Background: Sepsis is characterized by a simultaneous activation of inflammation and hemostasis in response to microbial infection. This systemic inflammatory response is due to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, pro-coagulants and adhesion molecules from immune cells and/or damaged endothelial tissue. Simultaneous activation of coagulation and fibrinolysis leads to consumption coagulopathy and severe vascular dysfunction. Profiling of biomarkers of hemostatic activation and inflammation along with the measurement of coagulation parameters has provided useful data in the understanding of the pathogenesis of sepsis. This study was designed to profile biomarkers of hemostatic activation, inflammation and endothelial dysfunction along with the measurement of coagulation parameters in a defined clinically confirmed sepsis population in conjunction with an IRB approved clinical trial.
Materials & Methods: Citrated blood samples were collected from sepsis patients with suspected or confirmed infection, and organ dysfunction as defined by a SOFA ³ baseline. Plasma samples from septic shock patients were collected in citrated tubes within 72 hours of ICU admission under an IRB approved protocol in conjunction with an ongoing trial at the University of Utah and Veteran's Affair FFC Health Care System VAMC. Normal controls were comprised of commercially available 25 male and 25 female citrated plasma samples (George King Biomedical, Overland Park, Kansas City). Such biomarkers as CRP, PAI-1, D-Dimer, vWF and microparticle tissue factor complex (MP-TF) were measured using a commercially available sandwich ELISA methods. Nitric oxide (NO) levels were measured using a commercially available Griess reaction based colorimetric method. PT/INR, aPTT and fibrinogen measurements were based on clot based assays. All results were compiled as mean ± SD and SEM. Correlation analysis was carried out to determine relevance between different parameters.
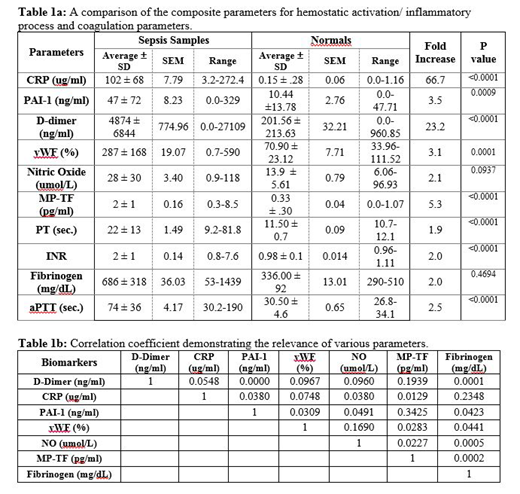
Results: Most of the biomarkers of hemostatic activation and inflammation were elevated in patients with sepsis as shown on table 1a, CRP (66 fold) and D-Dimer (23 fold) showed the most pronounced increase in comparison to the control. Other parameters also showed increase levels including MP-TF (5.3 fold), PAI-1 (3.5 fold), vWF (3.1 fold) and NO (3.0 fold). Clotting parameters such as PT/INR (2.0 fold), aPTT (2.5 fold) and fibrinogen (2.0 fold) were also significantly elevated in the sepsis patients. These differences were significant (p value ≤0.0009) for all of the parameters except for NO (p value 0.0937) and fibrinogen (p value 0.4694). As shown on table 1b, there was no correlation between various biomarkers and fibrinogen in the sepsis patients.
Summary & Conclusion: In comparison to the control group, the sepsis patients showed wide variations in all of the parameters investigated in this study. The marked prolongation of PT and aPTT are suggestive of both the extrinsic and intrinsic pathway defects and consumption of clotting factors. The aPTT data showed wider scatter in comparison to PT data. The fibrinogen levels were also elevated and nearly 1/3 of the patients showed >1000 mg/dL levels. The markedly higher level of CRP in the sepsis group are indicative of severe inflammatory response. Marked elevation of D-Dimer is indicative of endogenous fibrin formation and its consumption consistent with activation of secondary fibrinolysis. MP-TF, vWF and PAI-1 were also increased in the sepsis patients suggesting marked endothelial dysfunction. This is consistent with increased NO levels which may be due to induction of iNOS in the endothelial lining of sepsis patients. These results further underscore the multifactorial pathophysiology of sepsis which results in the dysregulation of hemostasis, upregulation of inflammatory responses and generalized endothelialopathy. Profiling of the biomarkers included in this study and coagulation parameters may be helpful in the risk stratification and clinical management of patients with sepsis and related disorders.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal