Abstract
Background: Novel agents capable of inducing deeper responses dramatically improve the prognosis of patients with multiple myeloma (MM). Innovative technologies such as multiparameter flow cytometry (MFC) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) are utilized to assess minimal residual disease (MRD) for further stratification of patients who achieve a complete response (CR). EuroFlow-next-generation flow (EuroFlow-NGF) is one of the gold standard MFC methods. Recently, both NGF and NGS have been used in many clinical trials to assess MRD levels associated with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). The present study prospectively assessed MRD levels by both NGF and NGS to elucidate the prognostic impact of both methods and clarify their characteristics in MM patients in an autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) setting.
Methods: We prospectively assessed the response in Japanese patients with newly diagnosed MM who underwent ASCT and lenalidomide-based maintenance therapy at multiple Japanese medical centers between September 2016 and July 2021. The diagnosis of MM and patients' responses to therapy were assessed using the IMWG criteria. Only patients with CR or stringent CR on days 100-365 post-ASCT were included, and bone marrow (BM) samples were obtained to assess MRD. Four milliliters of BM was divided equally. Cells derived from 2 mL BM were analyzed by the NGF method (Flores-Montero et al., Leukemia 2017) at Kanazawa University, and DNA extracted from the remaining 2 mL BM cells was processed by Adaptive Biotechnologies' standardized NGS-MRD assay (Seattle, WA) (Ching et al., BMC Cancer 2020) to assess MRD levels. MRD levels in BM were also monitored at 1-year (± 20 days) and 2-year (± 20 days) post-ASCT. The prognostic value of MRD levels in BM was assessed, and their correlation between NGF and NGS was compared at a cut-off value of 1×10 -5. Sustained MRD negativity was defined as the maintenance of MRD negativity in the BM for more than 6 months. BM cells were analyzed for high-risk cytogenetics (del(17p), t(4;14), and t(14;16)) by FISH.
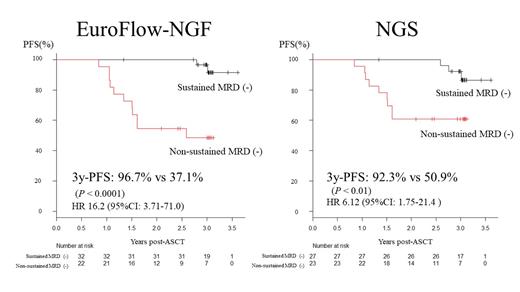
Results: A total of 60 patients (male = 29, female = 31) underwent bortezomib-based induction therapy, ASCT conditioned with high-dose melphalan, and lenalidomide-based maintenance. The median age was 62 years at the ASCT (range 36-71; ISS 1 [n = 13], 2 [n = 24], and 3 [n = 23]). Thirty-three percent of patients showed high-risk chromosomal abnormalities (del17p (n=11), t(4;14) (n=10), t(14;16) (n=2)), 3 patients had double hit diseases, and five patients had extramedullary diseases. With a median follow-up of 3 years, the 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were 69.2% and 94.2%, respectively. In total, 148 samples were analyzed using NGF and 138 were analyzed using NGS. The rates of MRD negativity at least once using NGF and NGS were 80% and 61%, respectively. The patients who achieved at least one MRD negativity exhibited significantly better 3-year PFS (82.9% by NGF; 84.8% by NGS) than those who did not (P < 0.0001, 0% by NGF; P = 0.005, 49.1% by NGS). Patients who sustained MRD negativity for more than 6 months also showed significantly better 3-year PFS (96.7% by NGF; 92.3% by NGS) compared with those without sustained MRD negativity (Figure; P < 0.0001, 37.1% by NGF; P < 0.01, 50.9% by NGS). The MRD levels between the NGF and NGS methods were significantly correlated with each other (r = 0.9295, P < 0.0001). Among the 17 patients who developed PD after ASCT, seven cases showed discrepancies in the MRD results and two cases in which one case was MRD-positive and the other was MRD-negative by both methods progressed with extramedullary diseases. Five of the seven cases were MRD-positive by NGS and MRD-negative by NGF.
Conclusions: In this prospective comparison study of MRD assessment in BM cells using EuroFlow-NGF and NGS approaches, MRD levels highly correlated with each other, and MRD negativity and sustained MRD negativity were significantly associated with prolonged PFS. Multiple MRD assessments by NGF or NGS are essential for predicting durable remission and prolonged clinical outcomes.
Takamatsu: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies, Eisai: Honoraria; SRL: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Yoshihara: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Matsumoto: Sanofi: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Ono: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria. Yamashita: Janssen: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria; celgene: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria. Fuchida: Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K.: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., Ltd.: Honoraria; Celgene Co., Ltd.: Honoraria. Hiragori: BML: Current Employment. Suzuki: Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; ONO: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria; Abie: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding. Nakao: Symbio: Consultancy; Kyowa Kirin: Honoraria; Novartis Pharma: Honoraria; Alexion Pharma: Research Funding. Durie: Amgen: Other: fees from non-CME/CE services ; Amgen, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, and Takeda: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal