Abstract
There is a scarcity of data on Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms (Ph-MPN): essential thrombocythemia (ET), polycythemia vera (PV), and primary myelofibrosis (PMF). This multicenter, observational, epidemiological study was conducted to collect data on patient characteristics, prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns, and impact of MPN on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) to identify the disease burden under routine medical practice in Egypt.
During the period between March 2018 and December 2020, a total of 135 Ph-MPN patients from three Egyptian hospitals (one hospital in each of Cairo, Alexandria, and Assiut governorates) were included in the study: 41.5% from Lower Egypt, 39.3% from Greater Cairo, and 19.3% from Upper Egypt. About 62% were females and 57.8% were urban community residents. The majority (83.7%) did not have family history of cancer and none of the patients had family history of MPN.
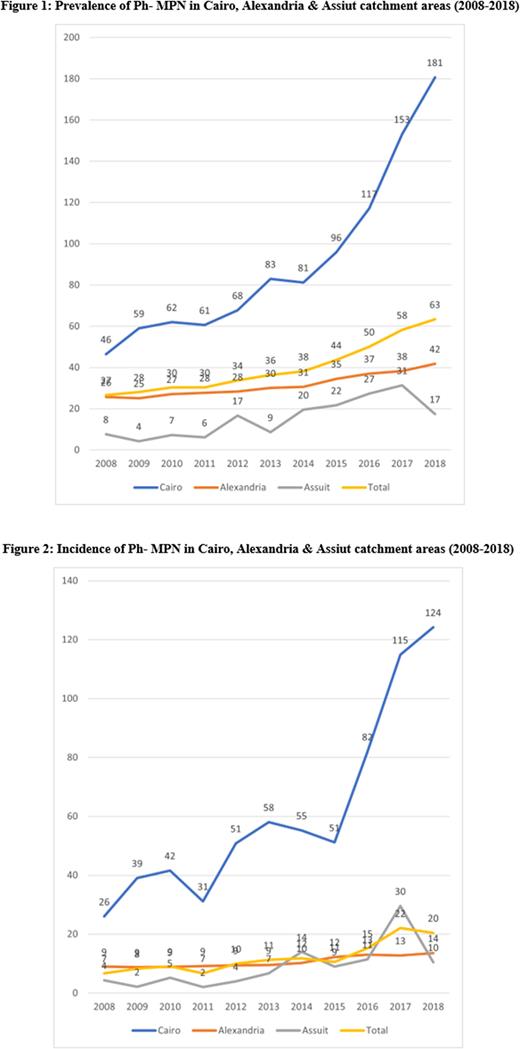
The prevalence and incidence of Ph-MPN were estimated to be 27-63 and 7-20 per 100,000 patients per year during 2008 and 2018, respectively (Figures 1 and 2, respectively). The predominant types of Ph-MPN reported were 34.8% of ET, 34.1% of PV, and 14.8% of PMF, with a median age of 44.4, 58, and 54.4 years, respectively.
About 19% had thrombosis history: 7.4% with PV, 7.4% with ET, and 2.2% with MF. Splenomegaly was reported in 57% while hepatomegaly was reported in 13.3%. Cytogenetic and mutational analyses were done for 108 patients. Of which, 88% had JAK2V617F mutation. Fatigue was the most reported Ph-MPN-associated symptom as reported in 41.5%, followed by bone pain (25.9%), and abdominal discomfort (23.7%). Around 21% presented with co-morbidities, four of which had history of malignancy (prostate cancer; n=2, breast cancer; n=1, and acute myeloid leukemia secondary to MPN; n=1). Three patients (2.2%) died over the study duration.
Hydroxyurea was the most commonly used medication for MPN (79.7%) followed by clopidogrel (11.4%). JAK2 inhibitors were used by 4.1% of the patients.
At baseline, International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS) scores indicated low risk, intermediate-1 risk, and high risk in 0.7%, 3%, and 0.7% of the MF group, respectively, while 10.3% of the MF group were unclassified. We found that IPSS did not change throughout the visits except for one patient who became high risk after being unclassified.
At the end of the study, we found that Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status significantly decreased throughout the visits (p=0.001); 31% had ECOG 0, 41.6% had ECOG 1, and 20.2% had ECOG 2, compared with 54.1% ECOG 0, 36.3% ECOG 1, and 7.4% ECOG 2 at baseline.
HRQoL was assessed by the Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Symptom Assessment Form Total Symptom Score (MPN-SAF TSS). The TSS (median [interquartile range]) at baseline was 20 (24) and significantly increased to reach 24 (13) at the end of the study (p<0.001).
Conclusion: This study showed that both prevalence and incidence of Ph-MPN in the catchment areas of Cairo, Alexandria, and Assiut increased from 2008 to 2018. In addition, patients with Ph-MPN have a severe disease burden and reduced HRQoL.
Disclosures
Kaooh:Novartis Pharma S.A.E Egypt: Current Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal