Abstract
Introduction: Diffuse large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most frequent subtype of lymphoma in the world. The IPI score is a powerful risk-stratification tool in patients with DLBCL. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has shown to be prognostic in patients with DLBCL in Asia, Europe and USA. The GELL is a recently formed group for the study of lymphomas in Latin America composed by large institutions from eleven countries. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether the NLR is a prognostic factor in Latin American patients with DLBCL.
Methods: We included patients with a pathological diagnosis of DLBCL who were diagnosed and treated at our institution between 2012-2013. IRB approval was obtained prior to research, and pathological samples were reviewed by hematopathologists at each of the participating institutions to confirm the diagnosis. Pertinent clinicopathological data were collected through chart review and are presented using descriptive statistics. The NLR was calculated by dividing the absolute neutrophil by the absolute lymphocyte count and dichotomized in NLR≥4 and NLR<4. Survival curves were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. Univariate Cox models were fitted to evaluate hazard ratios (HR) for overall survival (OS).
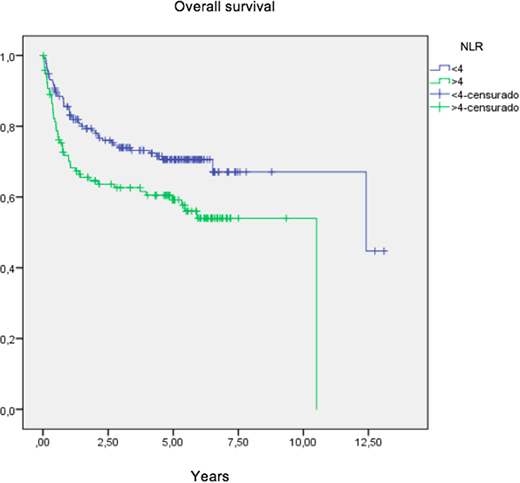
Results: A total of 329 patients with a diagnosis of DLBCL were included in this analysis. The median age at diagnosis was 64 years (range 18-83 years) with a slight female predominance (54%). Clinically, 59% of patients were 60 or older, 34% had ECOG >1, 29% had elevated LDH, and 70% had extranodal disease; 49% had early stage and 51% had stage III and IV. The IPI score was low risk in 36%, low-intermediate in 25%, high intermediate in 22% and high risk in 17%. 41% of patients had NLR ≥4. 89% of patients received standard R-CHOP, 2% received R-miniCHOP and 9% received other regimens. The overall response rate as 83%; 69% had complete response and 14% had partial response. The median follow-up for the entire group was 5 years (95% CI 4.9-5.4 years). The 5-year overall survival (OS) rate for the entire group was 65%. The 5-year OS rates for patients with NLR ≥4 and <4 were 59% and 71%, respectively (p=0.008). Patients with low, low-intermediate, high-intermediate and high IPI scores had 5-year OS rates of 80%, 65%, 56% and 45%, respectively (p<0.001). In the multivariate analysis, advanced stage (HR 3.1, 95% CI 1.9-5.0; p<0.001), LDH level (HR 2.2, 95% CI 1.2-4.2; p=0.016) and NLR ≥4 (HR 1.7, 95% CI 1.1-2.6; p=0.03) were statistically independent factors associated with worse OS. NLR ≥4 was an adverse prognostic factor after adjusting for IPI score (HR 1.7, 95% CI 1.1-2.6; p=0.01).
Conclusion: The NLR appears as a novel and easy to use prognostic factor for OS, independent of the IPI score, in previously untreated Latin American patients with DLBCL. Our findings support the need for validation of the NLR in larger retrospective or prospective studies in patients with DLBCL.
Chiattone:Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Castillo:Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal