Abstract
Background Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a rare hematological malignancy characterized by the accumulation of IgM-secreting clonal lymphoma cells with a lymphoplasmacytic morphological differentiation. Recently, BTK inhibition has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy in WM (Buske, JCO 2022; Tam, Blood 2020). However, in real life, a large part of patients(pts) continue to be treated by chemoimmunotherapy (Buske, Lancet Hematol2018) including bendamustine (B)-rituximab (R) in salvage (Tedeschi , Leukemia Lymphoma 2015) or first line MW (Treon, ASH2016).
We have previously reported a series of 69 WM pts treated by BR (Laribi, BJH 2018) and demonstrated that this regimen is efficient. However, the follow-up was relatively short and some questions remained unresolved in terms of long-range response and second cancer occurrence. Here we report results of this series with a longer follow-up.
Methods Sixty-nine symptomatic previously untreated pts with WM diagnostic criteria according to the second WM Workshop recommendations were enrolled in this retrospective multi-center study between January 2013 and December 2017 in 13 French centers.
MYD88L265P and CXCR4 mutations were searched using qPCR and or next generation sequencing. Del(17p) and/or TP53 mutation were investigated in 34 pts. All pts received a BR regimen consisting of 375 mg/m2 of R on day 1 and 90 mg/m2 of B on days 1 and 2, repeated every 4 weeks, with a maximum of 6 cycles. Cumulative incidence of secondary malignancies and high-grade lymphomas were computed, considering death free of malignancies as a competing event. Event-free survival (EFS), time to next treatment (TNT), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were plotted using the log rank test and Kaplan-Meier graphical comparison.
Results Pts median age was 69 years old (yo; range 45-88) at WM diagnosis and 71 yo (range 46-88) at therapy initiation. MYD88 and CXCR4 mutations were present in 45/51 (88%) and 11/44 (25%) of pts, respectively. A complex karyotype was disclosed in 6/44 (14%) pts, and 1/34 (3%) had TP53 alteration.
According to the IPSSMW score, 14 (22%) pts were low risk, 32(46%) intermediate, and 32 (46%) high risk.
Using consensus response criteria, the overall response rate was 97% (very good partial response [VGPR] with negative immunofixation 19%, VGPR 37%, PR40%, MR 1%) and the major response rate was 96%. Cumulative incidence of VGPR or better was 47.8%, 53.6%, 55%, and 56% at 6, 12, 18, and 24 months, respectively.
After a median observation time of 68.5 months (range 23.13-106) post BR, the median OS was not reached (83-NR) , and the median PFS was 82 months (75-NR). Median OS for pts with mutated or WT MYD88 was NR and 72.8 months, respectively (p=0.046). Median OS for pts with mutated or WT CXCR4 was 70.2 months and NR, respectively (p=0.64). Median OS related to disease or treatment was not reached, while median OS related to other causes was 106 months.
Sixteen (23.2%) pts relapsed. Fourteen received second line therapy and 2 supportive care. Eight patients received ibrutinib, and 6 chemo-immunotherapy. TNT was 31.55 months (range 2.66-82.43).
Median PFS after a second line of treatment (PFS2) was 45 (9.13-NR) or 21 months (range 9.13-NR), for pts receiving ibrutinib or not.
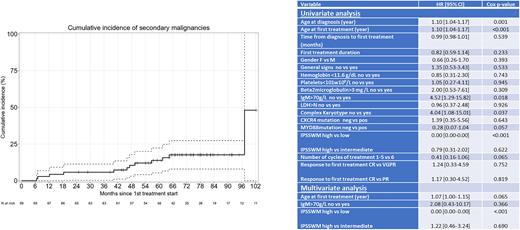
Eleven pts developed a second cancer: 9 solid tumors (2 pancreatic, 2 gastric, 1colic, 1 pulmonary, 1 breast, 1 cutaneous), and 2 treatment-related myeloid neoplasms (TRMN). Median EFS, defined as occurrence of death, relapse or second cancer was 82 months (61-NR). The cumulative incidence of second cancer was 2.90%, 5.80%, 10.49%, and 17.6% at 12, 24, 48, and 96 months, respectively (figure 1).
Univariate analyses on OS disclosed statistically significant differences for age at diagnosis (p=0.001), age at first therapy (p <0.001), IgM>70g/L (p: 0.018), complex karyotype (p=0.037), and high risk IPSSMW (p<0.01). In multivariate analysis, only IPSSMW remained statistically significant (p<0.001) (table1). Univariate analyses on PFS only singled out age at diagnosis (p=0.03) or at first therapy (p=0.049) as statistically significant. Mutated MYD88 or CXCR4 did not impact OS nor PFS.
Conclusion This study demonstrates that the BR regimen is efficient in treatment naïve WM pts, yielding long-term responses. The occurrence of secondary cancers, including TRMN, should be closely monitored in these patients.
Disclosures
Laribi:AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Beigene, Iqone, Janssen, Novartis, Takeda: Honoraria. Willems:Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: nature advantage (congress inscription) or convention; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: nature advantage (congress inscription) or convention; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Remuneration; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Remuneration. Herbaux:Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; MSD: Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Kite: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding. Dupuis:abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Le Calloch:AbbVie, Gilead, Janssen, Takeda: Honoraria. Leblond:Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Beigene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; MSD: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Lilly: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal