Background: While autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) can be curative for patients (pts) with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), relapse remains common. With the emergence of novel effective therapies, it is even more important to identify pts at high risk of treatment failure who may not benefit from ASCT, and pts with impending post-ASCT relapse who may be candidates for pre-emptive interventions. We assembled cohorts of DLBCL pts who underwent ASCT and had apheresis stem cell (ASC) samples or serially collected post-ASCT peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) and plasma samples. We hypothesized that circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) identified using immunoglobulin-based next generation sequencing (IgNGS) in ASC or PB samples could predict relapse.
Methods: Samples from 3 cohorts were analyzed. Pts in cohort 1 (C1) underwent ASCT at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) from 2003-2013 (Herrera, ASH 2015). Archival tumor tissue and ASC samples were retrospectively collected for analysis. Pts in cohort 2 (C2) were prospectively enrolled on a banking protocol at DFCI and underwent ASCT from 2014-2016. Pts in cohort 3 (C3) underwent ASCT from 2015-2016 and participated in a multicenter phase II trial of post-ASCT pembrolizumab maintenance (PM) (Frigault, Blood Adv 2020). Pts in C2/C3 had tumor tissue and serially collected post-ASCT PBMC and plasma samples as mandated by protocol, and a subset had available pre-ASCT PB or ASC samples. Because PM did not demonstrate a clear benefit in the trial, all cohorts were analyzed together. IgNGS (Adaptive Biotechnologies; Seattle, WA) was performed, as previously described (Armand, BJH 2013). In all cases, ctDNA testing was not performed in real-time or used to drive clinical decisions.
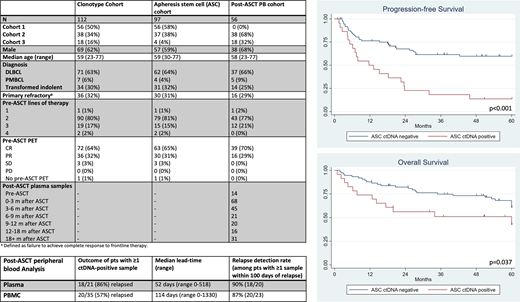
Results: 152 pts were enrolled. Among 141 pts with sufficient DNA for testing, a clonotype was identified in 112 (78%) with a higher detection rate in more recent cohorts - C2 (93%) and C3 (90%) vs C1 (67%).
Among 97 pts with an available ASC sample, 23 (24%) were ctDNA-positive (pos). With a median follow-up among survivors of 69 months (m) (range 13-185), the 5-year (y) progression-free survival (PFS) for ASC ctDNA-pos and ASC ctDNA-negative (neg) pts were 13% (95% CI 3-30%) and 52% (95% CI 40-63%), respectively (HR 2.8, p<0.001), while the 5y cumulative incidences of relapse were 83% (95% CI 66-99%) and 39% (95% CI 27-50%), respectively (HR 3.1, p<0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of ASC ctDNA for progression or death were 36% and 95%, respectively. ASC ctDNA (HR 2.5, p=0.002) was the only significant predictor of PFS in a multivariable model that included pre-ASCT positron emission tomography (PET), lines of therapy, age, and primary refractory status. Inferior overall survival was observed for ASC ctDNA-pos pts (HR 2.1 p=0.037). In an exploratory analysis, we examined 14 pts with an available pre-ASCT plasma sample. 2/14 were ctDNA-pos (14%) and both pts relapsed (HR for PFS 9.4, p=0.03). Among 13 pts with both pre-ASCT PB and ASC samples (drawn a median of 19 days apart [range 11-47]), results were concordant in 12/13 pts (92%).
56 pts had a median of 3 (range 1-8) post-ASCT plasma samples available for analysis. Within this cohort, 25 pts relapsed and 2 pts died in remission. 21 pts (38%) had detectable ctDNA in a median of 2 post-ASCT samples (range 1-5); among them, 18 (86%) relapsed with a median lead time from first ctDNA detection to relapse of 52 days (range 0-518). Among the 3 ctDNA-pos pts who did not relapse, 2 had detectable ctDNA at a single time point and subsequently became ctDNA-neg, and 1 developed acute myeloid leukemia and underwent allogeneic transplantation. Among 20 pts who relapsed and had ≥1 plasma sample available within 100 days of relapse, 18 (90%) had detectable ctDNA. PBMC testing had inferior performance characteristics (Table).
Conclusions: Identification of ctDNA using IgNGS within an ASC sample is a powerful predictor of post-ASCT relapse and provides (at least in this cohort) a better way to predict relapse than pre-ASCT PET. Detection of ctDNA in pre-ASCT plasma also appears to be predictive of relapse. In ctDNA-pos pts, given the dismal PFS, strong consideration could be given to alternative treatment strategies, e.g. CAR-T cell therapy. Furthermore, detection of ctDNA in post-ASCT plasma samples is closely associated with impending relapse, which provides an attractive platform for pre-emptive therapeutic intervention.
Brown:Dynamo Therapeutics: Consultancy; Morphosys: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other; Octapharma: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Acerta: Consultancy; Sun: Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy; Rigel Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Eli Lilly and Company: Consultancy; Juno/Celgene: Consultancy; Invectys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: DSMC; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astra-Zeneca: Consultancy; Janssen: Honoraria; Sunesis: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Loxo: Consultancy, Research Funding; Nextcea: Consultancy; MEI Pharma: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Catapult: Consultancy; BeiGene: Consultancy; Verastem: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy. Crombie:AbbVie: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding. Davids:Gilead Sciences: Consultancy; Zentalis: Consultancy; Sunesis: Consultancy; Syros Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Research to Practice: Honoraria; Merck: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; BeiGene: Consultancy; Ascentage Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Verastem: Consultancy, Research Funding; MEI Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Surface Oncology: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Fisher:Kyowa Kirin: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jacobsen:Merck, Pharmacyclics, F. Hoffmann-LaRoche, Novartis: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Acerta, AstraZeneca, Merck: Consultancy. LaCasce:BMS: Consultancy; Research to Practice: Speakers Bureau; UptoDate: Patents & Royalties. Dahi:Kite: Consultancy. Nieto:Secura Bio: Other: Grant Support; Novartis: Other: Grant Support; Affimed: Consultancy, Other: Grant Support; Astra Zeneca: Other: Grant Support. Chen:Incyte Corporation: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Magenta: Consultancy; Kiadis: Consultancy; Actinium: Other: Data and Safety Monitoring Board Member; Equillium: Other: Data and Safety Monitoring Board Member; AbbVie: Other: Data and Safety Monitoring Board Member. Herrera:Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Other: Travel, Accomodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc./F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Immune Design: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding. Armand:IGM: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Affimed: Consultancy, Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Infinity: Consultancy; Otsuka: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Tensha: Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Adaptive: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sigma Tau: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal