Abstract
Introduction: Despite the demonstrated efficacy of ruxolitinib (Rux) in patients (pts) with myelofibrosis (MF), suboptimal or declining responses to Rux occur, possibly due to persistent PI3K/AKT activation with chronic JAK inhibitor therapy. We evaluated the combination of INCB050465, a potent and highly selective PI3Kδ inhibitor (≥19,000-fold selectivity for PI3Kδ vs other isoforms) and Rux in pts with MF with suboptimal response to chronic Rux monotherapy.
Methods: Pts with primary, post-polycythemia vera or post-essential thrombocythemia MF with suboptimal response or loss of response (palpable spleen >10 cm below left subcostal margin [LSM], or splenomegaly 5-10 cm below LSM and presence of 1 symptom score ≥5 or 2 symptom scores ≥3 using the Screening Symptom Form) after ≥6 months of Rux monotherapy (5-25 mg twice daily, stable dose for ≥8 weeks [wks]), and ECOG performance status ≤2 were eligible for this phase 2 study (NCT02718300).
All pts in Part 1 (safety run-in) and Part 2 (expansion) received oral INCB050465 once-daily (QD) for 8 wks followed by once-weekly (QW) at the same dose plus Rux (existing stable dose for ≥8 wks). Part 1 assessed up to 3 dose levels of INCB050465 (5, 10, and 20 mg). In Part 2, pts were randomized to treatment groups (TGs) in a 1:1 ratio between two doses of INCB050465 determined in Part 1.
Primary endpoints were to identify tolerated INCB050465 dose in combination with Rux (Part 1) and percent change in spleen volume from baseline through wk 12 (Part 2).
Results: At data cutoff (May 01, 2018), 10 and 18 pts were enrolled in Parts 1 and 2, respectively. INCB050465 doses of 10 mg (TG10, n=3) followed by 20 mg (TG20, n=7) were explored in Part 1. No DLTs were observed, thus the 5 mg dose was not assessed, and the 10 mg (TG10, n=11) and 20 mg (TG20, n=7) doses were expanded in Part 2.
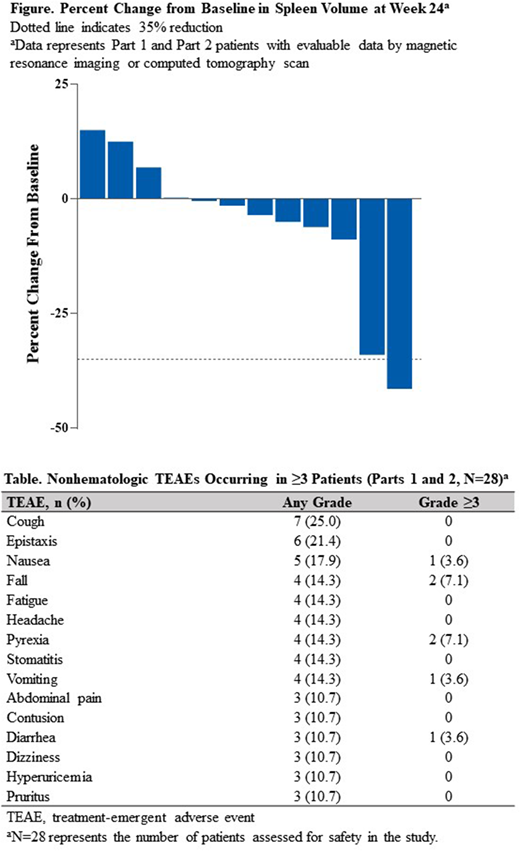
In Part 1 (n=10) (median age, 69 years [60-79]; males, 60%), median spleen volume (cm3) was 3058 (996-5324) at baseline. Five pts (50%) discontinued treatment due to progressive disease (n=1, TG10), physician decision (n=1; TG20), adverse event (AE; n=1; TG20, blood bilirubin increased), consent withdrawal (n=1; TG10), and decision to proceed to transplant (n=1; TG10). Median percent change in spleen volume was +4.3% and -2.0% at wks 12 and 24, respectively (Figure). By wk 16, 40% of pts reported that their MF-related symptoms were much improved on the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) form.
In Part 2 (n=18) (median age, 63.5 years [41-89]; males, 38.9%), median spleen volume (cm3) was 2201 (327-3569) and median total symptom score (TSS; by the Myeloproliferative Neoplasms Symptom Assessment Form [MPN-SAF]) was 30 (3-61) at baseline. One pt in TG20 discontinued treatment due to physician decision. Median percent change in spleen volume was -0.3% and -5.2% at wks 12 and 24, respectively (Figure). By wk 16, 33.3% of pts reported that their MF-related symptoms were much or very much improved on the PGIC. Median percent change in TSS by the MPN-SAF was -21.9% and -27.8% at wks 12 and 24, respectively. MPN-SAF TSS was a planned longitudinal endpoint only for Part 2 and updated data for Part 2 pts will be presented.
In both Parts 1 and 2, nonhematologic treatment-emergent AEs (TEAEs) occurring in ≥3 pts were primarily grade (Gr) 1/2 (Table). Most common new or worsening Gr 3/4 hematologic AEs were thrombocytopenia (Gr 3: 4 pts [14.3%]; Gr 4: 4 pts [14.3%]) and neutropenia (Gr 3: 2 pts [7.1%]; both pts had Gr 2 neutropenia at baseline). No serious TEAEs of interest were reported. TEAEs led to INCB050465 dose interruption in 11 pts (thrombocytopenia [n=8 events], pyrexia [n=2 events], and abdominal pain, diarrhea, alanine aminotransferase increased, and aspartate aminotransferase increased [n=1 event each]), and to Rux dose interruption in 3 pts (pyrexia [n=2 events] and thrombocytopenia [n=1 event]).
Conclusion: The add-on strategy of INCB050465 plus Rux demonstrated preliminary efficacy in MF pts with suboptimal spleen and/or symptom response to chronic Rux monotherapy. The dosing regimen (QD for 8 wks followed by QW) of INCB050465 in this study seemed to mitigate AEs observed with other PI3K inhibitors (limited Gr 3/4 TEAEs and no TEAEs of colitis or rash reported). Long term dosing strategies will be explored in Part 3 of the study, and additional trials are underway to identify optimal dosing of INCB050465 for enhanced safety and efficacy in combination with other agents.
Daver:Karyopharm: Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Alexion: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Otsuka: Consultancy; ImmunoGen: Consultancy; ARIAD: Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy; BMS: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Pfizer: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Kiromic: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy. Kremyanskaya:Incyte: Research Funding. O'Connell:Incyte: Research Funding. Dao:Incyte: Consultancy. Oh:Takeda: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; CTI Biopharma: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding. Gerds:Celgene: Consultancy; Apexx Oncology: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; CTI Biopharma: Consultancy. Verstovsek:Italfarmaco: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy. Erickson-Viitanen:Incyte: Employment, Equity Ownership. Zhou:Incyte: Employment, Equity Ownership. Assad:Incyte Corporation: Employment, Equity Ownership. Yacoub:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal