Introduction:TP53 mutations have been associated with adverse outcomes in AML and MDS. While these mutations occur in less than 15-20% of pts, they are often associated with complex karyotypes and therapy-related (t)-myeloid neoplasms (MN). Previous studies showed poor outcomes with intensive chemotherapy (IC) and lower-intensity therapies [LIT] (e.g. hypomethylating agents [HMA]), and higher relapse rates after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (alloSCT), leaving the question of optimal treatment unanswered.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of all adult pts with MN and pathogenic TP53 mutations who were treated at Yale University from 9/1/2015 to 5/31/2019. We collected data on age, sex, ethnicity, prior malignancies and their treatments, white blood cell (WBC), hemoglobin, platelet count, disease risk, initial and subsequent lines of therapies, and use of alloSCT. Responses were recorded using modified International Working Group (IWG) criteria 2003 for AML and 2006 for MDS. Overall survival (OS) was measured using Kaplan Meier methods.
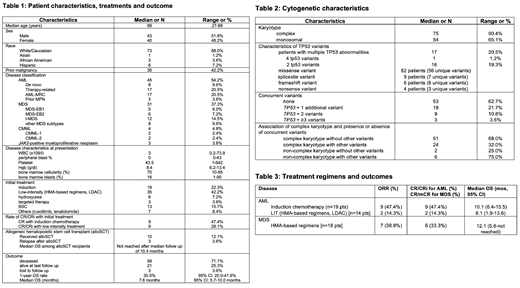
Results: We identified 83 pts with TP53-mutated MN (45 AML, 31 MDS, 4 chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, and 3 JAK2-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms). Median age was 69 years (range [R], 27-88 years), 52% were male, and 88% were Caucasian [Table 1]. Prior malignancy was noted in 35 pts (42%) and 29 (17 AML, 12 MDS) pts were classified as t-MN. Median WBC on presentation was 3 x 109 /L (R, 0.2 - 74x109) with a median of 0% peripheral blasts (R, 0-43%). Complex (n=75; 90%) and monosomal karyotypes (n=54; 65%) were highly prevalent. We identified 101 unique, pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations in the TP53 gene with 17 pts harboring more than 1 abnormal variant (16 pts with 2 mutations, 1 pt with 4 mutations). Missense variants were most commonly encountered (n=82 variants, 81%) followed by splicesite (n=9, 9%), frameshift (n=6, 6%), and nonsense variants (n=4, 4.0%). 52 pts had isolated somatic TP53 variants (63%). Among the other 31 pts DNMT3A (n=8 pts), JAK2 (n=6), and TET2 (n=5) variants were the most common somatic mutations. Of note, targetable driver mutations such as FLT3 (n=0), IDH1 (n=3), and IDH2 (n=1) were very rare. Notably, pts with complex karyotype were more likely to have isolated TP53 mutations compared to non-complex karyotype pts (complex karyotype + isolated TP53 mutations: 51 pts [68.0%] vs non-complex karyotype + isolated TP53 mutations: 2 pts [25.0%]; Fisher's exact test: p=0.024) [Table 2]. Median follow up of the cohort was 6.4 months (mos) [R: 0.2-55.3 mos]. Median OS in the entire study cohort was 7.6 mos (95% CI: 5.7-10.0 mos) with a 1-year OS rate of 30.5% (95% CI: 20.0-41.6%). Response rates and outcome for AML and MDS patients by treatment regimen are shown in Table 3. Among AML pts, IC did not appear to improve OS compared to pts receiving LIT (median OS 10.1 mos [95% CI: 6.4-15.5] vs 8.1 mos [95% CI: 1.9-13.6]; p=0.39). AML pts (median OS 6.7 mos [95% CI: 1.9-9.4]; 1-year OS: 23.2% [95% CI: 11%-38%]) had a statistically non-significant trend to poorer outcomes compared to MDS pts (median OS 10 mos [95% CI 5.7-12.9]; 1-year OS: 29.5% [95% CI 13.5-47.4%]; p=0.13). Notably, among the 10 pts who proceeded to alloSCT, only 3 pts relapsed after a median of 2.8 mos post-alloSCT. Relapse-free survival and median OS for pts who underwent alloSCT was not reached at a median follow up of 10.4 mos.
Conclusions: In this case series we confirm the poor prognosis for pts with TP53-mutated MN. Median OS was only 7.6 mos, and IC did not appear to improve OS compared to LIT for AML pts. With limited follow-up, pts who underwent alloSCT appeared to benefit. Novel therapies are urgently needed to improve outcomes of this pt population.
Podoltsev:Kartos Therapeutics: Research Funding; Samus Therapeutics: Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding; Sunesis Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; CTI Biopharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Other: Grant funding, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; AI Therapeutics: Research Funding; Arog Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Gore:Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding. Prebet:Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; Boehringer Ingelheim: Research Funding; pfizer: Honoraria; pfizer: Honoraria; pfizer: Honoraria; Tetraphase: Consultancy; novartis: Honoraria; novartis: Honoraria; Agios: Consultancy, Research Funding; novartis: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; pfizer: Honoraria; Genentech: Consultancy; pfizer: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; novartis: Honoraria; novartis: Honoraria. Isufi:Celgene: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy. Foss:Spectrum: Other: fees for non-CME/CE services ; Eisai: Consultancy; Acrotech: Consultancy; miRagen: Consultancy; Mallinckrodt: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Other: fees for non-CME/CE services . Huntington:AbbVie: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; DTRM Biopharm: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria; Genentech: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria. Neparidze:Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC: Research Funding; Eidos Therapeutics: Other: Member of Independent Diagnostic Committee; MMRF/Synteract: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Zeidan:Celgene Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Medimmune/AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Boehringer-Ingelheim: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Trovagene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Jazz: Honoraria; Ariad: Honoraria; Agios: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Daiichi Sankyo: Honoraria; Cardinal Health: Honoraria; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; BeyondSpring: Honoraria; Acceleron Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal