Background. Iron absorption from gastrointestinal tract was enhanced in a subset of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) exhibiting ineffective erythropoiesis. Duodenal iron absorption was achieved via an iron transporter divalent metal transporter (DMT)-1 and ferroportin which was downregulated by hepatic hepcidin. Recently, three erythroid regulators such as growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), twisted gastrulation protein homolog 1 (TWSG1) and erythroferrone (ERFE) which down regulated hepatic hepcidin production has been identified. However, it has been not yet clarified which molecules could contribute to the increased iron absorption in patients with MDS.
Materials and Methods. In the present study, we examined the expression level of GDF15, TWSG1 and ERFE mRNA during ex vivo erythroid differentiation from sodium butyrate (SB)-treated K562 and CD34+ bone marrow (BM) cells in the presence of 4 U/mL erythropoietin (EPO), 100 U/mL interleukin-3, 10 ng/mL stem cell factor, 20 ng/mL insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and 500 micro g/mL iron-saturated transferrin. We further analyzed the expression level of GDF15 and ERFE by using a GEO dataset (GSE58831). GEO dataset was downloaded as a matrix by GEOquery package (Bioconductor). The numerical data of the matrix were normalized by quantile normalization using limma package. Clinical and sequencing data were downloaded from supplementary materials. Those were combined with a GEO dataset (GSE58831) before analysis.
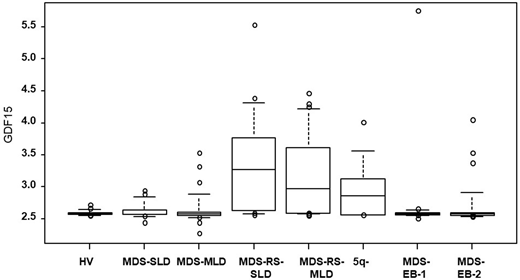
Results. The levels of ERFE and GDF15 mRNA were dramatically increased during erythroid differentiation from SB-treated K562 and normal CD34+ cells in response to EPO in vitro. Using GEO data sets (GSE58831), the levels of ERFE and GDF15 mRNA in CD34+ cells derived from MDS patients were significantly elevated as compared with that from healthy volunteers. Importantly, the levels of ERFE and GDF15 mRNA in CD34+ cells in a subset of MDS with ring sideroblasts (RS) or SF3B1 mutation were significantly and highly elevated as compared with other subsets of MDS (GSE58831). Additionally, the supernatant derived from SB-treated K562 reduced hepcidin level in HepG2 in the presence of EPO.
Conclusion. These results suggested that productions of ERFE and GDF15 in CD34+ MDS cells with RS or SF3B1 mutation may be associated with abnormal iron metabolism via hepcidin reduction. These findings may be useful to understanding the high ferritin level in a subset of MDS patients.
Kobune:Takeda Pharmaceutical Company: Research Funding; Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc: Research Funding; Novartis Pharma K.K.: Research Funding; ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD: Research Funding. Ikeda:Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc: Research Funding; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited: Research Funding; Novartis Pharma K.K.: Research Funding; Sanofi K.K.: Research Funding; ONO PHARMACEUTICAL CO., LTD: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal