Background and Objective:
Disease relapse remains the primary cause of morbidity and mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-HSCT) in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Oral azacitidine (5-aza) was associated with clinical benefit as maintenance therapy in transplant ineligible patients. However, contradicting data have been reported regarding the role of 5-aza as a maintenance therapy to reduce relapse rate -post-allo-HSCT. We conducted this systematic review to describe the efficacy and safety of 5-aza in this context.
Materials and Methods:
We systematically searched multiple databases, including PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and Clinicaltrials.gov. We also searched major conferences for oral or poster presentations. We used MeSH terms and keywords for MDS, AML, Allo-HSCT, and 5-aza. We included all retrospective and prospective studies of 5-aza (all formulations) published until March 2020. The primary database search yielded 1209 articles. We excluded irrelevant, duplicate, and review articles. The final search revealed 20 articles that we explored in detail for various efficacy and safety outcomes.
Results:
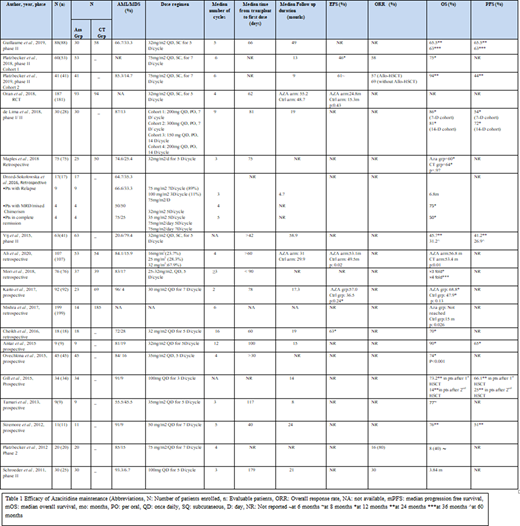
A total of 1211 patients were enrolled in 14 prospective and 6 retrospective studies. Of those, 1169 patients were evaluable.
Prospective studies
CALGB 100801 trial by Vij et al. (2015) reported overall survival (OS) of 45.7% and progression-free survival (PFS) of 41.2% at 24 months following reduced intensity conditioning (RIC) in a phase 2 trial of 41 patients. In a randomized control trial, Oran et al. (2018) evaluated relapse-free survival (RFS) as the primary outcome after 12 cycles of 5-aza at 32 mg/m2/day (n=187). Only 30% of the patients in the azacitidine arm completed the targeted number of cycles. The study showed a median RFS of 24.8 months in the treatment arm vs 15.3 months in the control arm (p=0.43). In a phase 2 trial conducted by Guillaume, T et al. (2019) the cumulative incidence of relapse was 27.6% in patients who received 5-aza, compared with 41.9% in 58 matched patients control group (p=0.21). Platzbecker et al. (2018-2019) studied a higher dose of azacitidine (75mg/m2/day) in a phase 2 trial as a pre-emptive strategy for patients who develop minimal residual disease (MRD) within 24 months. The 12-month OS and PFS were 94% and 44%, respectively. De Lima et al. (2018) studied the role of maintenance Oral 5-aza in Phase I/II trial (n=30). A dose-escalation design was used with a dosage ranging from 150 mg to 400 mg, received in a 7- or 14-day cycles. The 12-month PFS was 54% and 72% and estimated survival was 86% and 81% among 7-days and 14-days cycles, respectively. (Table 1)
Retrospective studies:
Mishra et al. (2017) reported a better OS in 14 patients who received 5-aza maintenance compared with a control arm (p-value 0.026). Cheikh et al. reported a 12-month OS of 70%. Ali, N et al. (2020) (n=107) compared 5-aza group vs. control group retrospectively. EFS was 53.1% vs. 49.5% (p=0.02) while OS was 56.8 and 53.4 months (p=0.01) in the treatment arm vs the control arm respectively.
Safety:
The most common grade 3 or 4 hematological adverse effect was neutropenia, while some patients also experienced grade 3 or 4 anemia, thrombocytopenia, or lymphopenia. The main non-hematological adverse effects were infections, fatigue, and gastrointestinal distress. The incidence of acute graft versus host disease varied from 13% to 50%. The most common reason for treatment discontinuation was disease relapse. A minority of patients discontinued treatment due to side effects.
Conclusion:
To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive systematic review for the role of 5-aza maintenance -post-Allo-HSCT in patients with MDS or AML. The heterogeneity of the studies, in terms of dosing regimens, variable duration of treatment and patient selection, precludes definitive conclusions. Despite that, 5-aza seems to improve relapse rates and OS at least numerically but also significantly in some studies, as illustrated in this review. Low number of patients involved in most of these studies contributed to non-significant p-values. Azacitidine remains a valid and safe option, especially in patients with high risk of relapse. Further studies aiming at those high risk patients, such as AML with myelodysplasia related changes (AML-MRC) and high-risk MDS following RIC, are of utmost need.
Anwer:Incyte, Seattle Genetics, Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Celegene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals.: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Fazal:Takeda: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Agios: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Stemline: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Karyopharm: Speakers Bureau; Jazz: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal