Background
Oral anticoagulants are the preferred therapy for the treatment of venous thromboembolism and for stroke prevention among patients with atrial fibrillation. Given their widespread use, clinicians must balance efficacy of anticoagulation with their associated bleeding risks. Specifically, intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) is the most feared complication as this form of bleeding has the highest mortality and morbidity. To date, clinical trials suggest a lower incidence of ICH and better safety profile among patients prescribed the direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) compared with traditional vitamin k antagonists (VKAs). Although promising, further understanding is needed to appreciate the clinical impact once a DOAC-related bleeding event does occur. The aim of this study was to evaluate anticoagulation use, in-hospital mortality rates and functional outcome among patients presenting with ICH to a large tertiary care center in Canada.
Methods
In this study, we present data from a retrospective chart review of patients who presented to The Ottawa Hospital with ICH between January 2016 and December 2017. Patients were identified using ICD-10 codes from the Ottawa Hospital Data Warehouse. Patient demographics, type of anticoagulant/antiplatelet agent and indication for therapy were collected. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality rates among patients prescribed oral anticoagulants compared with those not anticoagulated or on antiplatelet therapy. A secondary outcome was functional assessment of survivors at hospital discharge using the modified Rankin Scale (mRS), a validated tool used widely in contemporary stroke research to measure the degree of disability after a neurological event.
Results
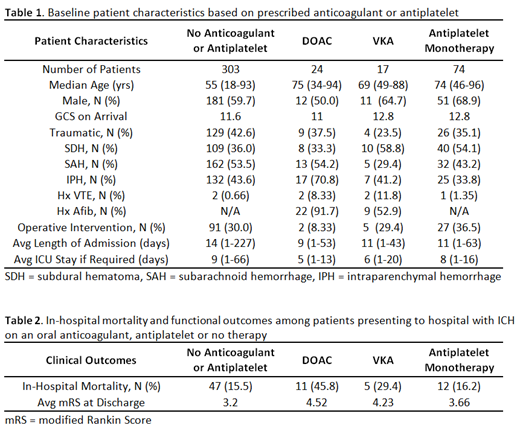
481 patients were identified in the Data Warehouse and manual chart review confirmed 429 patients diagnosed with ICH. Patients not taking any anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy tended to be younger and had lengthier admissions with longer stays in the ICU. The most common indication for anticoagulation in those presenting with ICH was atrial fibrillation. Intraparenchymal bleeding was most common among patients on DOACs, while patients on warfarin tended to have more subdural hematomas (Table 1). In-hospital mortality was 45.8% in DOAC-related ICH, 29.4% in warfarin-related ICH and 15.5% in patients not on an anticoagulant or antiplatelet. Average modified Rankin Scale at the time of discharge was 4.52 in DOAC-related ICH, 4.23 in warfarin-related ICH and 3.2 in patients not on an anticoagulant or antiplatelet (Table 2).
Conclusions
In this cohort of patients presenting with ICH to a large academic hospital, the in-hospital mortality rate was higher in patients receiving oral anticoagulation compared to those not on anticoagulants. DOAC-related ICH tended to have worse outcomes with higher in-hospital mortality and worse functional outcomes among survivors on discharge. Although the DOACs are reported in the literature to have an overall lower incidence of ICH, further information is still needed to understand the clinical impact when a bleeding event does occur.
Castellucci:BMS: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria; LEO Pharma: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Aspen: Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal