Abstract
Background
The development of an immunogenic response to FVIII and the appearance of neutralizing antibodies - "inhibitors" - against FVIII is the most important adverse event in hemophilia treatment. Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) via the long-term, intravenous administrations of high-dose FVIII is the only proven strategy to eradicate inhibitors. The success rate is about 60-70% and no formal demonstration of its mechanism of action has been provided yet. Indeed, the mechanisms underlying successful ITI have been unclear, and not much is known about the major factors determinant of success vs. failure.
Our aim is to understand the process of activation and immune regulation in response to FVIII in patients undergoing ITI, and comparing the immunological events in patients who successfully eradicate anti-FVIII antibody to those in patients failing to achieve FVIII tolerance.
Methods
This is a multicenter, observational, prospective cohort study enrolling severe HA patients who developed high-titer inhibitors, candidate to ITI. A blood sample has been collected before starting and during the course of ITI, until ITI ends (5 blood samples during the first year, 3 during the second year if ITI treatment is not already ended, plus a final sample 30 days after ITI conclusion). Total PBMCs have been used to establish cell cultures where cells are re-stimulated with the same FVIII used during the ITI or medium alone.
To identify candidate genes, key proteins and cell subsets associated to differential outcomes to ITI, immune cells are used for gene expression profiling (Human Inflammation & Immunity Transcriptome Targeted RNA Panel, Qiagen) together with extensive phenotypic characterization of immune cells via the CyTOF (Cytometry by Time Of Flight mass spectrometry) technology. To identify potential biomarkers predictors of ITI outcomes metabolomics analysis and multiplex cytokine arrays are performed in plasma collected at each time point during ITI and in supernatants from cells cultures. Plasma samples, are collected at each time point and stored at -80°C for cytokine determination and metabolomic analysis. Total anti-FVIII antibody (and their isotypes) and inhibitor titer are also determined in plasma samples by Nijmegen methodology in the central laboratory as described previously (1).
Results
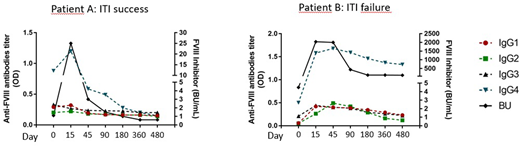
Currently, 18 subjects have been enrolled among 8 Hemophilia Centers. Among these 5 subjects, two patients reached the study endpoint of ITI success by study criteria (negative inhibitor titer, a normal FVIII recovery, a normal FVIII half-life and the absence of anamnesis upon further FVIII exposure) while three were assessed as ITI failure. The analysis of anti-FVIII antibody isotypes revealed the presence of IgG4 as the most relevant component of the total anti-FVIII antibodies. The inhibitor clearance was also accompanied by the disappearance of IgG4 anti-FVIII antibodies in both tolerized patients, while those who failed to eradicate the inhibitor showed a sustained IgG4 anti-FVIII response (Fig. 1). The evaluation of the cytokines in the supernatants from in vitro cultured cells showed a consistent increase in production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to FVIII (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-12, IL-17A, IL-15) at all time points only in patients who continued to produce high-titer inhibitors.
Conclusions
Here we report an interim analysis of a prospective study of the immunological mechanisms of immune tolerance induction. The preliminary results obtained so far suggest that anti-FVIII IgG4 are a major component of the total anti-FVIII antibodies and their persistence is associated with unfavourable ITI outcome. We expect that the ongoing immune gene expression profiling, immune-phenotypic characterization and determination of soluble marker of activation/regulation of the immune system in supernatants and plasma in this cohort of patients will provide substantial knowledge to increase our current understanding of the complex immunological pathways involved in the development of tolerance to FVIII. Ultimately, this could lead to the discovery of biomarkers of ITI success/failure and to the generation of focused and strategic intervention to modulate the immune system during this treatment.
References
1. Matino D, Gargaro M, et al. "IDO1 suppresses inhibitor development in hemophilia A treated with factor VIII". J Clin Invest. 2015 Oct 1;125(10):3766-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI81859.
Matino:Sobi: Speakers Bureau. Peyvandi:Sobi: Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk: Speakers Bureau; Kedrion: Consultancy; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Octapharma US: Honoraria; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk: Speakers Bureau; Kedrion: Consultancy; Grifols: Speakers Bureau; Octapharma US: Honoraria; Octapharma US: Honoraria; Novo Nordisk: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Grifols: Speakers Bureau; Ablynx: Other: Member of Advisory Board, Speakers Bureau; Grifols: Speakers Bureau; Ablynx: Other: Member of Advisory Board, Speakers Bureau; Octapharma US: Honoraria; Ablynx: Other: Member of Advisory Board, Speakers Bureau; Grifols: Speakers Bureau; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Sobi: Speakers Bureau; Sobi: Speakers Bureau; Roche: Speakers Bureau; Sobi: Speakers Bureau; Sobi: Speakers Bureau; Kedrion: Consultancy; Novo Nordisk: Speakers Bureau; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Kedrion: Consultancy; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Octapharma US: Honoraria; Grifols: Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk: Speakers Bureau; Shire: Speakers Bureau; Kedrion: Consultancy. Santagostino:Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sobi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kedrion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CSL Behring: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Grifols: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bioverativ: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novo Nordisk: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Iorio:NovoNordisk: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with Novo Nordisk; Shire: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with Shire; CSL: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with CSL; Grifols: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with Grifols; Octapharma: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with Octapharma; Bayer: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with Bayer; Pfizer: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with Pfizer; Roche: Other: Alfonso Iorio's Institution has received project based funding via research or service agreements with Roche.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal