Background
Primary and secondary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL/SCNSL) are rare brain malignancies with an aggressive clinical course and dismal outcomes. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has activity in a range of B-cell lymphomas. Phase I and II studies of ibrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory PCNSL have demonstrated promising results, with response rates of up to 81%. Response rates of up to 69% have also been seen in SCNSL. Ibrutinib has been combined with other systemic agents (e.g. rituximab and methotrexate) in phase 1 trials with promising results (Grommes et al Blood 2019); combination with more intensive combination chemotherapy regimens also appears efficacious but has exhibited a potentially limiting toxicity profile, in particular invasive fungal infections. (Lionakis et al Cancer Cell 2017). However, data for ibrutinib in PCNSL and SCNSL outside the clinical trial setting are scarce.
Methods
We performed a national, multicentre, retrospective study of the clinical outcomes and safety of patients (pts) with PCNSL and SCNSL who received ibrutinib between December 2015 and June 2019.
Results
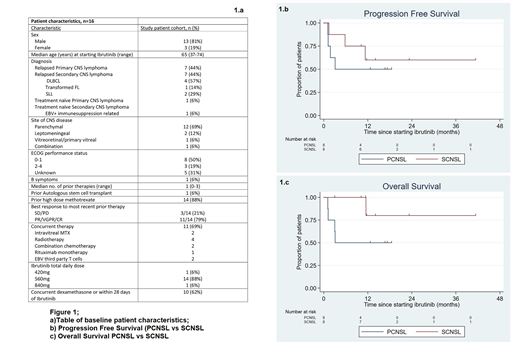
The baseline characteristics of the 16 eligible pts are summarised in the table (Figure 1a). 88% (n=14) had relapsed/refractory disease, with two patients receiving ibrutinib as a component of multiagent frontline therapy. The most common target daily dose was 560mg (range 420-840mg); this was reached in all pts. Among all pts, the objective response rate (ORR) was 69%, with a complete remission (CR) rate of 63%. Both patients receiving ibrutinib in combination frontline therapy achieved a CR. ORR in PCNSL pts was 50% (n=4) and SCNSL pts was 88% (n=7), (P=0.28). ORR was 80% (n=4) when ibrutinib was administered as monotherapy, 80% (n=4) when administered with chemotherapy and 75% (n=3) when administered concomitant with whole brain radiotherapy. MYD88L265P mutation at time of starting ibrutinib was only tested in two patients with PCNSL and none with SCNSL. The mutation was detected in both PCNSL cases, and both later attained a CR. With a median follow up of 14 months, calculated using median observation period among patients alive at last follow-up, median progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were not reached. 12 month PFS was 56% for the entire cohort (95% confidence interval [CI] 29-76); 50% for PCNSL (95% CI 15-77) and 60% for SCNSL (95% CI 20-85%) (Figure 1b). 12 month OS was 66% for the entire cohort (95% CI 36-85) ; 50% for PCNSL (95% CI 15-77) and 80% for SCNSL (95% CI 20-97%) (Figure 1c). Ten pts had PFS >6 months (longest 41.3 months), and 11 pts (69%) remained alive, with 9/11 being free from disease progression. Seven pts remain on ibrutinib at time of data analysis, 3 with PCNSL and 4 with SCNSL. Nine pts (56%) have discontinued therapy; 6 due to progressive disease (PD), 1 due to atrial fibrillation with hypotension requiring inotropic support and 2 in remission, one of whom subsequently underwent autologous stem cell transplant. Dose interruptions or reductions were required in 6 pts (37%), due to bleeding (n=2), infection (n=3) and neutropenia (n=1). Grade 3/4 adverse events were infection (31%, n=5), neutropenia (25%, n=4), febrile neutropenia (12%, n=2) and one each (6%, n=1) of atrial fibrillation, thrombocytopenia, and anaemia. No invasive fungal infections were observed, despite use of 8-16mg daily dexamethasone immediately prior to or during ibrutinib therapy in 10 pts (62%).
Conclusions
In this small real-world, majority methotrexate-refractory population, ibrutinib demonstrates encouraging efficacy and durable responses despite doses lower than used in clinical trials. No unexpected adverse events were observed. Invasive fungal infections were not seen, despite most patients receiving concurrent dexamethasone and/or chemotherapy. We observed substantial variety in additional therapy during ibrutinib treatment, and the optimal way to use ibrutinib in this heterogenous patient group remains unclear.
Manos:NovoNordisk Pharmaceuticals: Other: Travel; Janssen: Honoraria. Ho:Celgene: Consultancy, Other: Advisory role. Grigg:Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MSD: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Other: Travel. Gandhi:Amgen: Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Other: Travel Support; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Hawkes:Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Mundi pharma: Research Funding; Janssen-Cilag: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck KgA: Research Funding; Merck Sharpe & Dohme: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Cheah:Roche: Other: Travel expenses; Roche, Janssen, MSD, Gilead, Loxo Oncology, AstraZeneca, TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene, Roche, Abbvie: Research Funding.
Ibrutinib is not currently approved for use in DLBCL/CNS lymphoma.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal