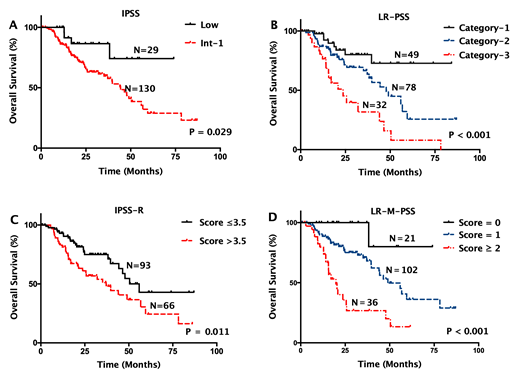
Patients with lower-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (LR-MDS) as defined by the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) have more favorable prognosis in general, but significant inter-individual heterogeneity exists. In this study, we examined the molecular profile of 15 MDS-relevant genes in 159 patients with LR-MDS using next-generation sequencing. In univariate COX regression, shorter overall survival (OS) was associated with mutation status of ASXL1 (P=0.001), RUNX1 (P=0.031), EZH2 (P=0.049), TP53 (P=0.016), SRSF2 (P=0.046), JAK2 (P=0.040), and IDH2 (P=0.035). We also found significantly shorter OS in patients with a TET2 variant allele frequency (VAF) ≥18% versus those with either a TET2 VAF <18% or without TET2 mutations (median: 20.4 vs. 47.8 months; P=0.020; HR=2.183, 95%CI: 1.129-4.224). After adjustment for the IPSS, shorter OS was associated with mutation status of ASXL1 (P<0.001; HR=4.306, 95%CI: 2.144-8.650), TP53 (P=0.004; HR=4.863, 95%CI: 1.662-14.230) and JAK2 (P=0.002; HR=5.466, 95%CI: 1.848-16.169), as well as a TET2 VAF ≥18% (P=0.008; HR=2.492, 95%CI: 1.273-4.876). Also, OS was increasingly shorter as the number of mutational factors increased (P<0.001). A novel prognostic scoring system based on the IPSS and the presence/absence of the 4 independent mutational factors further stratified LR-MDS patients into three prognostically different groups (P<0.001).The newly developed scoring system re-defined 10.1% (16/159) of patients as higher-risk group, who could not be predicted by the currently prognostic models. In conclusion, integration of IPSS with mutation status/burden of certain MDS-relevant genes may improve the prognostication of patients with LR-MDSand could help identify those with worse-than-expected prognosis for more aggressive treatment.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal