Introduction: The type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, obinutuzumab (OBI) is an effective therapy approved for chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and follicular lymphoma (FL). Data are limited for use of OBI as monotherapy in CLL/SLL as well as across other lymphoma subtypes, other than the GAUSS, GADOLIN, and GAUGUIN trials. We describe our experience of OBI as monotherapy without chlorambucil in the CLL/SLL population and OBI as monotherapy or in combination regimens across non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs).
Patients and Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of all adult pts who received OBI for CLL/SLL and NHL at the University of Pennsylvania between 2/2013 and 6/2019. Demographics, overall response, survival, and toxicities were examined. The primary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS; defined as time from OBI start to disease progression or regimen change, death due to CLL/SLL or NHL or last-follow-up in remission), and overall survival (OS) using the Kaplan-Meier method. All other analyses were descriptive. Indolent lymphomas included follicular, marginal zone, and mantle cell lymphomas. Aggressive lymphomas included diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Richter transformation, transformed follicular lymphoma, and transformed marginal-zone lymphoma.
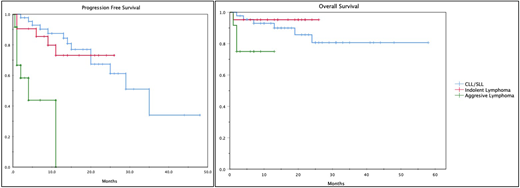
Results: We identified 78 pts for this analysis. Disease subtypes included CLL/SLL (58%; n=45), follicular lymphoma (13%; n=10), MZL (8%; n=6), MCL (5%; n=5), DLBCL/transformed disease (15%; n=12). Median age of OBI start was 67 years (27-89); CLL/SLL patients (pts) were median Rai Stage 2 and ECOG performance 0. NHL pts were median Ann Arbor Stage IV and ECOG performance 1. Median number of prior therapies was 1 (Range 1-7) in CLL/SLL and 3 in NHL (Range 0-9) with a median time to OBI initiation from last therapy of 12 months (mos) and 1 mos respectively. Of the CLL/SLL population 60% were rituximab naïve and 18% were rituximab refractory; 9% of NHL pts were rituximab naïve and 52% were rituximab refractory. Overall response rate (ORR) for the CLL/SLL cohort was 91%, 80% for FL, 83% for marginal zone lymphoma (n=6), 80% for mantle cell lymphoma (n=5), and 25% for aggressive lymphomas (n=12). For NHL, 50% received OBI as monotherapy, with 33% ORR. Median PFS subdivided by histologic cohorts were: 35 mos for CLL/SLL, not reached in indolent lymphomas, and 4 mos for aggressive lymphomas. Median overall survival divided by histologic subtype were 17 mos for CLL/SLL, 14 mos in indolent lymphoma and 45 mos in aggressive lymphomas. (Figure 1). OBI monotherapy in the indolent lymphoma group (n=8) had a 75% ORR and aggressive lymphoma group (n=6) had a 33% ORR. Of note, 2 aggressive lymphoma pts were successfully bridged to CAR T-cell therapy.
Adverse events (AEs) occurred in approximately 91% of CLL/SLL pts and 61% of NHL pts. AEs for the CLL/SLL group included: infusion related reactions (IRRs) (62%), neutropenia (16%), thrombocytopenia (40%), infection (22%), neutropenic fever (7%), and diarrhea (9%). AEs for the NHL group included: IRRs (24%), neutropenia (18%), thrombocytopenia (27%), infection (9%), and diarrhea (24%). In the CLL/SLL population 62% experienced an IRR on the first dose and 6 of those pts experienced a second infusion reaction in the first cycle of OBI. Despite a high rate of reactions in this population, most were confined to grade 2 reactions (93% grade 2; 7% grade 3). In the NHL population, all 8 pts (24%) experienced an infusion reaction on the first dose of OBI and one patient experienced a subsequent infusion reaction on the second dose.
Conclusion: We describe our experience of OBI therapy across histological subtypes of NHL outside the setting of a clinical trial, including OBI used as part of multi-agent salvage therapy in indolent and aggressive NHL. We observed high ORRs and durable PFS and OS in both CLL/SLL and indolent lymphoma cohorts. As expected, the aggressive lymphoma cohort had an ORR of 25% with a median PFS of 4 mos. Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were manageable with close supportive care, yet are critical parameters to monitor while on OBI regimens. IRRs were high in the CLL/SLL cohort and mainly confined to grade 2 reactions. OBI remains an effective and well tolerated agent in NHL and should continue to be considered for utilization in clinical trials to develop novel combination regimens for aggressive NHL as well as a partner to cellular therapy.
Hughes:Acerta Pharna/HOPA: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genzyme: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Schuster:Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Genentech: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Acerta: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; Nordic Nanovector: Consultancy, Honoraria; Loxo Oncology: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Patents & Royalties: Combination CAR-T and PD-1 Inhibitors, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Svoboda:AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Celgene: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kyowa: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Landsburg:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Curis, INC: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Triphase: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Triphase: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Speakers Bureau; Curis, INC: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Barta:Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bayer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mundipharma: Honoraria; Celgene: Research Funding. Gerson:Abbvie: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy. Chong:Tessa: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Merck: Research Funding. Rhodes:DAVA Oncology: Honoraria. Stadtmauer:Celgene: Consultancy; Abbvie: Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Tmunity: Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy. Dwivedy Nasta:Debiopharm: Research Funding; Aileron: Research Funding; ATARA: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria; Millenium/Takeda: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; 47 (Forty Seven): Research Funding; Rafael: Research Funding.
Obinutuzumab was investigated as a monotherapy agent as opposed to in combination for CLL. Additionally, obinutuzumab was only studied in follicular lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. This retrospective analysis includes lymphomas outside of specified indications.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal