Abstract
Background: The somatic mutation KIT D816V is a diagnostic criterion for systemic mastocytosis (SM) and can be found in the majority of patients. Therefore, sensitive detection of KIT D816V in blood and bone marrow (BM) is important for diagnosis of SM. Additionally, precise quantification of the KIT D816V allele burden is relevant clinically as it helps to predict multilineage involvement and prognosis in advanced SM and might be useful as a biomarker for treatment response to midostaurin or other interventional drugs. However, despite the high relevance of reliable KIT D816V allele burden measurement, no single assay for the detection and quantification of the KIT mutation has been accepted as a global standard. In addition, differences in calibration material and data normalization hamper the standardization of KIT D816V quantification and complicate the comparison of results obtained in different study groups. Digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) is a promising new method for sensitive detection and accurate quantification of somatic mutations.
Methods: We performed a validation study of the PrimePCR ddPCR mutation assay for KIT wild-type and the KIT D816V point mutation using the QX-200 droplet-reader on 302 DNA samples from 156 patients with mastocytosis (median age 56 years; 85 females, 71 males) in comparison to melting curve analysis after peptide nucleic acid-mediated PCR clamping (clamp-PCR) (Sotlar et al., 2003, AJP 162, 737-74) and allele-specific quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) (Kristensen et al., 2011, JMD 13, 180-188). According to WHO criteria, 16 patients were diagnosed with cutaneous mastocytosis, 5 with mastocytosis in the skin, 105 with indolent SM, 7 with smoldering SM, 1 with BM mastocytosis, 8 with aggressive SM, 12 with SM with associated hematologic neoplasm, and 2 with mast cell leukemia. Data were analyzed using the Bland-Altman plot, ordinary least squares regression and Passing-Bablok regression for method comparison, Kaplan-Meier survival plots, and log-rank test.
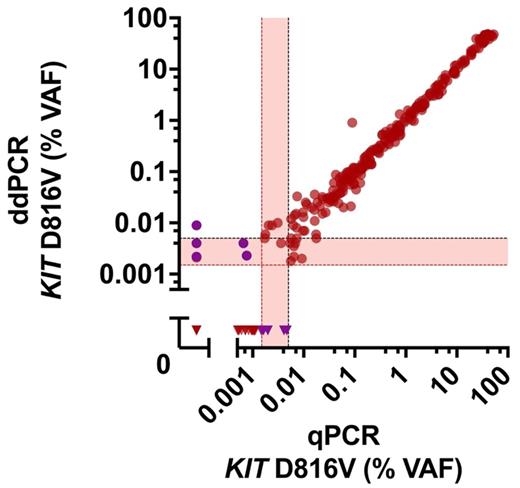
Results: ddPCR was found to be highly sensitive, specific and precise in detecting KIT D816V with a limit of detection of 0.005% variant allele fraction and a coefficient of variation <20%. ddPCR identified the mutation in 90% of all mastocytosis patients compared to 89% with qPCR and 70% with clamp-PCR indicating a superior diagnostic yield of ddPCR over clamp-PCR (p<0.001). In addition, ddPCR was also found to be suitable to detect and quantify KIT D816V in DNA isolated from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) BM sections. In peripheral blood and BM aspirates, ddPCR for KIT D816V showed a high concordance to qPCR (r=0.99). No systematic deviation for the conversion from qPCR to ddPCR was found (slope of 1.00 of log-transformed data; 95% confidence interval 0.98 to 1.02). In a next step, we confirmed the clinical value of KIT D816V allele burden measurements by ddPCR. In these studies, patients with advanced SM showed a significantly higher KIT D816V allele burden (median 2.43%) compared to patients with indolent SM (median 0.14%; p<0.001). Moreover, ddPCR confirmed the prognostic significance of a high KIT D816V allele burden regarding survival of KIT D816V+ SM patients (n=115) using a cutoff level of 2% mutant alleles. In the group with <2% mutant allele burden the median survival was not reached, whereas in patients with a KIT D816V allele burden of ≥2% the median survival was 7.7 years (p<0.001).
Conclusion: We performed a comprehensive validation of ddPCR for KIT D816V in peripheral blood and BM in order to establish a new reliable, quantitative qPCR technique for patients with mastocytosis. ddPCR is highly sensitive and specific for detection and quantification of KIT D816V, gives highly reproducible results even at a very low variant allele fraction level, and confirms the clinical value of KIT D816V allele burden measurement in blood and BM aspirates. In addition, ddPCR for quantification of KIT D816V can be performed in FFPE BM section material. Finally, ddPCR-based quantification of KIT D816V is not limited by the necessity to use generally accepted calibration material for assay standardization. In this regard, we propose to assess the ddPCR for KIT D816V in multicentric studies to increase comparability of allele burden data from different study groups. These studies will be a next crucial step towards the implementation of KIT D816V allele burden measurement as a global standard in clinical practice.
Sperr: Teva: Honoraria; Novartis: Other: Register; Meda: Research Funding; Phadia: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Valent: Blueprint: Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Ariad: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Deciphera: Honoraria, Research Funding; Teva: Honoraria. Hoermann: Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria; Ariad: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal