Introduction
Standard first line treatment for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in fit patients is induction with cytarabine containing chemo-immunotherapy and a consolidative autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). Responses are excellent but there is a continuous pattern of relapse. Progression within 24 months (POD24) of standard first line therapy including ASCT has been shown to predict poorer outcomes, which may be ameliorated by alloSCT. Ibrutinib, a Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor, is an effective therapy for relapsed MCL. However, there is a paucity of published data of ibrutinib's efficacy in patients treated at relapse after standard first line treatment with ASCT and very little regarding the impact of POD24 on outcomes after ibrutinib and outcomes of subsequent alloSCT.
Methods
This was a retrospective analysis of the EBMT registry. The inclusion criteria were: patients with MCL ≥18 years old, 1st line therapy containing cytarabine and rituximab, ASCT in first CR/PR between 2009 and 2016 and received ibrutinib for 1st relapse after ASCT. POD24 was defined as progressive disease in less than 24 months after ASCT.
Results
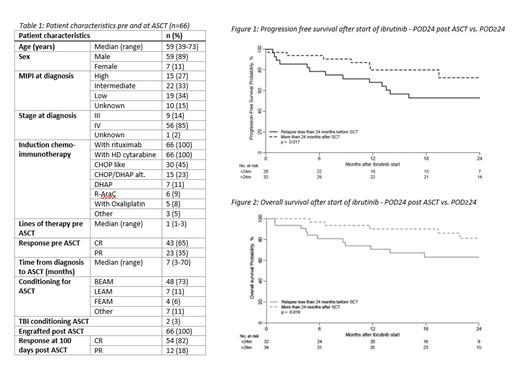
66 patients met the inclusion criteria (Table 1) relapsing at a median of 25 months (range 15-33) post ASCT. Thirty-two patients progressed in less than 24 months after ASCT. Ibrutinib was started at a median of 30 days after relapse (range 10-54). Overall response rate (ORR) was 74% [32 (48%) achieving CR and 18 (27%) PR]. The median duration of response was 10.1 months (available for 28 patients). There were no significant differences in the duration of response to ibrutinib for patients with POD24 (median: 10.4 months, IQR 4.0-15.4) compared to POD after 24 months or more (POD≥24) [(median 9.8 months, IQR 6.5-20.7) p=0.9]. Relapse after/during ibrutinib occurred in 21 patients (33%) at a median of 12 months (range 1-34). 13 of those patients were on ibrutinib at the time of relapse and the remaining 8 after ibrutinib had been stopped for a SCT or because of toxicity. Ibrutinib therapy continues at last follow-up in 23 (35%) patients. Ibrutinib was stopped for the following reasons: 16 patients subsequent SCT, 13 relapse, 5 toxicity (cytopenia, infection, tachycardia, hepatitis and poor tolerance, 1 case each), 9 other/unknown reasons.
Second SCT was undertaken in 23 patients (22 alloSCT, 1 ASCT), 16 of whom were in CR/PR after only ibrutinib at the time of relapse. For alloSCT recipients, the donor was MUD in 11, MSD in 5 and mismatch related in 6. The majority (n=19) had reduced intensity conditioning. 50% of the patients developed acute GvHD and 50% chronic GvHD (3 extensive). With a median follow up of 17 months post alloSCT, 18 (63%) are in remission. There were no significant differences in PFS (p=0.173) or OS (p=0.336) post alloSCT for patients with POD24 and POD≥24.
At last follow up (median follow-up of 22 months after starting ibrutinib), 35 (71%) patients were in CR and 4 (8%) in PR. 17 patients have died; the most common reason was MCL (14 patients), 2 deaths were secondary to alloSCT toxicity and in 1 case the cause of death was unknown. 2-year OS after starting ibrutinib was 72% (69% for alloSCT patients) and 2-year PFS 62%. PFS after starting ibrutinib was significantly better for patients with POD≥24 compared to those with POD24 (72% vs. 53% at 2 years post ASCT, p=0.017) and this translated to an OS benefit (80% vs. 68% at 2 years post ASCT, p=0.019) (figures 1 and 2).
Conclusion
Ibrutinib therapy did not overcome the poor outcome for patients with POD24 after first line therapy and although there was a high ORR to ibrutinib the median duration of response is only 10.1 months. AlloSCT should therefore be undertaken if possible, in our retrospective cohort of patients it appeared to overcome the poor prognosis of POD24 patients.
Hunter:Jazz pharamceuticals: Honoraria, Other: speaker fees, Meeting attendance support; Novartis: Honoraria, Other: speaker fees; celegene: Other: Meeting attendance support. Peggs:Autolus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Foà:Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Shire: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Amgen Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celltrion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celltrion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Pillai:Celgene: Honoraria. Mufti:Celgene Corporation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Cellectis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal