Abstract
Introduction: Optimal treatment remains to be defined for Black patients with transplant-eligible NDMM. The primary analysis of the randomized phase 2 GRIFFIN study (NCT02874742) demonstrated that frontline therapy of DARA plus RVd (D-RVd) had superior clinical benefit versus RVd in the overall study population (Voorhees PM, et al. Blood. 2020). A post hoc subgroup analysis of Black patients in the GRIFFIN study was previously reported; this analysis occurred after 1 year of maintenance therapy with lenalidomide (R) ± DARA (median follow-up, 27.4 mo) and showed that D-RVd improved depth of response versus RVd among Black patients, with a comparable safety profile to White patients (Nooka AK, et al. Blood Cancer J. 2022). Here, we present the end-of-study final analysis of GRIFFIN by race (median follow-up, 49.6 mo), which occurred after all patients completed study therapy and 1 year of long-term follow-up, discontinued, or withdrew.
Methods: Patients with transplant-eligible NDMM were randomized 1:1 to receive D-RVd or RVd. All patients received 4 D-RVd/RVd induction cycles, autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT), 2 D-RVd/RVd consolidation cycles, and up to 2 years of maintenance with R ± DARA. During induction/consolidation, all patients received 21-day cycles of R (25 mg PO on Days [D] 1-14), V (1.3 mg/m2 SC on D1, 4, 8, 11), and d (40 mg PO QW) ± DARA (16 mg/kg IV QW in Cycles 1-4 and D1 in Cycles 5-6). During maintenance (28-day cycles), patients received R (10 mg PO on D1-21; if tolerated, 15 mg Cycles 10+) ± DARA (16 mg/kg IV Q8W/Q4W or 1800 mg SC Q4W per protocol amendments). After completion of study therapy, patients could continue on R maintenance therapy per local standard of care. The primary endpoint was sCR rate post-ASCT consolidation treatment.
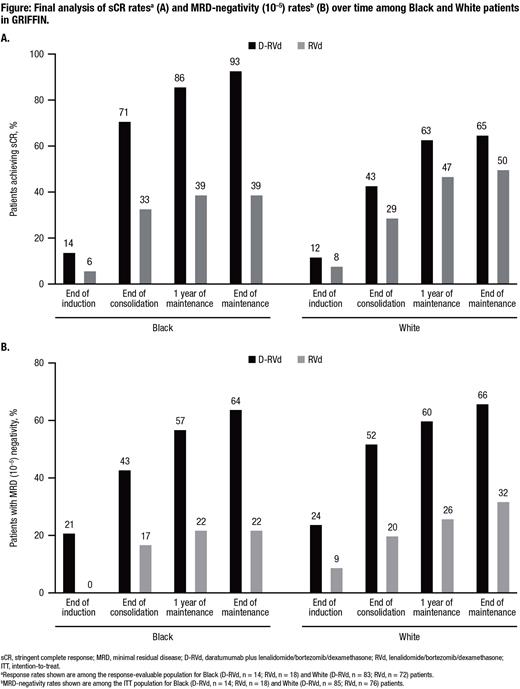
Results: Of 207 randomized patients (D-RVd, n = 104; RVd, n = 103), 32 (15%) were Black (D-RVd, n = 14; RVd, n = 18) and 161 (78%) were White (D-RVd, n = 85; RVd, n = 76). Baseline characteristics were generally similar between Black and White patients. sCR rates by the end of maintenance were higher for D-RVd versus RVd in Black (93% vs 39%, P = 0.0021) and White (65% vs 50%, P = 0.0589) patients (Figure A). MRD-negativity (10-5) rates by the end of maintenance were higher for D-RVd versus RVd for Black (64% vs 22%, P = 0.0293) and White (66% vs 32%, P < 0.0001) patients (Figure B). With median overall follow-up of 49.6 months, D-RVd reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 61% in Black patients (HR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.07-2.24, P = 0.2767) and 53% in White patients (HR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.19-1.18, P = 0.1003), compared with RVd. For Black patients, estimated 48-month PFS rates were 79% for D-RVd and 65% for RVd; among White patients, estimated 48-month PFS rates were 89% for D-RVd and 74% for RVd. There were no deaths among Black patients, and there were 12 deaths among White patients (D-RVd, n = 6; RVd, n = 6).
The most common (≥30%) grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were neutropenia (Black: D-RVd, 50% vs RVd, 22%; White: D-RVd, 47% vs RVd, 18%) and lymphopenia (29% vs 39%; 23% vs 16%). Serious adverse events occurred more frequently in the RVd group in Black patients (D-RVd, 43% vs RVd, 56%) and were similar for both treatment arms in White patients (D-RVd, 47% vs RVd, 49%). Infusion-related reactions occurred in 29% of Black patients and 53% of White patients who received D-RVd. TEAEs that led to study treatment discontinuation occurred in 64% and 39% of Black D-RVd and RVd patients, respectively, and 29% and 26% of White D-RVd and RVd patients, respectively. Peripheral neuropathy was seen more frequently in the RVd group both in Black (D-RVd, 57% vs RVd, 67%) and White patients (D-RVd, 64% vs RVd, 78%); most events were grade 1/2. No deaths occurred due to TEAEs among Black patients, and 1 White patient in the D-RVd group had a death due to a TEAE (pneumonia).
Conclusions: In this final end-of study analysis of GRIFFIN by race, the frontline therapy of DARA plus RVd for induction/consolidation and DARA plus R maintenance continued to demonstrate clinical benefit among Black patients. However, 48-month PFS rates for both D-RVd and RVd were lower in Black patients than in White patients, and this may be attributed to the higher rates of study treatment discontinuation following TEAEs in Black patients. More investigations of treatment delivery and TEAE management in Black patients compared to White patients are warranted.
Disclosures
Nooka:Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Takeda, Amgen, Adaptive, GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, Oncopeptides, Karyophram, SecureBio, and BeyondSprings: Consultancy, Honoraria. Kaufman:AbbVie, Genentech, and Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; AbbVie: Other: Member of steering committee; Incyte: Other: Member of data safety monitoring committee . Rodriguez:Janssen, BMS, Takeda, AbbVie, karyopharm, Artiva: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Jakubowiak:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Efebera:Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; GSK: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria. Reeves:Incyte, BMS, PharmaEssentia, CTI Biopharma: Honoraria; Hemostasis & Thrombosis Research Society Mentored Research Award sponsored by CSL Behring: Research Funding. Wildes:Carevive: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy. Holstein:Secura Bio: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; GSK: Consultancy, Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding. Anderson:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Prothena: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Beigene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GSK: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Badros:Amgen: Consultancy; GSK, BMS: Research Funding. Pei:Janssen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Cortoos:Janssen: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Patel:Companies of Johnson & Johnson: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Lin:Janssen: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Richardson:Regeneron: Consultancy; GlaxoSmithKline: Consultancy; Secura Bio: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy, Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Protocol Intelligence: Consultancy; Takeda, Celgene, and GSK: Honoraria; Takeda: Research Funding; Takeda, Abbvie, GSK, and Celgene: Consultancy; Takeda and GSK: Other: Travel expenses from Takeda and GSK. Usmani:Amgen, BMS, Janssen, Sanofi: Speakers Bureau; Abbvie, Amgen, BMS, Celgene, EdoPharma, Genentech, Gilead, GSK, Janssen,Oncopeptides, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, SecuraBio, SkylineDX, Takeda, TeneoBio: Consultancy; Amgen, Array Biopharma, BMS, Celgene, GSK, Janssen, Merck, Pharmacyclics, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, SkylineDX, Takeda: Research Funding. Voorhees:Abbvie, Amgen, BMS, GSK, Karyopharm, Novartis, Oncopeptides, Pfizer, Sanofi, SecuraBio: Consultancy, Honoraria.
OffLabel Disclosure:
The specific regimen combination is not yet approved, but individual components are.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal