INTRODUCTION
Several phase 3 randomized studies have validated the use of novel 3-drug regimens with lenalidomide (LEN) and dexamethasone (Rd) in combination with carfilzomib (ASPIRE), elotuzumab (ELOQUENT-2), ixazomib (TOURMALINE-MM1), and daratumumab (POLLUX) in relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma (MM) with ≥ 1 line of prior therapy. However, these studies notably excluded patients (pts) who were LEN-refractory since the control arm in these studies received Rd. In practice though, many MM pts at first relapse for which these LEN-based triplets are often utilized are progressing on low-dose LEN maintenance therapy, and their outcomes have not been well characterized in the context of these pivotal trials that excluded such pts. In this single-center retrospective analysis, we report the outcomes of LEN-retreatment with a novel LEN-based triplet in pts progressing on LEN-based maintenance therapy, and compare to a smaller, similar cohort of pts treated with a pomalidomide (POM)-based regimen.
METHODS
MM pts progressing on LEN-based maintenance therapy between 1/1/2015 and 6/30/2018 at MD Anderson Cancer Center after autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) who were then treated with a LEN-based triplet or POM-based therapy were eligible for this study. Post-maintenance LEN-based triplet regimens included Rd in combination with bortezomib (VRd), carfilzomib (KRd), elotuzumab (ERd), ixazomib (IRd), and daratumumab (DRd). Disease response and progression were assessed by International Myeloma Working Group response criteria. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), and cohorts were compared by log-rank test. Pts who had not progressed were censored at the time of last disease evaluation prior to any change in therapy or data cut-off of 6/23/2019.
RESULTS
A total of 88 pts with a median of 1 prior line of therapy were eligible for the study. Baseline characteristics and prior treatment history are summarized in the Table. 66 pts received a LEN-based triplet, and 22 pts received a POM-based regimen after disease progression on LEN-based maintenance. A similar proportion of pts had high-risk cytogenetics (del 17p, t(4;14), and/or t(14;16)) in the LEN-based (21%) and POM-based (18%) post-maintenance treatment groups. The most common LEN-based maintenance regimens included LEN monotherapy (66%), ixazomib and LEN (14%), and elotuzumab and LEN (10%). Median PFS after ASCT on LEN-based maintenance was 26.0 months, and similar between the LEN-based (25.7 months) and POM-based (29.1 months) post-maintenance treatment groups, suggesting enrichment of pts with early progression on LEN-based maintenance in this analysis.
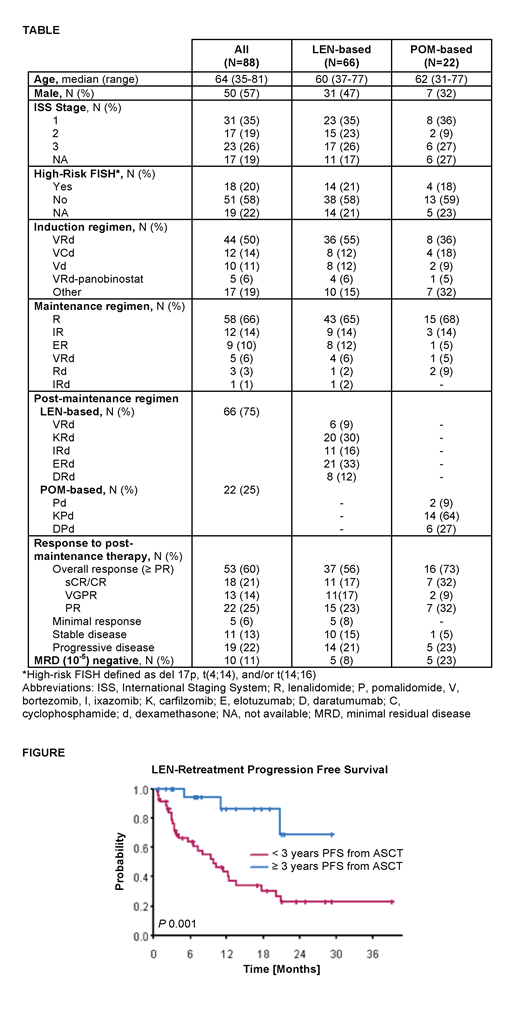
In pts retreated with LEN-based therapy, the median LEN dose increased from 10 mg during maintenance therapy to 25 mg in the post-maintenance regimen. The overall response rate (ORR, ≥ PR) to LEN-based retreatment was 56% (≥ VGPR 33%) and median duration of response (DOR) was 11.7 months (95% CI 9.23 - NA). In comparison, the ORR and DOR with POM-based treatment were 73% (≥ VGPR 41%) and 19 months (95% CI 7.88 - NA), respectively. At a median follow-up time of 20.5 months, median PFS and OS were 13.6 and 40 months, respectively, with LEN-based retreatment versus 21.4 months (P 0.7) and not reached (P 0.6) with POM-based therapy. There was no significant difference in PFS or OS between LEN-based triplet regimens (VRd, KRd, ERd, IRd, and DRd). In the LEN-based retreatment group, high-risk cytogenetics did not significantly impact PFS (10.1 vs. 13.6 months, P 0.9), although OS was worse (22.5 vs. 42.8 months, P 0.003). However, pts who progressed on LEN-based maintenance ≥3 years after ASCT had a significantly better median PFS with LEN-based retreatment compared to pts who progressed <3 years after ASCT (median not reached vs. 9.9 months, P 0.001, Figure).
CONCLUSION
In pts progressing on LEN-based maintenance therapy, retreatment with a LEN-based novel triplet to maximize LEN dose intensity and synergy with other novel agents can lead to deep and durable responses in select pts, particularly in those with a more indolent disease course and longer (≥3 years) PFS after ASCT. However, ORR and PFS may favor switching to a POM-based regimen over LEN-based retreatment in this patient population, and warrants further investigation in studies evaluating optimal sequencing strategies in relapsed and/or refractory MM.
Manasanch:Sanofi: Research Funding; Quest Diagnostics: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Skyline Diagnostics: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Bashir:Imbrium: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Spectrum: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; StemLine: Research Funding; Acrotech: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding. Patel:Poseida Therapeutics, Cellectis, Abbvie: Research Funding; Oncopeptides, Nektar, Precision Biosciences, BMS: Consultancy; Takeda, Celgene, Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kaufman:Janssen: Other: travel/lodging, Research Funding. Iyer:Novartis: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Arog: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Thomas:Xencor: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding. Orlowski:Poseida Therapeutics, Inc.: Research Funding. Qazilbash:Bioclinical: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Other: Advisory Board; Autolus: Consultancy; Genzyme: Other: Speaker. Lee:Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline plc: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal