Abstract
Introduction:
In 2015, U.S. Food and Drug Administration granted daratumumab approval, based on two phase II studies, as monotherapy (16 mg/kg in heavily treated patients) for MM patients who have received at least three prior lines of therapy, including a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent, or patient's double refractory to these agents [1]. Daratumumab is a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting CD38, expressed at high levels on malignant cells in multiple myeloma (MM) [2].
METHODS AND METHODOLOGY:
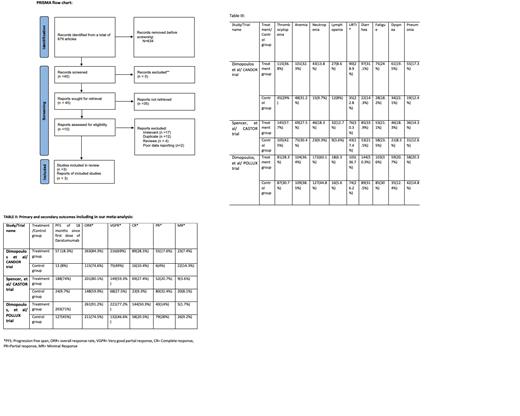
This meta-analysis was conducted according to Cochrane Collaboration guidelines and reported as per PRISMA guidelines and its summary is given in Figure 1. Two authors (AA and MZ) performed a systematic literature search using databases such as MEDLINE (via PubMed), Embase, and Cochrane library using the medical search terms: "daratumumab, refractory, relapsed, multiple myeloma". Three of the totals of 679 articles reviewed were selected as having identical primary and secondary outcomes
Results:
A total of 3 studies including 1533 patients (849 in Daratumumab treatment group while 684 patients in control group) were included in the study (Figure I). Mean age was 65 years in both groups. 54.4% had a progression free survival in daratumumab group as compared to 8% in control. Overall response rate, very good partial response, and complete response favors treatment group while minimal and partial response outcome favored control group. Adverse effects were more common in treatment group as compared to treatment group.
Discussion:
In ELOQUENT-3 trial, role of Elotuzumab was studied in RRMM patients which showed ORR of 53% in treatment group in comparison to our study which showed ORR of 85.2% with significant p-value of <0.001 [3]. Similar kind of results were seen with Eloquent-2 trial which showed overall response rate of 79 % respectively [4].
References:
1. Overdijk MB, Jansen JH, Nederend M, Lammerts van Bueren JJ, Groen RW, Parren PW. The Therapeutic CD38 Monoclonal Antibody Daratumumab Induces Programmed Cell Death via Fcγ Receptor-Mediated Cross-Linking. 2016;197(3):807-13.
2. Dima D, Dower J, Comenzo RL, Varga C. Evaluating Daratumumab in the Treatment of Multiple Myeloma: Safety, Efficacy and Place in Therapy. Cancer management and research. 2020;12:7891-903.
3. Dimopoulos MA, Dytfeld D, Grosicki S, et al. Elotuzumab plus Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone for Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 8;379(19):1811-1822.
4. Zhang T, Wang S, Lin T, Xie J, Zhao L, Liang Z, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of novel monoclonal antibodies for treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(20):34001-17.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal