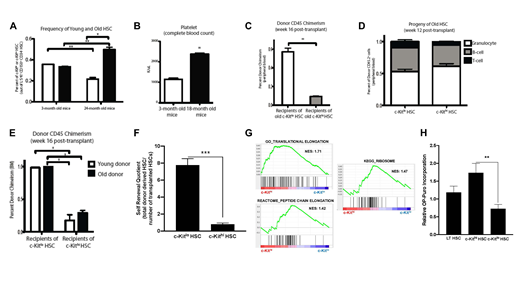
Aging hematopoiesis is characterized by increased numbers of immunophenotypic HSCs that exhibit impaired self-renewal and long-term reconstitution potential, both in competitive and noncompetitive settings. We previously demonstrated that normal young mouse HSCs (CD34-CD150+LSK) can be fractionated into subsets based on expression of c-Kit surface expression, with c-Kithi HSCs exhibiting reduced self-renewal and megakaryocytic biased differentiation (Shin et al., 2014). We therefore hypothesized that the expansion of c-Kithi HSCs in old mice could potentially explain the age-related decline in immunophenotypically defined old HSC function. Evaluation of the bone marrow of 24-month-old C57Bl/6 mice revealed that the frequency of c-KithiHSCs (out of total HSCs) is 1.5-fold higher in old mice than in 3-month old mice (P=0.04), while the frequency of c-Kitlo HSCs was 1.5-fold lower in old mice (P=0.007; Fig 1A). This finding is consistent with our previous observation of a megakaryocytic-bias in c-KithiHSCs, since peripheral blood analysis of old mice revealed a 2.1-fold increase in platelets compared to young mice (p<0.01) (Fig 1B).
To test the long-term reconstitution potential of aging HSCs, we competitively transplanted 400 c-Kitloor c-Kithi HSCs from 24-month old mice, along with 300,000 competitor bone marrow cells, into lethally irradiated young recipients. Sixteen weeks post-transplantation, mice receiving old c-Kithi HSCs exhibited significantly lower donor peripheral blood chimerism levels compared to old c-Kitlo HSC recipients (9.4% vs 57.1%, P=0.02) (Fig 1C). Both old c-Kithiand old c-Kitlo HSCs exhibited similar myeloid-reconstituting potential (Fig 1D). Furthermore, mice transplanted with old c-Kitlo HSCs exhibited 78% donor HSC chimerism, achieving 6.4-fold higher chimerism levels than mice transplanted with old c-Kithi HSCs, this was comparable to the differences observed with young c-Kitlo and c-Kithi transplanted HSCs (Fig 1E). To quantify the self-renewal capacity of old HSCs, we calculated the "self-renewal quotient" (Challen et al., 2010). This analysis showed that the self-renewal potential in old c-Kithi and c-Kitlo HSCs were 0.8 and 7.8 respectively, indicating higher self-renewal potential in c-Kitlo than c-Kithi HSCs (Fig 1F). Collectively, these data suggest that myeloid-biased differentiation is an age-associated change in hematopoiesis that may not be associated with decreased self-renewal in all HSCs.
To gain mechanistic insights underlying these qualitative differences, we interrogated transcriptional profiles of microarray data from c-Kitlo and c-Kithi HSCs, to identify potential pathways critical for HSC maintenance. Gene Ontology and pathway analyses showed several differentially expressed pathways between c-Kithiand c-KitloHSCs, of which genes related to protein translation and mitochondrial activity was significantly enriched in c-Kithi HSCs (Fig 1G). Given the underrepresentation of translation-related genes in c-Kitlo HSCs, we tested whether they exhibit reduced global translation using OP-Puro incorporation assays. These studies confirmed that old c-Kitlo HSCs show lower global translation levels than c-KithiHSCs (Fig 1H).
Overall, our studies demonstrate functional heterogeneity among old HSCs and identify a novel strategy to identify old HSCs with preserved self-renewal and long-term reconstitution capacity. The ability to identify and prospectively fractionate old HSCs offers a novel approach to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying HSC aging.
Figure legend. (A) Frequency of c-Kithior c-Kitlo HSCs was assessed by flow cytometry. (B) Circulating platelet numbers were assessed using a Hemavet counter. Competitive transplants of old c-Kitlo and c-Kithi HSCs into lethally irradiated recipients (C-F). Donor chimerism (C) and lineage potential (D) was evaluated in the peripheral blood of primary recipients. Bone marrow was analyzed at 16 weeks, for donor-derived HSC chimerism (E) and self-renewal quotient (F). (G) Enrichment plots comparing microarray data generated from c-Kithiand c-Kitlo HSCs, using pathways translation-related gene sets. (H) OP-Puro incorporation assays in 24-month old mice. Results are representative of three independent experiments, and shown as mean ± SEM. n = 4-5 mice. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal