Abstract
Introduction
The oral anti-apoptotic B-cell lymphoma 2 protein inhibitor (venetoclax) combined with hypomethylating agents (azacitidine) has shown promising activity in patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, there are no single center real-world research results with relatively large sample size in China. The purpose of this study is to explore the safety and short-term efficacy of venetoclax combined with azacitidine (Ven + AZA) in previously untreated patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy and patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) AML in China.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted on 60 previously untreated patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy and patients with R/R AML who received Ven + AZA (venetoclax,100mg D1、200mg D2、400mg D3-28;azacitidine, 75mg/m2 D1-7) in the Peking University Institute of Hematology from March 15, 2019 to May 20, 2021. The incidence of adverse events (AE), complete remission (CR)/CR with incomplete hematological recovery (CRi) rate, objective remission rate (ORR) and minimal residual disease (MRD) status in patients with different risk stratification and different gene subtypes were analyzed.
Results
Patient Characteristics
The median age was 54 (18-77) years, 33 males (55.0%), and the median follow-up time was 4.8 (1.4-26.3) months. Among the 60 patients, 24 (40.0%) were previously untreated patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy and 36 (60.0%) were R/R patients. The median cycles of Ven + AZA in the two groups were both 1 (1-5). The median follow-up time of them were 2.9 (1.5-13.2) and 118 (1.4-26.3) months, respectively.
In the previously untreated patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy, 2 were over 75 years old, 16 cases were diagnosed with active infection, 6 had organ dysfunction. According to the risk stratification of NCCN, it was divided into 8 cases of favorable-risk, 2 cases of intermediate-risk and 14 cases of poor-risk. According to the time from CR to hematological recurrence, the R/R group was divided into 12 cases in the favorable-risk group (CR to hematological recurrence ≥18 months) and 24 cases in the poor-risk group (CR to hematological recurrence <18 months, no remission after 1 cycle of therapy, no remission after ≥2 cycles of therapy).
Efficacy
In the previously untreated patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy, after the first cycle of Ven + AZA treatment, 17/24 (70.8%) cases achieved CR/CRi, 3/24 (12.5%) cases achieved partial remission (PR), and the ORR was 83.3%. Among the CR/CRi patients, 8/17 (47.1%) achieved MRD negative after 2 cycles of therapy. Four patients achieved CR/CRi after the first cycle of Ven + AZA, ineligible factors (active infection) were eliminated, followed by chemotherapy, and MRD achieved negative after 1-2 cycles of consolidation therapy.
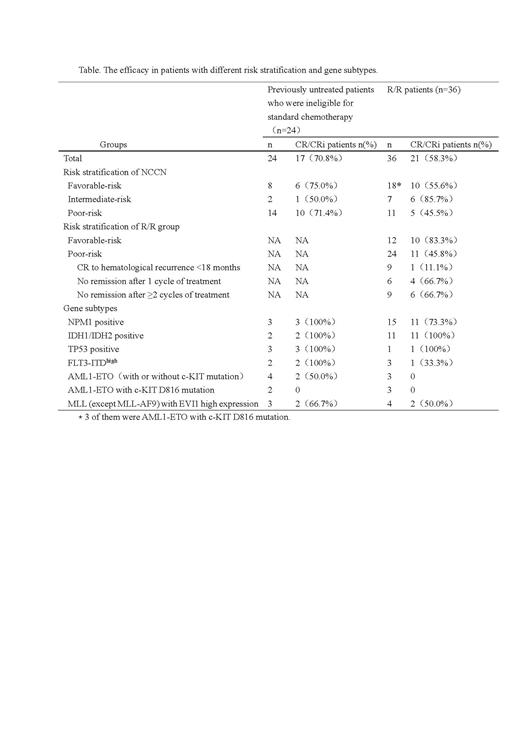
The median duration of induction therapy in R/R group was 28 (14-28) days, and the total CR/CRi rate was 58.3%. 11/24 (45.8%) cases achieved CR/CRi after one cycle of Ven + AZA in the poor-risk R/R group, and 10/12 (83.3%) cases achieved CR/CRi in the favorable-risk R/R group, which was significantly superior than that in the poor-risk group (P = 0.031). The efficacy in patients with different risk stratification and gene subtypes are displayed in Table.
Safety
The incidence of hematological AEs was 100%, and the incidence of neutropenic fever was 40.0% (24/60). The incidence of grade 3-4 leukopenia was 86.7% (52/60), of which 60.0% (36/60) occurred before therapy, and the incidence of grade 3-4 leukopenia caused by therapy was 26.7% (16/60). The incidence of grade 3-4 anemia was 71.7% (43/60), of which 51.7% (31/60) occurred before therapy, and the incidence of grade 3-4 anemia caused by therapy was 20.0% (12/60). The incidence of grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia was 76.7% (46/60), of which 60.0% (36/60) occurred before therapy, and the incidence of grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia caused by therapy was 16.7%. The most common non hematological AE was infection, followed by gastrointestinal AE. Infection mainly included pneumonia (13.3%) and soft tissue infection (6.7%), both of which were grade 3-4.
Conclusion
Ven + AZA has acceptable safety in previously untreated patients who were ineligible for standard chemotherapy and patients with R/R AML, can achieve a high response rate, and some patients can achieve MRD negative in China. It is effective in patients with NPM1, IDH1/IDH2 and TP53 positive.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal