Abstract

Introduction: Severe COVID-19 with adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is characterized by hyperinflammation and small vessel endothelitis. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have shown therapeutic effects in a pathogenetically not dissimilar disease, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) after stem cell transplantation. MSCs could thus be, in principle, therapeutically efficacious in severe COVID-19 ARDS. Prior to initiation of clinical trials, designated pre-clinical studies considering some of the distinguishing features of COVID-19 ARDS vs. GvHD, are warranted. Specifically, permissiveness of MSCs to SARS-CoV-2, especially in inflammation-activated MSCs, as well as potential changes to the MSC phenotype in response to SARS-CoV-2, had to be studied. Such evidence must be sought for each MSC preparation, since not necessarily will different MSC preparations respond similarly.
Obnitix is a clinical bone-marrow-derived MSC product with a national license in Germany. In the indication GvHD, Obnitix is very safe. To support clinical assessment of Obnitix for COVID-19 ARDS, cells were activated or not, exposed to relevant doses of SARS-CoV-2 and queried for expression of cellular receptors for SARS-CoV-2, ability to replicate and produce infectious virus, virus-induced phenotypic changes or altered transcription of inflammation-associated genes.
Results:
At first Obnitix MSCs were analysed for the expression of receptors for SARS-CoV-2 entry, namely ACE-2 and TMPRSS2. FACS staining was performed 72 h after incubation with and without virus and in the presence or absence of IFN-γ. Obnitix MSCs displayed very low expression of both ACE-2 and TMPRSS2, importantly, also under inflammatory conditions as Obnitix MSCs may encounter in vivo in COVID-19 or GvHD patients. In detail the frequencies of ACE-2 expression were 1.2±0.5 % for MSCs, 2.3±1.2 % for MSCs+IFNγ, 1.2±0.1 % for MSCs+SARS-CoV2 and 2.3±1.0 % for MSCs+SARS-CoV2+IFNγ (mean±SD; n=3). Frequency of TMPRSS2 expression was 1.3±0.4 % for MSCs, 2.1±0.6 % for MSCs+IFNγ, 1.6±0.4 % for MSCs+SARS-CoV2 and 2.3±1.4 % for MSCs+SARS-CoV2+IFNγ (mean±SD; n=3).
In addition, the immunophenotype of Obnitix MSCs was not affected by the virus and the MSCs showed an inflammatory signature after stimulation, with up-regulated HLA class I and II antigen expression. This was the same with/without virus.
Obnitix mRNA was analysed for expression of a panel of inflammation-mediated genes. The IFN-γ activated MSC samples showed an inflammation signature with up-regulated IL-8, IL-12a and IL-15, but the presence of SARS-CoV-2 did not noticeably affect inflammatory gene expression. Between Obnitix batches, cytokine and phenotypic patterns were remarkably similar in quality and particular also quantity, confirming the overwhelming dose-to-dose similarity of Obnitix MSCs.
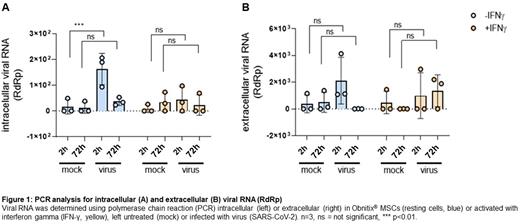
Neither at rest, nor under the influence of IFNγ, are the receptors for SARS-CoV-2 expressed. To corroborate that finding, the infectibility of Obnitix MSCs was evaluated. Supernatants and cells exposed to SARS-CoV-2 from three independent MSC Obnitix batched were collected after 2 and 72 hours post exposure and tested for viral RNA in triplicates. No increase in intracellular nor extracellular viral RNA over the time course was detected (Figure 1), suggesting, that Obnitix MSCs are not permissive for SARS-CoV-2 replication. After 2 hours low levels of viral RNA was found in the cells, reflecting spontaneous, vesicle-associated viral uptake. Such uptake was not detected in IFNγ-treated cells, presumably reflecting the known anti-viral activity of IFNγ. Moreover, supernatants collected at the 72 h time point failed to infect SARS-CoV-2 target cells. Obnitix MSCs are thus resistant to SARS-CoV-2 infection and cannot serve as reservoir for the virus.
Conclusion: In summary, because of the lack of SARS-CoV2 surface receptors ACE2 and TMPRSS2, Obnitix MSCs cannot be infected with SARS-CoV-2. We consistently observe an inflammatory cellular phenotype and transcriptome which is, however, entirely unaffected by the presence of SARS-CoV-2. These studies support the expectation of safety of Obnitix use in COVID-19 ARDS.
Disclosures
Kuci:medac GmbH: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Kuci:medac GmbH: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding. Bader:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Medac: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Riemser: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Neovii: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Speakers Bureau; Miltenyi: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal