Introduction: Polycythemia Vera (PV) is a myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by excessive red cell production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines resulting in increased thrombotic risk, presence of systemic symptoms and reduced overall survival (OS). Abnormal body mass index (BMI) and comorbidities, as categorized by the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), were found to influence treatment success and survival in several hematological malignancies, including myelofibrosis (MF). We evaluated the impact of CCI and BMI on the outcome of PV pts on the basis of real-world data.
Methods: A network called "PV-NET" started in January 2019 including clinical/laboratory data of 2016 WHO-defined PV pts diagnosed and followed in 16 European Hematology Centers. Data cut-off was June 2019. OS was calculated from PV diagnosis to last contact or death (log-rank p). Cumulative incidences of events (thromboses, hemorrhages, infections, second neoplasia, and evolution into blast phase [BP] or MF) were conducted with Fine & Gray model with death as competing risk. Therapies were treated as time-to-event variables.
Results: A total of 530 PV pts were collected. Median follow-up was 5.4 yrs (0.5-34) (total observation: 3633 pt-yrs).
Main characteristics at diagnosis were: median age: 62.4 yrs (18.3-89.5); males: 53.4%; median (range) leukocyte/platelet count, x109/l: 9.8 (1.1-33)/448 (143-1386); median hemoglobin (g/dl)/hematocrit (%): 18.6/56 (males); 17.6/54.4 (females). Sixty-four (12.1%) and 34 (6.4%) pts had a thrombosis prior to or at diagnosis, respectively. At least one cardiovascular risk factor (CVRF) among smoke, diabetes, and hypertension was present in 343 pts (64.7%). Age-adjusted CCI was 0 (15.9%), 1 (18.9%), 2 (23.8%), and ≥3 (41.5%). Median BMI was 24 (17.4-37.3); 3.3%, 51.2%, 35.9% and 9.6% were underweight (BMI<18.5), normal weight (18.5-24.9), overweight (BMI≥25) or obese (BMI≥30), respectively. Baseline features were comparable across BMI and CCI categories, but male pts were significantly more likely to have a BMI≥25 than female (p<0.001).
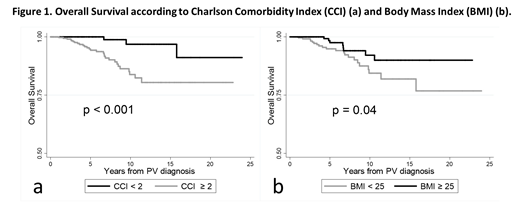
During follow-up, 64 all-grades thromboses (arterial, 56.3%), 29 bleedings, 56 infections and 66 second neoplasia were recorded. Overall, 13 pts progressed to BP and 32 to MF. Thirty-three pts died, because of BP (27.3%), second neoplasia (24.2%), MF (15.2%), old age (9.1%), thrombosis (6.1%) or other causes (18.1%). Incidence rates per 100 pt-yrs of all-grades events were: 1.5 (thromboses), 0.7 (bleedings), 1.4 (infections), 1.6 (second neoplasia), 0.4 (BP) and 0.9 (MF). Pts with CCI≥2 had a significantly higher rate of second neoplasia (p=0.01) and infections (p=0.03) over time and a worse OS (p<0.001) compared to pts with CCI<2. A BMI<25 was associated with a higher probability of MF progression (p=0.02) and with reduced OS (p=0.04) (Fig.1). Notably, thrombotic risk was not influenced by CCI (p=0.16) and BMI (p=0.43).
Pts received phlebotomies (PHL) (92.1%), hydroxyurea (HU) (82.6%), interferon (IFN) (7.9%), busulfan (2.6%), and ruxolitinib (RUX) (10.9%). Pts with CCI≥2 were significantly less treated with IFN (p<0.001) and received more frequently HU (p<0.001); notably, CCI did not influence the decision to start RUX (p=0.41). All pts treated with IFN but two had a BMI>18.5; both underweight pts discontinued IFN due to intolerance. Overall, 0.8%, 19.4%, and 38.1% of pts had grade≥2 toxicity and/or stopped therapy because of intolerance during PHL, HU, and IFN, respectively. IFN intolerance tended to be more frequent in pts with CCI≥2 (p=0.06).
Conclusions: CCI and BMI are rarely assessed in PV but may influence treatment strategy and survival. Particularly, CCI/BMI oriented the choice of IFN, but not RUX. Overweight PV pts had an improved survival, mimicking the "obesity paradox" observed in non-malignant CV diseases (Elagizi, et al. 2018). However, BMI may not be a reliable measure of adiposity. In cancer pts, an under/normal-weight may mask a hypercatabolic state with lean mass loss caused by a more aggressive disease, as supported by a higher rate of MF evolutions in pts with BMI<25. Quantified body composition and careful control of comorbid conditions can improve PV management, prognostication and outcome.
Benevolo:Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Elli:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Latagliata:Novartis: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria. Tiribelli:Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Heidel:Celgene: Consultancy; CTI: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Cavazzini:Pfize: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Bonifacio:Pfizer: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria. Crugnola:Incyte: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Cuneo:Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Krampera:Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cavo:amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel accommodations, Speakers Bureau; sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel accommodations, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; bms: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; novartis: Honoraria. Breccia:Celgene: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Palumbo:Hospira: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Teva: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria. Palandri:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal