Introduction: Dysbiosis of the gut microbiome during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) is associated with adverse post-transplant outcomes such as graft-versus-host disease, bloodstream infections, and mortality. In order to learn more about the role of the microbiome in HCT in adverse clinical outcomes, researchers collect stool samples from patients at various time points throughout HCT. However, unlike blood samples or skin swabs, stool collection requires active subject participation, particularly in the outpatient setting, and may be limited by patient aversion to handling stool. By providing study participants with compensation for their stool samples, we hypothesize that we can significantly increase stool collection rates.
Methods: We performed a prospective cohort study on the impact of financial incentives on stool collection rates for microbiome studies. The intervention group consisted of allogeneic (allo)-HCT patients from 05/2017-05/2018 who were compensated with a $10 gas gift card for each stool sample. The intervention group was compared to a historical control group consisting of allo-HCT patients from 11/2016-05/2017 who provided stool samples before the incentive was implemented. To control for potential changes in collections over time, we also compared a contemporaneous control group of autologous (auto)-HCT patients from 05/2017-05/2018 with a historical control group of auto-HCT patients from 11/2016-05/2017; neither auto-HCT groups were compensated. Allo-HCT patients were required to give samples at pre-HCT, day 0 (the day of HCT), and days 7, 14, 21, 30, 60, and 90 post-HCT. Auto-HCT patients were required to give samples at pre-HCT and days 7, 14, and 90 post-HCT. Collection rates were defined as the number of samples provided divided by the number of time points for which we attempted to obtain samples. Patient characteristics were summarized by proportions for categorical variables and median with interquartile ranges for continuous variables. Chi-square tests or Fisher's exact tests were used to compare categorical variables, as appropriate, and Wilcoxon Rank Sum tests or t-tests were used to compare continuous variables, as appropriate. This study was approved by the Duke Institutional Review Board, and informed consent was obtained from all patients.
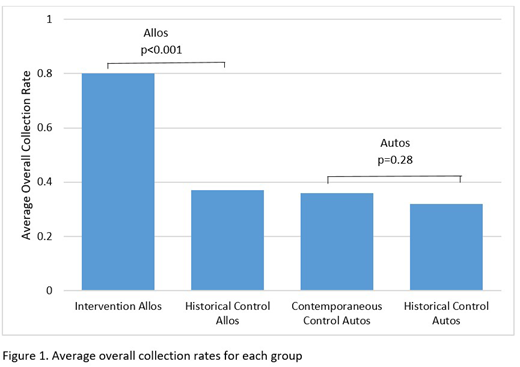
Results: There were 35 allo-HCT patients in the intervention group, 19 allo-HCT patients in the historical control group, 142 auto-HCT patients in the contemporaneous control group, and 75 auto-HCT patients in the historical control group. Groups were similar with regard to baseline demographics such as age, race, and gender. While allo-HCT patients were more likely to have leukemia and auto-HCT patients were more likely to have lymphoma and multiple myeloma, there were no differences in disease rates across the study periods. Allo-HCT patients in the intervention group had significantly higher average overall collection rates when compared to the historical control group allo-HCT patients (80% vs 37%, p<0.001), as well has significantly higher average outpatient collection rates (84% vs 23%, p<0.001) and average inpatient collection rates (71% vs 46%, p=0.04). In contrast, there were no significant differences in overall average collection rates between the auto-HCT patients in the contemporaneous control and historical control group (36% vs 32%, p=0.28), as well as the average outpatient collection rates (30% vs 28%, p=0.54) and the average inpatient collection rates (46% vs 59%, p=0.25).
Discussion: Our results demonstrate that even a modest incentive can significantly increase collection rates. Use of a contemporaneous control group to account for potential differences in stool collection rates over time strengthens our finding that financial incentives increase stool collection rates. Furthermore, the significant increase in collection rates in the outpatient setting highlights the role of the incentive when patient participation is needed, as opposed to the inpatient setting in which the nurse assists with collection. While this study uses a specialized HCT patient population, these results may be generalizable to future studies and aid other researchers in obtaining stool samples needed for future microbiome studies.
Peled:Seres Therapeutics: Other: IP licensing fees, Research Funding. van den Brink:Acute Leukemia Forum (ALF): Consultancy, Honoraria; Juno Therapeutics: Other: Licensing; Merck & Co, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria; Seres Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Therakos: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Flagship Ventures: Consultancy, Honoraria; Evelo: Consultancy, Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Magenta and DKMS Medical Council: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sung:Novartis: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Seres: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal