Background - Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) generally affects patients with a median age of 71 years. Majority of elderly MCL patients are transplant ineligible and are not suitable for intensive chemoimmunotherapy. Considering these limitations, our efforts are focused on developing "chemotherapy-free" modalities to treat these patients. We have previously reported high efficacy from a combination of ibrutinib with rituximab (IR) in relapsed MCL (Wang M et al Lancet Oncology 2015). We will now present the efficacy/safety analysis of our single center, phase II clinical trial using IR in previously untreated elderly (age ≥65 years) patients (pts) with MCL.
Methods - We enrolled previously untreated elderly (≥65 years) MCL pts (n=50) in this study (NCT01880567). Pts with Ki-67% ≥ 50%, blastoid/pleomorphic histology and those with clinically uncontrolled co-morbidities (including atrial fibrillation) were excluded from this study. Pts received IR combination - ibrutinib 560 mg orally daily for 28 days (one cycle) continued until disease progression or discontinued for any reason. Rituximab was given on days 1, 8, 15 and 22 +/- 1 day by intravenous infusion (IV) at a fixed dose of 375 mg/m2 (Cycle 1, followed by rituximab on day 1 of every cycle starting in Cycles 3 - 8. Following cycle 8, rituximab was given on day 1 of every other cycle for up to 2 years. The primary objective was to assess the response rate and safety of IR in elderly MCL. Among evaluable samples, minimal residual disease (MRD) by flow cytometry at best response and whole exome sequencing (WES) from baseline tissue samples was performed.
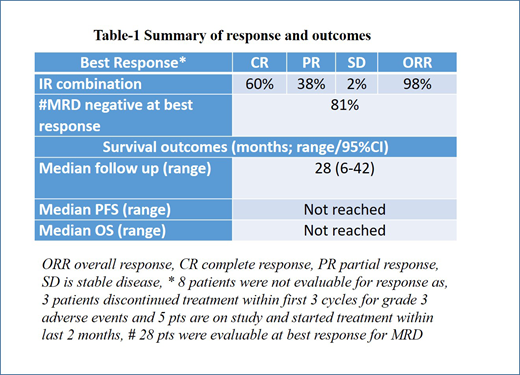
Results - Forty nine pts were included in this analysis. Median age was 71 years (range 65-84), 75% were males, ECOG PS was (0/1) in 48 (98%) pts, 16% had high risk simplified MIPI score and 28% had high risk biologic MIPI score. Forty seven patients (96%) had initial bone marrow involvement by MCL. The Ki-67% was low (<30%) in 37 (76%) and high (≥30-50%) in 12 (24%) pts, and 9% had complex karyotype. Eleven pts had prior history of atrial fibrillation. Overall, the median number of IR cycles was 16 (1-47). At the time of last follow up, 30 pts remained on study and 19 (39%) discontinued therapy for various reasons - atrial fibrillation (n=7; 3 had new onset and 4 had prior history of atrial fibrillation), disease progression (n=4), bleeding (n=3; 2 were on systemic anticoagulation and one pt was on aspirin 81 mg), infections (n=2) and one pt each due to myocardial infarction, esophageal cancer (unlikely related to drug) and patient choice. Dose reduction was performed in 26 (53%) pts for various reasons (7 atrial fibrillation, 6 infections, 5 bleeding, 3 myalgias and 5 miscellaneous). Most frequent grade 3-4 toxicities were 14% myalgias, 14% fatigue, 10% shortness of breath, 8% neutropenia and 8% new onset atrial fibrillation. Most of the atrial fibrillation events occurred early on in 2015-2016. These events were very infrequent in most recently enrolled pts which underwent meticulous cardiology screening and follow up. Seven pts were not evaluable for response assessment. The best overall response (ORR) was 98% (60% CR, 38% PR, 2% stable disease). Median number of IR cycles to reach CR was 8 (3-23). Thirty nine pts had baseline PET done and 34/39 were positive (87%) at baseline, of these 34 pts, 31 were evaluable for PET based response and 26/31 (84%) had CR, 4/31 (13%) had PR. Among the evaluable patients (n=26), minimal residual disease (MRD) negative CR by flow cytometry at best response was observed in 21 (81%). Overall, the median follow up was 28 months (6-42) and the median duration of pts on study was 19 months (range 1-45). Four pts progressed (3 transformed to blastoid/pleomorphic MCL) on study after taking IR for 4, 9, 13 and 33 months. Two pts died (one due to disease progression and another unknown etiology). The Median PFS and OS were not reached. Among pts with low and high Ki-67%, median PFS was not reached in both groups (p=0.26) and OS was not reached (p=0.01). Pts who achieved CR had a clear trend of longer PFS and OS compared to those who didn't achieve CR.
Conclusions - IR combination is an excellent frontline treatment option for elderly pts with MCL. Pts with baseline arrhythmias or pre-existing cardiac comorbidities could be managed cautiously and successfully while on this combination and are recommended to closely follow up with cardiology and may need an adjustment of anti-arrhythmic or ibrutinib dosing for optimal management.
Lee:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding. Westin:Juno: Other: Advisory Board; 47 Inc: Research Funding; Unum: Research Funding; Celgene: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Novartis: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Genentech: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Kite: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; Janssen: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding; MorphoSys: Other: Advisory Board; Curis: Other: Advisory Board, Research Funding. Nastoupil:Spectrum: Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; Genentech, Inc.: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Neelapu:Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Cell Medica: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Precision Biosciences: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Karus: Research Funding; Poseida: Research Funding; Unum Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Allogene: Consultancy. Fowler:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Wang:Juno Therapeutics: Research Funding; Aviara: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Honoraria; Loxo Oncology: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; MoreHealth: Consultancy, Equity Ownership; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Guidepoint Global: Consultancy; BioInvent: Consultancy, Research Funding; VelosBio: Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Ibrutinib and rituximab in frontline mantle cell lymphoma
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal