Abstract
BackGround
Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of high grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL); representing 31% of all NHL. DLBCL primarily arises from nodal sites. Roughly 30 -40 % of DLBCL cases arise from extranodal sites. Central nervous system (CNS) involvement in patients with DLBCL is an uncommon yet serious complication. Risk factors for CNS involvement include: high individual international prognostic index (IPI), testicular/adrenal/kidney extranodal involvement and high LDH values.
Aim
To investigate the risk factors for CNS involvement in DLBCL patients at our medical center.
Methods
All patients diagnosed with DLBCL at King Abdulla University Hospital (KAUH) between January 2003 and December 2016 were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical and laboratory data at time of diagnosis including gender, age, presenting symptoms and lactate dehydrogenase level (LDH) were studied. Diagnosis of DLBCL and extranodal involvement was confirmed by histopathology, cytopathology , CT scan, MRI and PET/CT scan.Patients with primary CNS lymphoma were excluded from the study. All patients received the same treatment regimen. None of our patients received prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy.
Results
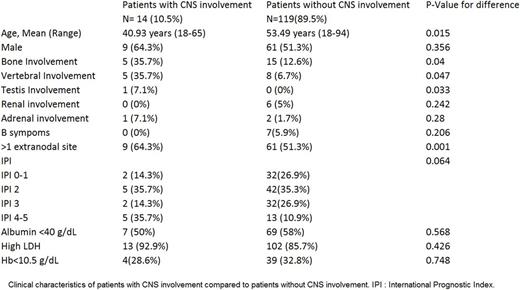
Among 133 patients diagnosed with DLBCL 70 patients (52.63%) were males while 63 patients (47.4%) were females. Patient characteristics are summarized in the table. 79 patients (59.39%) had extranodal sites involvement. 24 patients (18.04%) had more than one extranodal sites involvement. 25 patients(18.79%) had a pure primary extranodal involvement at presentation. Extranodal involvement were: Bone 20 patients (15%) ,followed by gastric 16 patients (12 %), CNS 14 patients (10.5%), Liver 11 patients (8.3%), Lung 8 patients (6%), Renal 6 patients (4.5%), Skin 6 patients(4.5%), Breast 3 patients (2.3%), Adrenal gland 3 patients (2.3%), bowel 3 patients (2.3%) and testis 1 patient (.75%). There was significant association between bone involvement and CNS involvement (P-value=.040); 35.7% of patients with CNS involvement had bone involvement. CNS involvement was significantly associated with vertebral bodies involvement (P-value=.047); 5 patients (71.4%) with CNS involvement had vertebral bodies metastasis. Also, CNS involvement was significantly associated with more than one extranodal site involvement (P-value<.0001), Age < 60 years (P-value=.011) and testis involvement (P-value=.033). The mean age of patients with CNS involvement was significantly lower than the mean age of patients without CNS involvement (P-value=.015). In multivariate analysis bone involvement (P-value=.023), testis involvement (P-value=.003) and age <60 years (P-value=.024) were associated with CNS involvement. No significant association found between CNS involvement and renal involvement (P-value=.242), adrenal involvement (P-value=.280) , IPI score (P-value=.064) and Hb <10.5 g/dL (P-value=.748).
Summary
Risk factors of CNS involvement in DLBCL patients at our center include : vertebral bone involvement , more than one extranodal site, age <60 years and testicular involvement. Prophylactic intrathecal chemotherapy is recommended for high-risk patients with bone metastasis.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal