Abstract
Introduction: The chemotherapy regimen dose adjusted (DA)-EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide) is a first line option for peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), but for most subtypes relapses are common and long-term outcomes are poor. Checkpoint blockade is an immunotherapeutic approach that has shown efficacy as a single agent in relapsed PTCLs. The combination of checkpoint blockade and cytotoxic chemotherapy can have additive or synergistic activity by increasing the expression of neoantigens and overcoming mechanisms of resistance to immunotherapy such as weak tumor immunogenicity and an immune suppressive tumor microenvironment.
Methods: We conducted a single arm, open-label clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of the anti-PD1 antibody nivolumab (Nivo) in combination with DA-EPOCH in newly diagnosed PTCLs with ≥Stage II disease by Ann Arbor criteria. Pts were allowed to receive one cycle of chemotherapy prior to enrollment. Pts received Nivo (360 mg) followed by DA-EPOCH every 21 days for a planned six cycles unless treatment was stopped early for progression. For any immune related adverse event (irAE), Nivo was held until resolution to grade 1 and on ≤10mg prednisone. For serious grade 3-4 irAEs, Nivo was omitted with remaining DA-EPOCH cycles. DA-EPOCH was dose adjusted according to CALGB 50303 with the exception that pts could begin treatment at dose level -1 (i.e. 600 mg/m2 cyclophosphamide), at investigator's discretion. Pts who received one cycle of chemotherapy prior to enrollment received five cycles of Nivo + DA-EPOCH. After completing six cycles of chemotherapy, pts had the option to proceed with consolidative autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) versus surveillance, according to patient/physician preference. Responses were assessed by PET/CT after 2 cycles of Nivo + DA-EPOCH and after the last cycle, using RECIL criteria. PFS events were defined as start of new treatment, progression, or death. Targeted next generation sequencing and multiplex immunohistochemistry of diagnostic tumor tissue are being performed.
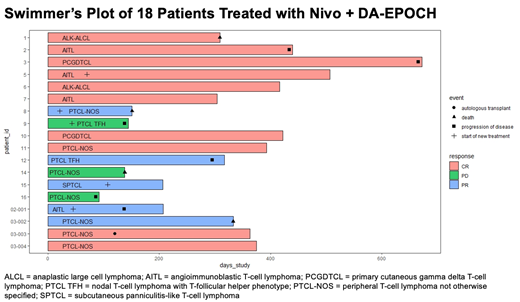
Results: We enrolled 18 pts: 4 angioimmunoblastic TCLs, 2 nodal PTCLs with T-follicular helper phenotype, 7 PTCL-NOS (not otherwise specified), 2 primary cutaneous gamma delta TCLs, 2 ALK negative anaplastic large cell lymphomas, and 1 subcutaneous panniculitis-like TCL who had progressed on methotrexate. Median age was 66 (range 43-77). International Prognostic Index (IPI) was high (4-5) in 50% (N=9), intermediate (2-3) in 33% (N=6), and low in 17% (N=3) of pts. Immune related AEs of all grades occurred in 78% (N=14) of pts and 39% (N=7) of pts experienced ≥grade 3 irAEs. 44% (N=8) of pts required discontinuation of Nivo due to irAEs. In the 8 pts whose irAEs resulted in discontinuation of Nivo, the irAE occurred prior to the second or third cycle of Nivo + DA-EPOCH. None of the 6 pts who received a cycle of anthracycline based chemotherapy prior to enrolling on trial experienced an irAE resulting in dose hold or discontinuation of Nivo, whereas 8 of 12 pts who did not receive a prior cycle of anthracycline based chemotherapy experienced an irAE requiring a dose hold or discontinuation of Nivo. The most common non-hematologic non-immune related ≥grade 2 AEs were related to infectious complications. Interim and end of induction overall response rates were 100% and 83%, respectively. We observed 10 CR, 5 PR, and 3 PD at the end of induction. There were 2 pts who received consolidation with ASCT. With a median follow up of 375 days (range 207-422), median modified PFS was 333 days (range 138-666) and median OS was not reached. The three pts with PD during induction were 2 PTCL-NOS (with a cytotoxic phenotype) and 1 AITL (with PD1+ tumor cells). Further correlative studies are ongoing to identify predictors of response.
Discussion: In this pilot study using Nivo + DA-EPOCH for newly diagnosed PTCLs, we observed early immune related dose limiting AEs. Pts who received a cycle of anthracycline based chemotherapy prior to enrollment did not experience any dose limiting irAEs. We postulate that T-cell lymphoma pts are immunologically primed for irAEs, which can be mitigated by pre-treatment with chemotherapy. In a study in which half of pts were high risk by IPI, Nivo + DA-EPOCH led to encouraging high initial responses and lengthy responses in 2 PCGDTCL pts, thus warranting further investigation of this chemoimmunotherapeutic strategy.
Haverkos: Viracta Therapeutics: Consultancy. Zain: Secura Bio, DaichiSankyo, Abbvie: Research Funding; Secura Bio, Ono , Legend, Kiyowa Kirin, Myeloid Therapeutics Verastem Daichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Kiyoaw Kirin, Secura Bio, Seattle Genetics: Honoraria. Kamdar: KaryoPharm: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Celgene (BMS): Consultancy; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; SeaGen: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Other; AbbVie: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Genetech: Other. Smith: Syros: Research Funding; Kura: Research Funding; Argenx: Research Funding. Porcu: Viracta: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Innate Pharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BeiGene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Daiichi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Kiowa: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy; DrenBio: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal