs) to a safe hemostatic level. However, there are no controlled data to support the use of combination therapy over IVIG alone in children with severe thrombocytopenia [PC <20 x109/L] and/or life-threatening bleeding.
We conducted a randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled, multicenter, prospective study to evaluate 2 regimens: IVMP (Solu-Medrol®, UpJohn) 30 mg/kg (max. 1 gram) over 1 hour (h) followed by IVIG 1 g/kg (Gammunex 10%, Bayer) given at a rapid infusion rate (over a maximum of 3 h), vs IV placebo over 1 h followed by IVIG 1 g/kg in children with primary ITP. The goal was to evaluate the rapidity of the PC increment and associated adverse events with both regimens.
Eligible patients were children [ages: 1 to 17 years (y)] with acute (defined at the time of study initiation as <6 months (mo.) since diagnosis) or chronic primary ITP (>6 mo.), with PCs <20x109/L in whom it was decided to treat with IVIG. Exclusion criteria included: previous splenectomy, life/organ threatening hemorrhage, renal disease, diabetes, hypertension, sepsis, fever >38.5°C, disseminated intravascular coagulation, pregnancy or a previous documented lack of response to IVIG.
Baseline studies included: a complete blood count (CBC), a reticulocyte count, Coombs test and renal and liver function tests. CBCs were repeated at the end of the IVIG infusion, at 8±1h, 24±2h, 72±4h, day 7±2 day (d) and day 21±3d following the start of the placebo/IVMP.
The primary outcome measure was the PC increment over the first 24 h following the administration of therapy; the main secondary outcome measures were the attainment of a PC of ≥20x109/L and ≥50x109/L at times + 8, +24 and +72h.
Sample size was estimated based on the assumption that patients treated with placebo + IVIG would attain a mean PC at +24h of 30x109/L vs. 50x109/L for those treated with IVMP + IVIG. For 80% power to show a difference in PC of 20x109/L (at +24h)with an a of 0.025 (two-sided) and a b of 0.2, 32 patients were required.
Patients were stratified by block randomization according to type of ITP (acute vs. chronic) and according to center. The trial was registered in ClinicalTrials.gov. (NCT00376077).
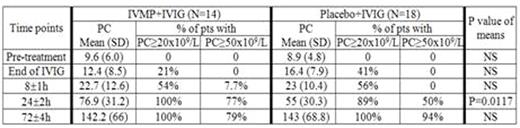
Thirty two patients were enrolled (ages: median 8 y; min. 1.2 y; max: 17.5 y; 22 male: 10 female; 16 acute: 16 chronic; 11 were blood type O; 14 blood type A and 7 blood type B). Fourteen patients were randomized to IVMP+IVIG while 18 were randomized to placebo+IVIG. Randomization was not equal as 1 patient was randomized and then immediately declined to participate and another patient was incorrectly assigned; both were assigned to the placebo group. PCs for the 2 groups of patients at the different time points are shown in table 1. The difference in PC was statistically significant at the 24 hr time point (p<0.0001). At this time the proportion of patients achieving a PC of ≥50x109/L was 77% in the IVMP+IVIG vs 50% in the placebo+IVIG.
No patient experienced a severe bleed or an unexpected severe adverse event during the study. There was a statistically significant drop in mean Hb post-treatment among all patients (baseline 133.3 (13.6) g/L to 121.6 (14.2) g/L at time +8h) but there was no difference between O and non-O blood type patients or between treatment groups.
This study showed that PCs increased rapidly following administration of IVIG with or without IVMP such that by 8h post initiation of therapy 55% (17/31) of all patients had achieved a PC ≥20x109/L. The mean PC was significantly different between the groups at time +24h. Our findings provide level 1 evidence to support the use of combination therapy (IVMP+IVIG) in life threatening situations where it is deemed to important to attain as rapidly as possible a hemostatic platelet count.
Blanchette:Shire: Consultancy, Other: Member of a Data Safety Monitoring Board, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; CSL-Behring: Research Funding; Octapharna: Other: Member of a Data Safety Monitoring Board; Biogen Idec: Research Funding; Bayer Healthcare: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal