Abstract
Introduction: Romiplostim is a thrombopoietin receptor agonist (TPO-RA) used in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) to increase platelet production. Small retrospective observational studies suggest that TPO-RAs in pregnancy and postpartum may be safe, but there are no available human data about romiplostim pharmacokinetics in pregnancy or lactation. Romiplostim has unique peptide sequences that we leveraged to measure drug levels in blood and breastmilk samples by mass spectrometry. We report the first-in-human data on romiplostim drug levels in cord blood, breastmilk and blood from a woman with chronic refractory ITP and her newborn infant, compared to controls.
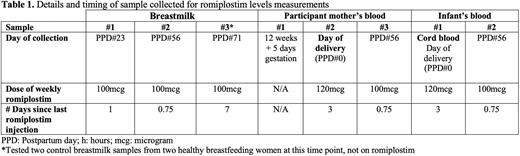
Methods: Semi-quantitative romiplostim drug levels were measured by mass spectrometry in blood, cord blood and breastmilk at pre-determined intervals in a G1P1 woman with chronic refractory ITP who was taking romiplostim 100-120 mcg daily starting after the first trimester of pregnancy. Sample timepoints included blood during first trimester not on romiplostim, at the time of delivery on romiplostim, cord blood at delivery, and postpartum (Table 1). Postpartum, samples were drawn on the same day from the participant mother's blood, breastmilk, and the infant's blood. Serial platelet count values and clinical outcomes were recorded for her infant. Blood and breastmilk samples were tested in two control non-pregnant participants who were not taking romiplostim (University of Calgary Conjoint Health Research Ethics Board #REB21-0401).
Blood and breastmilk samples were separated by SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis. Bands of ~60 kDa were cut, trypsinized and subjected to liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry. Data was analyzed using MaxQuant (v 1.6.0.1). Peptides identified at 1% false discovery rate (FDR) with a score having a confidence higher than 99% were compared across different samples based on their mass spectral counting.
Results: As a qualitative measure of drug presence, we identified two unique domain peptides (QWLAAR and AGGGGGGGGIEGPTLRQWLAARA). As evidence of romiplostim drug presence, the unique peptides were present in the participant's blood when she was taking romiplostim, cord blood, breastmilk and infant's blood. These same unique peptides were absent in the participant's blood when she was not taking romiplostim, and in the breastmilk and blood samples from two non-pregnant controls.
On the day of delivery at 36 weeks and 4 days gestation, the neonatal platelet count and liver enzymes were normal. Breastfeeding was initiated after birth and thrombocytosis was detected on day 9 of life. After at least 3 weeks of breastfeeding, milk samples were tested and had a higher romiplostim level 1 day post-dose, compared to 7 days post-dose (p=0.006). On postpartum day 56 (0.75 days post-dose), the participant mother's blood had 13 times more drug detected, compared to the infant's blood taken at the same time (p=0.0002).
At 11 weeks postpartum, the participant discontinued breastfeeding as the infant had persistent thrombocytosis (peak 799 x 109/L) and immature blast-like cells on peripheral blood smear. Two weeks following cessation of breastfeeding, no further immature cells were identified, and the platelet count improved.
Conclusion: We report for the first time romiplostim drug levels measured by mass spectrometry in cord blood, breastmilk and blood in a prospective case study of a woman with chronic refractory ITP and her newborn infant, compared to controls. We identified romiplostim in the infant's cord blood confirming that this drug crosses the blood-placental barrier in detectable amounts. Moreover, our study revealed that this TPO-RA is excreted into the breastmilk and can be subsequently absorbed by the breastfed infant leading to measurable drug levels in the infant's blood and associated thrombocytosis. Confirmatory studies of romiplostim safety in pregnancy and lactation are needed.
Disclosures
Clarke:GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria; GlaxoSmithKline: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria. Skeith:CSL Behring: Research Funding; Leo Pharma: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Romiplostim use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal