Abstract
Aims: The onset of blast crisis (BC) in initially chronic phase (CP) CML patients that entered treatment-free remission (TFR) after TKI is an exceptional event, however, there is emerging evidence that this may occur in such patients (pts), although the pathogenesis remains unclear to date.
Methods: Anonymous clinical case retrospective data collection from patients' datafiles, after written agreement of living patients, centralisation of available frozen nucleic acid collection from diagnosis and from blast crisis and reanalysis by Next-Generation Sequencing of samples (ASXL1, ASXL2, BCOR, CALR, CBL, CEBP alpha , CSF3R, DNMT3A, EP300, ETNK1, ETV6, EZH2, FLT3, GATA2, IDH1, IDH2 JAK2, KIT, , KRAS,MPL, NPM1, NRAS, PHF6, PTPN11 , RAD2, RUNX1, SETBP1, SF3B1, SH2B3, SMC1A, SMC3, SRSF2, STAG1, STAG2, TET2, TP53, U2AF1, WT1 and ZRSR2 genes analysed) on Illumina platform. CNV analysis were performed using VisCAp or in-house pipelines and/or by Multiplex Ligation Dependant Probe Amplification (MLPA). ABL1 tyrosine kinase domain mutations were screened by NGS on cDNA or directly on DNA. BCR-ABL1 transcripts are expressed in % (IS) with at least 32,000 copies of ABL1 as control. All patients discontinued their TKI after 2 years of MR4.5 and a TKI was resumed in case of MMR loss.
Results: Along 15-year experience of TFR in our country and ≥ ~800 patients experiencing a TKI cessation attempt, informations from 4 (~0.5%) TFR CML patients entering BC have been collected. All patients harboured Major BCR transcripts.
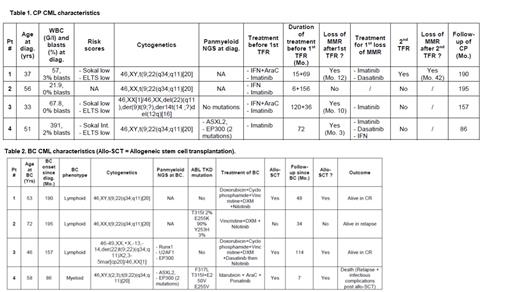
The chronic phase characteristics are mentioned in Table 1.
All these long-lasting CP CML pts were ELTS risk score low, and 1 was harbouring ACA at diagnosis. One pt was mutated for ASXL2 and 2 mutations for EP300, found again at BC. Three pts had IFN-a prior to imatinib for all. Three out of 4 lost their MMR after a first cessation attempt at 12, 10 and 3 months after cessation. Pt #1 experienced a 2 nd cessation attempt 52 months after re-initiation of TKIs and entered lymphoid BC 6 months after a second resumption of TKI for a 2 nd MMR loss.
The BC characteristics are mentioned in Table 2.
Three out of 4 BC were lymphoid, one had ACA different from those at CP diagnosis. Two pts explored had multiple mutations in Runx1, U2AF1, EP300 and ASXL2 genes, not present at CP diagnosis, in addition to multiple ABL1 mutations in 2 out of 4 pts (2 T315I, 3 P-Loop mutations). All pts underwent chemotherapy + various TKI leading to complete remission (CR) in all and 3 out of 4 pts could be allotransplanted in CR, one relapsed shortly after transplant, and a second one 34 months after transplant. Overall 3 pts are alive with 1 in controlled relapse.
Conclusions: The onset of BC after TFR for sustained deep molecular response remains an exceptional event and is probably not induced by this therapeutic procedure. These 4 cases underline the need for a sustained long-lasting molecular follow-up of pts in TFR, although the majority of these BC seem sudden.
Bauduer: Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Rea: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Nicolini: Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding; Sun Pharma Ltd.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kartos Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte Biosciences: Honoraria, Other: travel, accommodations, expenses, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal