INTRODUCTION
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) affects approximately 3% of children 1 to 3 years of age and is associated with poor neurocognitive outcomes. Children of Hispanic/Latino ethnicity, from primarily Spanish-speaking homes, and/or those of low socioeconomic status, are disproportionately affected. Oral iron therapy for 3 to 6 months is considered standard care therapy and mitigates these effects. Yet non-adherence often results in treatment failure, prolonging the treatment course and negative health consequences of IDA. Limited previous work has focused on interventions to improve adherence to iron therapy. Behavior change interventions, particularly when designed within a theoretical framework, can improve rates of treatment adherence. Our objective was to design a theoretically-based behavioral intervention to improve adherence to oral iron therapy in young children with nutritional IDA.
METHODS
Formative research was conducted via a mixed-methods study of 20 children with nutritional IDA and their primary caretaker. Demographic information, including number of children and caregivers in the home, was obtained from the primary caregiver. Clinical aspects of patients' IDA diagnosis and iron therapy were obtained from the electronic medical record. Semi-structured interviews with caregivers were conducted to characterize barriers to and facilitators of iron therapy.
A framework for a technology-based intervention, named IRONCHILD, was created to coincide with clinical visit time points over a three-month period. Results from the formative research, along with constructs from the self-determination theory of motivation (autonomy, competence, relatedness), informed message content for the intervention scripts. This theory was selected because the degree to which its three principle constructs (basic psychological needs) are met drives levels of motivation to perform a specific behavior such as medication adherence. Three scripted online intervention sessions were developed, professionally translated into Spanish, and then animated by a professional animation and web design studio. Audio recording with a professional bilingual voice actor provided the narration for online sessions.
RESULTS
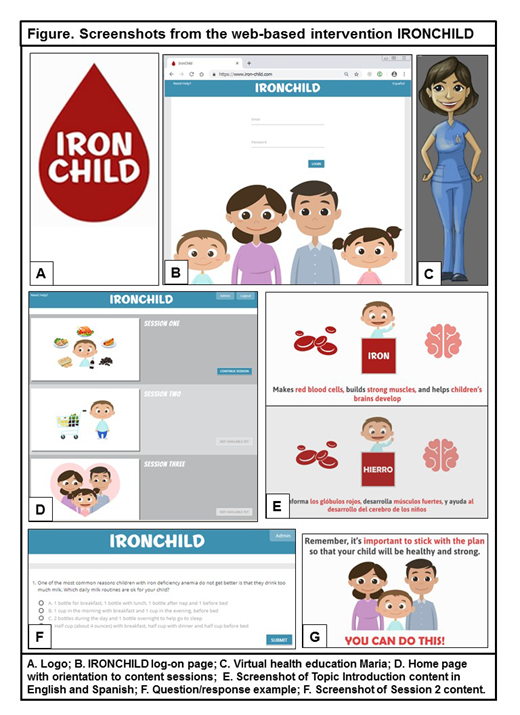
IRONCHILD is an interactive website with specific message content designed to be delivered at three standard of care clinical visits (Figure). At the initial visit, participants are introduced to a relational agent or virtual health educator, Maria, who is a pediatric nurse and mother of a child formerly treated for IDA. Maria provides an introduction to the overall program format and content and guides each session. Participants next view a Topic Introduction animation that provides an overview of the diagnosis of IDA, its clinical consequences, and a typical treatment course with oral iron therapy. This is followed by two unique content segments that provide information on (1) dietary counseling and (2) administration of oral iron therapy. Following each of the content segment, participants view question/response options, make a selection, and receive feedback. At the end of the session, participants select goal(s) related to therapy adherence for the interval between clinical visits.
The second session provides two additional content segments that focus on (1) problem-solving for difficulties related to medication administration and (2) identifying motivating factors to adhere to therapy. The third session allows users to access all previous content and provides closing information about adhering to any ongoing treatment recommendations from their child's provider. Between visits, access to the website occurs via a unique username and password caregivers can use to logon to the website and view previous sessions. All aspects of IRONCHILD are available in both English and Spanish. Finally, an administrative dashboard for IRONCHILD captures program usage information as families log onto the program and navigate the sessions (e.g., number of log-ins; responses to question prompts; goals set; goal attainment).
CONCLUSIONS
IRONCHILD is a theoretically-based online intervention designed to improve adherence to oral iron therapy in caregivers of young children with nutritional IDA. Further research is needed to assess the effectiveness of the intervention on adherence as well as factors that affect implementation into routine clinical care.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal