Abstract
The immunoglobulin (Ig) variable region (V) genes expressed by IgM chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) B cells display little or no somatic mutations. However, preliminary findings have shown that Ig V genes of IgA and IgG CLLs may be somatically mutated, suggesting that isotype-switched CLLs may represent a “subtype” of the disease. To investigate the degree and nature of somatic mutations and the role of antigen (Ag) in the clonal selection and expansion of isotype-switched CLLs, and to determine whether specific oncogene or tumor suppressor gene mutations are associated with isotype-switched CLLs, we analyzed the expressed Ig VH gene, bcl-1 and bcl-2 proto-oncogene, and p53 tumor suppressor gene configurations of 3 IgA-, 1 IgG-, and 1 IgA/IgG-expressing CLLs. These isotype-switched CLL B cells expressed surface HLA-DR, CD19, CD23, and CD5, and displayed no alterations of the bcl-1 and bcl-2 oncogenes and the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. The cDNA VH -D-JH gene sequence was joined with that of the Cα gene in the B cells of the three IgA CLLs, and with that of the Cγ gene in the IgG CLL B cells. In the IgA/IgG-coexpressing CLL B cells, identical VH -D-JH cDNA sequences were spliced to either Cα or Cγ genes. In all five CLLs, the pattern of Cμ DNA probe hybridization to the digested genomic DNAs was consistent with deletion of the Cμ exon from the rearranged Ig gene locus, suggesting that these CLL B cells had undergone DNA switch recombination. In one IgA CLL, the expressed VH gene was unmutated. In all other class-switched CLLs, the Ig VH segment gene was mutated, but the point mutations were not associated with intraclonal diversification. In one IgA and in the IgA/IgG-coexpressing CLL, the nature and distribution of the mutations were consistent with Ag selection. These findings suggest that IgA- and/or IgG-expressing CLLs represent, in their VH gene structure, transformants of B cells at different stages of ontogeny. They also suggest that Ag may play a role in the clonal selection of some of these isotype-switched leukemic cells, but bcl-1 and bcl-2 oncogene rearrangements and p53 tumor suppressor gene mutation are not associated with the pathogenesis of isotype-switched CLLs.
CHRONIC LYMPHOCYTIC leukemia (CLL) B cells coexpress various B-cell–associated antigens (Ag), including HLA-DR, CD19, CD20, and CD23, and the T-cell–associated CD5 molecule.1 They also express IgM containing unmutated or virtually unmutated variable region (V) gene segments, suggesting that the malignant transformation of these cells generally occurs at an early stage of B-cell ontogeny (virgin B cell), before somatic diversification of the expressed Ig V genes and clonal selection.2,3 A small proportion of CLLs is characterized by the expression of isotype-switched Ig.4-10 The reported structural analysis of one IgA- and eight IgG-expressing CLLs suggests that the Ig V segments of these leukemic B cells were somatically mutated.8-10 Because of the limited number of cases analyzed, it is not known whether the somatic mutations detected in these CLLs represent a sporadic phenomenon or whether they are peculiar to the isotype-switched “variant” of CLL. Under physiological conditions, Ig heavy (H) chain class switch occurs along with somatic hypermutation of the Ig V segments, during the late primary and early secondary immune response following Ag-induced B-cell activation and clonal expansion.11,12 Because of the apparent temporal correlation of isotype switch with hypermutation,13,14 it has been proposed that these two processes are mechanistically related in B-cell ontogeny. However, recent evidence suggests that Ig V gene somatic hypermutation already occurs in IgM of the late primary response before isotype-switch,15 and isotype-switch can occur in the absence of somatic mutations,16 17 suggesting that these two somatic processes can occur independently.
The molecular pathogenesis of B-CLL is largely unknown. The involvement of oncogenes such as bcl-1 and bcl-2 dominantly acting in B-cell lymphomas and leukemias has been documented in CLLs.18,19 However, recent investigation of a large series of B-CLLs found no alterations of bcl-1 and bcl-2 oncogenes.20 The inactivation of p53 in a subset of B-CLLs, especially in clinically progressed and histologically transformed cases, also has been reported.21-23 Whether bcl-1 and bcl-2 oncogene rearrangements and p53 tumor suppressor gene mutation are involved in the pathogenesis of isotype-switched CLLs remains an open question.
To determine whether isotype-switched CLL B-cell clones express mutated or unmutated Ig VH genes, and if they do, whether the somatic point mutations display a pattern consistent with selection by Ag, we analyzed the Ig VH genes expressed by five IgA and/or IgG isotype-switched CLLs. We also analyzed rearrangements of the bcl-1 and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes and mutation of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene in these cases to determine whether oncogene and/or tumor-suppressor gene alterations are associated with isotype-switched CLLs. We found that all but one of these CLLs expressed Ig VH genes in mutated configuration. In two of the mutated CLLs, the nature and distribution of the replacement (R) somatic point mutations were consistent with selection by Ag, but alterations of the bcl-1 and the bcl-2 oncogenes and the p53 tumor suppressor gene were not associated with isotype-switched CLLs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients and pathologic samples.Heparinized peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) aspiration samples were collected during the course of routine clinical evaluation from five patients with documented CLL. The diagnosis of CLL was based on clinical, morphologic, and immunophenotypic criteria.1 None of the patients were previously exposed to chemotherapy. Mononuclear cells were separated from the PB and BM samples by Ficoll-Hypaque (Pharmacia Fine Chemicals, Piscataway, NJ) density gradient centrifugation, and were cryopreserved in a viable state in 50% fetal calf serum (FCS), 10% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), and 40% RPMI in liquid nitrogen until needed for analysis.
Phenotypic characterization.The phenotype of the CLL B cells was determined at the time of diagnosis by direct and indirect immunofluorescent flow cytometry analysis of cell suspensions using a FACScan fluorescence-activated cell sorter (Becton Dickinson, Mountain View, CA) and/or by immunohistochemical staining of cytospin cell preparations using a three-step avidin-biotin immunoperoxidase technique, as previously described.24 The following polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) were used: cALLa (CD10), Leu20 (CD23), IgA1, IgA2 (Becton Dickinson), B4 (CD19), B1 (CD20; Coulter Immunology, Hialeah, FL), IgM, IgD, kappa, lambda (Tago Inc, Camarillo, CA), IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4 (Sigma Chemical Company, St Louis, MO), HLA-DR, T3 (CD3), T1 (CD5; United Biomedical Inc, Hauppauge, NY), and cyclin D1 (Pharmingen, San Diego, CA).
Isolation of genomic DNA.Genomic DNA was extracted from cryopreserved mononuclear cell suspensions using a salting-out procedure.25 Briefly, cells were resuspended in 3 mL of nuclei lysis buffer containing 10 mmol/L TrisHCl, 400 mmol/L NaCl, and 2 mmol/L EDTA; 200 μL of 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and 500 μL of proteinase K solution (1 mg proteinase K in 1% SDS and 2 mmol/L EDTA) were subsequently added. After overnight digestion at 37°C, 1 mL of saturated NaCl was added. This mixture was centrifuged at 2,500 rpm for 20 minutes and 2 vol of 100% ethanol were added to the supernatant to precipitate DNA, which was then washed thoroughly in 70% ethanol.
Preparation of RNA and first-strand cDNA synthesis.Total RNA was isolated from cryopreserved mononuclear cell suspensions using the guanidine isothiocyanate technique.26 Five micrograms of RNA was transcribed into cDNA using M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Superscript RNase H-Reverse Transcriptase; GIBCO-BRL, Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY) in conjunction with a poly(dT)12-13 primer according to the manufacturer's instructions. After cDNA synthesis, RNA was degraded by RNase H.
Southern blot analysis.Five-microgram aliquots of genomic DNA were digested with the appropriate restriction endonucleases according to the manufacturer's instructions (Boehringer-Mannheim, Indianapolis, IN), electrophoresed in 0.8 or 1% agarose gels, denatured with alkali, neutralized, and transferred to nitrocellulose filters (Schleicher & Schuell, Keene, NH).27 The filters were hybridized in 50% formamide/3× standard citrate (SSC) buffer at 37°C to cDNA probes that had been [α-32P] labeled by the random hexamer primer extension method according to the manufacturer's instructions (Boehringer-Mannheim GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). Filters were washed in 0.2× SSC/0.5% SDS at 60°C for 2 hours and then autoradiographed at −70°C for 16 to 48 hours.28
DNA probes.Ig H chain gene rearrangement analysis was performed using a JH probe29 on EcoRI and BamHI, and a Cμ probe30 on BamHI-digested DNAs. The configuration of the bcl-1 locus was analyzed using probes MTC31 and p94PS32 on HindIII and EcoRI DNA digests, respectively. The bcl-2 locus was analyzed by a 5′ bcl-2 probe (pB16) spanning the exons 1 and 2 of the bcl-2 gene33 and 3′ bcl-2 probes specific for the MBR (pFL-1)33 and mcr (pFL-2)34 breakpoints of the bcl-2 gene on BamHI-digested DNAs.
Polymerase chain reaction–single-strand conformation polymorphism (PCR-SSCP) analysis of the p53 tumor suppressor gene.The PCR-SSCP analysis was performed as previously described.20
PCR amplification, cloning, and sequencing of the expressed and the germline Ig VH genes.The expressed Ig VH genes were amplified from first-stranded cDNA by PCR using Ig family-specific sense leader35 and Cα- [CGGGAAGACCTTGGGGCTGG], Cγ- [CAGGGGGAAGAC(G/C)GATGGGC], or Cμ- [CGAGGGGGAAAAGGGTTGGGGC] specific antisense primer pairs.8 The Cα and Cγ primers were designed to anneal to the sequences of Cα1 and Cα2 and Cγ1-4 genes, respectively.36,37 Genomic DNAs were amplified to analyze the sequences of the DP-14 (V1-18) and VH26 (V3-23) germline genes in cases KA and TE, respectively. The DP-14 (V1-18) germline gene was amplified using the CDR1-specific sense primer [ACCAGCAATGGTATCAGCTGG] in conjunction with the antisense primer specific for VH1 heptamer recombination signal sequence [GGAATTCT(C/G)TGG(G/T)TT(C/T)TCACACTG].38 The VH26 (V3-23) germline gene was amplified using the CDR1-specific sense primer [TTTAGCAGCTATGCCATGAGC] in conjunction with the antisense primer specific for the VH3 gene heptamer recombination signal sequence [GGAATTC(A/C)TG(A/G)C(C/T)TCCCCTC(A/G)CT(C/G)].38 Thirty cycles of amplification were performed. Each cycle consisted of denaturation (94°C for 1 minute), annealing (60°C for 1 minute), and extension (72°C for 2 minutes). PCR products were cloned in pCR 1000 vector using the TA cloning system (Invitrogen Corp, San Diego, CA), following the manufacturer's instructions. DNA sequencing was performed directly from a small-scale plasmid preparation using the Sequenase version 2.0 (United States Biochemical, Cleveland, OH) system according to the manufacturer's instructions. DNA sequences were analyzed using the MacVector version 4.5 (Eastman-Kodak Co, New Haven, CT) software and the GenBank data base.
Analysis of mutations.We calculated the number of expected replacement (R) mutations in complementary determining regions (CDR) and framework regions (FR) for the Ig VH genes using the formula RCDR or RFR = n × CDR Rf or FR Rf × CDRf or FRf , where n is the total number of observed mutations; Rf is the replacement frequency intrinsic to each Ig VH gene,39 and CDRf and FRf are the relative sizes of the CDRs and FRs. A binomial probability model was used to evaluate whether the observed R mutations in CDRs and the scarcity of silent (S) mutations in the FRs were due to chance alone39: p = [n!/k!(n-k)!qk(1-q)n-k, where q = probability an R mutation will localize to CDR or FR (q = CDRrel or FRrel × CDR Rf or FR Rf), and k = number of observed R mutations in the CDRs or FRs.
RESULTS
Phenotypic analysis.The results of immunophenotypic analysis of the leukemic B cells of the five IgA and/or IgG CLLs are summarized in Table 1. In all five cases, the B-cell origin of the leukemic cells was confirmed by the expression of B-cell–associated Ags HLA-DR, CD19, and CD20 and absence of the T-cell–associated Ag CD3. In all five CLLs, the neoplastic B cells coexpressed CD5 and CD23, but lacked CD10 and cyclin D1. The CLL B cells expressed surface IgA1 in 3 CLLs, surface IgG3 in 1 CLL, and coexpressed surface IgA1 and IgG3 in 1 case. No CLL B cells expressed IgM or IgD. Four CLLs expressed κ chain, and one expressed λ chain.
Phenotype, Genotype, Proto-Oncogene Configuration, and Suppressor Gene Mutation of Leukemic Cells in Five IgA and/or IgG CLLs
| Phenotypic Markers cDNA Probes and Primers . | Restriction Enzymes . | Patients . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | TR % . | KA % . | GR % . | TE % . | SC % . |
| IgM | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| IgD | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IgA1 | 65 | 77 | 84 | 90 | 0 | |
| IgA2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IgG1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| IgG2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IgG3 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 90 | 55 | |
| IgG4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| κ | 62 | 0 | 86 | 90 | 43 | |
| λ | 15 | 75 | 0 | 2 | 8 | |
| HLA-DR | 66 | 95 | 89 | 88 | 86 | |
| CD10 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| CD19 | 66 | 86 | 87 | 90 | 65 | |
| CD20 | 61 | 89 | 86 | 92 | 60 | |
| CD23 | 64 | 90 | 86 | 92 | 58 | |
| CD3 | 19 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 15 | |
| CD5 | 61 | 89 | 87 | 91 | 60 | |
| Cyclin D1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| JH | EcoRI | R (1) | R (1) | R (2) | R (1) | R (1) |
| JH | BamHI | R (2) | R (1) | R (2) | R (1) | R (1) |
| Cμ | BamHI | G | G | D | G | G |
| bcl-1 (MTC) | HindIII | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-1 (p94PS) | EcoRI | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-2 (pFL-1) | BamHI | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-2 (pFL-2) | BamHI | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-2 (pB16) | BamHI | G | G | G | G | G |
| p53 exon 5 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 6 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 7 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 8 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 9 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| Phenotypic Markers cDNA Probes and Primers . | Restriction Enzymes . | Patients . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | TR % . | KA % . | GR % . | TE % . | SC % . |
| IgM | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| IgD | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IgA1 | 65 | 77 | 84 | 90 | 0 | |
| IgA2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IgG1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| IgG2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| IgG3 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 90 | 55 | |
| IgG4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| κ | 62 | 0 | 86 | 90 | 43 | |
| λ | 15 | 75 | 0 | 2 | 8 | |
| HLA-DR | 66 | 95 | 89 | 88 | 86 | |
| CD10 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| CD19 | 66 | 86 | 87 | 90 | 65 | |
| CD20 | 61 | 89 | 86 | 92 | 60 | |
| CD23 | 64 | 90 | 86 | 92 | 58 | |
| CD3 | 19 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 15 | |
| CD5 | 61 | 89 | 87 | 91 | 60 | |
| Cyclin D1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| JH | EcoRI | R (1) | R (1) | R (2) | R (1) | R (1) |
| JH | BamHI | R (2) | R (1) | R (2) | R (1) | R (1) |
| Cμ | BamHI | G | G | D | G | G |
| bcl-1 (MTC) | HindIII | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-1 (p94PS) | EcoRI | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-2 (pFL-1) | BamHI | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-2 (pFL-2) | BamHI | G | G | G | G | G |
| bcl-2 (pB16) | BamHI | G | G | G | G | G |
| p53 exon 5 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 6 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 7 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 8 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
| p53 exon 9 | WT | WT | WT | WT | WT | |
Abbreviations: D, deleted; G, germline; R (1-2), rearranged (number of rearranged bands); WT, wild type.
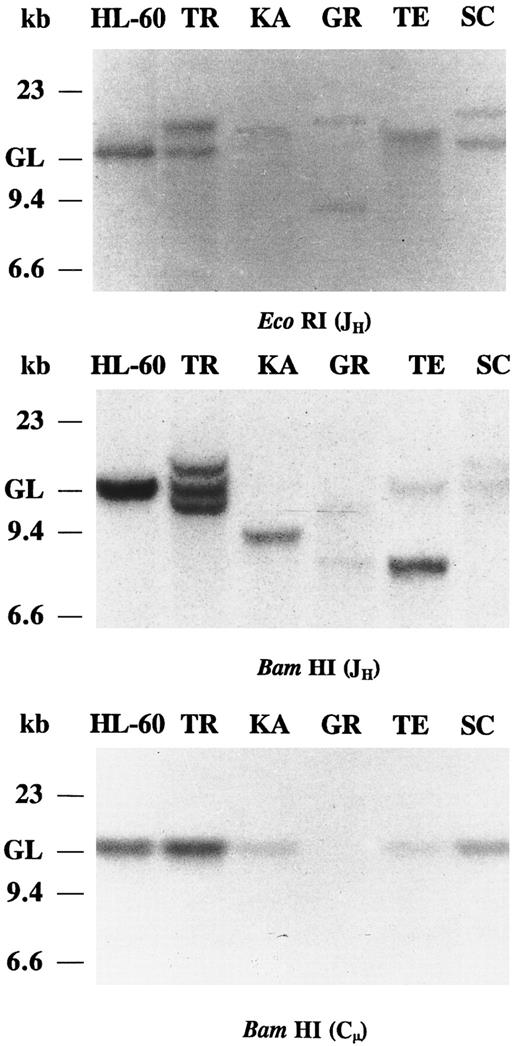
Southern blot analysis of IgH chain gene rearrangements.In all five IgA and/or IgG CLLs, JH probing of the EcoRI and BamHI-digested DNAs revealed clonal Ig gene rearrangements (Fig 1). In cases KA, GR, and TE the JH probe showed strong rearranged bands and very weak germline bands, suggesting bi-allelic JH rearrangements. In cases KA and TE, the other IgH allele has been deleted or partially deleted. The presence of two rearranged IgH bands in BamHI digest of case TR is not observed in the EcoRI digest. In case TR, the discordant hybridization pattern of the two digests may have resulted from a mono-allelic rearrangement where somatic mutation of the IgH gene generates a BamHI restriction site or, alternatively, in a bi-allelic rearrangement, one of the rearranged alleles comigrated with the other allele or with the germline bands in the EcoRI digest. The relatively strong germline bands of case TR may derive from nonneoplastic cells. Only one nongermline band hybridization was detected in the IgA/IgG-coexpressing CLL (TE), consistent with a common clonal origin of both IgA and IgG molecules. In case SC, the intensity of the rearranged and the germline IgH bands were similar, suggesting a mono-allelic rearrangement. The BamHI-digested DNAs of the five IgA and/or IgG CLLs were hybridized with the Cμ probe (Fig 1). In all five cases, the Cμ probe hybridized only with DNA restriction fragments of germline motility, consistent with a deletion of the Cμ gene in the clonally rearranged IgH chain gene. The intensity of the germline Cμ bands is very weak in KA, GR, and TE, further indicating bi-allelic IgH gene rearrangement with deletion of the Cμ gene. Hybridization of the Cμ probe to germline DNA may represent a minor nonneoplastic cell population also present in the CLL sample and/or the nonrearranged Ig gene allele of the CLL B cells.
Southern blot analysis of IgH chain rearrangements in five cases of IgA and/or IgG CLLs. DNAs were digested with EcoRI and BamHI restriction endonucleases and probed with JH and Cμ. The migration of germline (GL) DNA as well as molecular-weight markers are indicated.
Southern blot analysis of IgH chain rearrangements in five cases of IgA and/or IgG CLLs. DNAs were digested with EcoRI and BamHI restriction endonucleases and probed with JH and Cμ. The migration of germline (GL) DNA as well as molecular-weight markers are indicated.
Configuration of the bcl-1 and bcl-2 oncogenes and the p53 tumor suppressor gene.Restriction endonuclease digests of DNAs from five IgA and/or IgG CLLs were subjected to Southern blot hybridization analysis using probes for the bcl-1 and bcl-2 loci. The bcl-1 proto-oncogene major translocation cluster (MTC) was analyzed using the MTC probe31; the breakpoint site located 5′ of the MTC was analyzed using the p94PS probe.32 The bcl-2 proto-oncogene 5′-breakpoint, major cluster region (MCR), and the minor breakpoint region (MBR) were analyzed using the pB16, pFL-1, and pFL-2 probes, respectively.33,34 40 No rearrangements of the bcl-1 or bcl-2 proto-oncogenes were detected in any of the five cases (not shown). Exons 5 through 9 of the p53 tumor suppressor gene were analyzed in genomic DNA of five IgA and/or IgG CLLs by the PCR-SSCP technique. Nucleotide fragments displaying an altered electrophoretic mobility by SSCP were not detected (not shown).
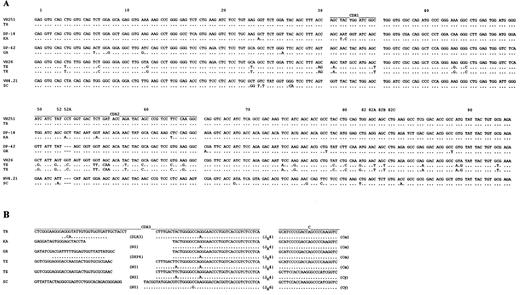
Sequence analysis of the expressed Ig VH genes.To analyze the Ig VH genes expressed by the five IgA and/or IgG CLLs, first-strand cDNA was synthesized from total RNA of leukemic cells and subsequently PCR-amplified using family-specific sense leader and antisense Cα, Cγ, or Cμ primer pairs. In three CLLs (TR, KA, and GR), the leader-Cα, in one CLL (SC), the leader-Cγ, and in one CLL (TE), both the leader-Cα and leader-Cγ primer pairs yielded DNA amplification products. No cDNA was amplified in any of the five IgA and/or IgG CLLs by leader-Cμ primer pairs. The amplified DNAs were cloned and sequenced. In each CLL, 6 to 10 different bacterial isolates were sequenced. In all cases, only identical and unique sequences were detected from analysis of the multiple isolates. The nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the VH segments of the five IgA and/or IgG CLLs are depicted in Figs 2 and 3, respectively. The nucleotide differences and predicted amino acid changes when compared with the reported closest germline VH gene sequences are summarized in Table 2. In case TR, the expressed Ig VH gene sequence displayed 100% identity to that of the VH251 (V5-51) germline gene.41,42 In the other four cases, the rearranged Ig VH gene sequences displayed 97.9% (KA), 97.6% (GR), 88.8% (TE), and 95.9% (SC) identity to those of the DP-14 (V1-18), DP-42 (V3-53), VH26 (V3-23), and VH4.21 (V4-34) germline genes, respectively.38,42,43 In patient TE, the PCR products amplified by the leader-Cα and leader-Cγ primer pairs were identical in the VH-D-JH gene sequence, suggesting a clonal identity of the expressed IgA and IgG molecules. D-segment sequences in cases TR and GR displayed the highest degree of identity to those of germline DLR3 and DXP4, respectively.44 The CDR3 sequences of three CLLs (KA, TE, and SC) did not display any identity to those of known germline D genes. The JH4 gene was used in four cases and the JH6 gene was used in one case. None of the five IgA and/or IgG CLLs displayed intraclonal divergence as inferred from sequence analysis of six independent isolates from each PCR amplification product.
(A) Nucleotide acid sequences of the expressed Ig VH genes from five cases of IgA and/or IgG isotype CLLs. In each cluster, the top amino acid sequences are given for comparison and represent those of the closest reported germline VH gene. The letters below represent differences from the published germline genes. (B) Nucleic acid sequences of the rearranged D and JH genes from five cases of IgA and/or IgG isotype CLL. Each sequence is compared to the known D and JH sequences that have the greatest homology. Identity is indicated by a dot and differences are shown. Solid lines above each cluster depict the CDR sequences. These sequences are available from the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ under accession numbers: U22381, U22387, U22388, U22389, U22390, and U22391.
(A) Nucleotide acid sequences of the expressed Ig VH genes from five cases of IgA and/or IgG isotype CLLs. In each cluster, the top amino acid sequences are given for comparison and represent those of the closest reported germline VH gene. The letters below represent differences from the published germline genes. (B) Nucleic acid sequences of the rearranged D and JH genes from five cases of IgA and/or IgG isotype CLL. Each sequence is compared to the known D and JH sequences that have the greatest homology. Identity is indicated by a dot and differences are shown. Solid lines above each cluster depict the CDR sequences. These sequences are available from the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ under accession numbers: U22381, U22387, U22388, U22389, U22390, and U22391.
Deduced amino acid sequences of the rearranged Ig VH -D-JH -C genes from five cases of IgA and/or IgG isotype CLLs. Single-letter amino acid code is used. Identity is indicated by a dot and differences are shown. Solid lines above each cluster depict the CDR and C gene sequences. Identity is indicated by a dot and differences are shown.
Deduced amino acid sequences of the rearranged Ig VH -D-JH -C genes from five cases of IgA and/or IgG isotype CLLs. Single-letter amino acid code is used. Identity is indicated by a dot and differences are shown. Solid lines above each cluster depict the CDR and C gene sequences. Identity is indicated by a dot and differences are shown.
Ig VH , D, JH , and CH Genes of Leukemic B Cells in Five IgA and/or IgG CLLs
| Patient . | CH Gene . | VH Gene . | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | Closest Germline Gene . | Nucleotide Identity % . | CDR1 and CDR . | FR1, FR2, and FR3 . | D Gene . | JH Gene . | Intraclonal Divergence . | . | ||||
| . | . | . | . | R . | p . | S . | R . | p . | S . | . | . | . | . |
| TR | α | VH251 (V5-51) | 100.0 | 0 (0.00) | — | 0 | 0 (0.00) | — | 0 | LR3 | JH4 | No | |
| KA | α | DP-14 (V1-18) | 97.9 | 4 (1.17) | 1.65 × 10−2 * | 1 | 1 (4.07) | 2.17 × 10−2 * | 0 | ND | JH4 | No | |
| GR | α | DP-42 (V3-53) | 97.6 | 0 (0.00) | — | 0 | 2 (5.29) | 2.50 × 10−2 * | 5 | XP4 | JH4 | No | |
| TE | α/γ | VH26 (V3-23) | 88.8 | 13 (7.70) | 1.93 × 10−2 * | 1 | 11 (25.33) | 9.00 × 10−6 * | 8 | ND | JH4 | No | |
| SC | γ | VH4.21 (V4-34) | 95.9 | 1 (3.36) | 0.10 | 0 | 7 (10.89) | 3.71 × 10−2 | 4 | ND | JH6 | No | |
| Patient . | CH Gene . | VH Gene . | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | Closest Germline Gene . | Nucleotide Identity % . | CDR1 and CDR . | FR1, FR2, and FR3 . | D Gene . | JH Gene . | Intraclonal Divergence . | . | ||||
| . | . | . | . | R . | p . | S . | R . | p . | S . | . | . | . | . |
| TR | α | VH251 (V5-51) | 100.0 | 0 (0.00) | — | 0 | 0 (0.00) | — | 0 | LR3 | JH4 | No | |
| KA | α | DP-14 (V1-18) | 97.9 | 4 (1.17) | 1.65 × 10−2 * | 1 | 1 (4.07) | 2.17 × 10−2 * | 0 | ND | JH4 | No | |
| GR | α | DP-42 (V3-53) | 97.6 | 0 (0.00) | — | 0 | 2 (5.29) | 2.50 × 10−2 * | 5 | XP4 | JH4 | No | |
| TE | α/γ | VH26 (V3-23) | 88.8 | 13 (7.70) | 1.93 × 10−2 * | 1 | 11 (25.33) | 9.00 × 10−6 * | 8 | ND | JH4 | No | |
| SC | γ | VH4.21 (V4-34) | 95.9 | 1 (3.36) | 0.10 | 0 | 7 (10.89) | 3.71 × 10−2 | 4 | ND | JH6 | No | |
Abbreviations: R, number of detected and (expected) R mutations; S, number of detected S mutations; p, probability; ND, not determined.
Statistically significant.
Identification of the germline DP-14 (V1-18) and VH26 (V3-23) genes in cases KA and TE, respectively.The expressed Ig VH gene sequences of cases KA and TE were 97.9% and 88.8% identical to those of the germline DP-14 (V1-18) and VH26 (V3-23) genes, respectively, and possibly arose by mutations of these templates. To test the hypothesis that copies of these germline genes existed in the genomes of patients KA and TE, we PCR-amplified, cloned, and sequenced genomic DNAs from the PB mononuclear cells of the two patients. In patient KA, genomic DNA was amplified using the sense primer specific for CDR1 sequence of DP-14 (V1-18) germline gene in conjunction with the antisense primer specific for the conserved recombination signal sequence heptamer of VH1 genes. In patient TE, genomic DNA was amplified using sense primer specific for the CDR1 sequence of VH26 (V3-23) germline gene in conjunction with the antisense primer specific for the VH3 gene heptamer recombination signal sequence. Thus, our PCRs were designed to amplify only germline forms of DP-14 (V1-18) or VH26 (V3-23) genes, because the heptamer recombination signal sequences are lost in rearranged Ig V genes. Using these oligonucleotide primers, we were able to identify and analyze the putative germline genes in both CLLs because the PB and BM samples contained nonneoplastic cells in low numbers. In each case, the PCR product was cloned, and plasmid DNAs originated from six independent bacterial isolates were sequenced. In patient KA, the nucleotide sequences of the six independent isolates were 100% identical to one other, but they showed a single nucleotide difference from that of the reported germline DP-14 (V1-18) at codon 23 (TAT → AAT), resulting in the substitution Cys → Asn. In patient TE, two cloned plasmids contained inserts identical in sequence to that of the DP-3038; the remaining four incorporated sequences that were 100% identical to that of the reported VH26 (V3-23) germline gene. Thus, these findings are consistent with the hypothesis that the VH genes expressed by CLL B cells of cases KA and TE arose by somatic mutation of genes identical or virtually identical to DP-14 (V1-28) and VH26 (V3-23) germline genes, respectively.
Analysis of somatic mutations detected in the rearranged VH genes.In the absence of negative or positive selection pressure on a gene product, nucleotide changes yielding amino acid replacement (R mutations) and nucleotide changes not yielding amino acid replacement (S, or silent mutations) are randomly distributed throughout the coding sequence. If a DNA segment displays a number of R mutations higher than that expected by chance, it is likely that positive pressure was exerted on the gene product to select for these mutations. Conversely, if a DNA segment displays a number of R mutations lower than expected by chance, it is likely that positive pressure was exerted on the gene product to select against R mutations so that the protein structure is preserved.39 The number of expected R mutations and the probability that the R mutations in the CDRs or FRs of the Ig VH arose by chance was calculated in the five VH segments expressed by the IgA and/or IgG isotype-switched CLLs (Table 2). The Ig VH gene sequences of cases KA and case TE displayed higher and lower numbers of R mutations in the CDRs and FRs, respectively, than theoretically expected. The likelihood that the excess of putative R mutations in the CDRs arose by chance alone was p = 1.65 × 10−2 in case KA and p = 1.93 × 10−2 in case TE. The likelihood that the scarcity of R mutations in the FRs was due to chance alone was p = 2.17 × 10−2 in case KA and p = 9.0 × 10−6 in case TE. Thus, consistent with Ag selection in these two clones, the Ig VH gene segments were under positive pressure to mutate the CDRs, but were under negative pressure to mutate the FRs. In case SC, the likelihood that the excess of putative and verified R mutations in the CDRs and FRs arose by chance alone was p = 0.10 and p = 3.71 × 10−2, respectively. No R mutations were detected in the VH gene CDRs of cases TR and GR.
DISCUSSION
In the studies presented here, we have shown that the Ig VH genes expressed by isotype-switched IgA and/or IgG CLL B cells may or may not be somatically mutated. We have also shown that, when present, these mutations can be in random configuration or can be consistent in nature and distribution with Ag selection. Whether Ag-selected or not, the Ig VH segment somatic mutations analyzed here were not associated with intraclonal diversification.
The IgA and/or IgG CLL B cells resembled “conventional” IgM CLL B cells in phenotype. They expressed CD19, CD20, and CD5 but lacked CD10 and cyclin D1. Their CLL nature was further strengthened by the expression of CD23, which is present on the surface of IgM CLL B cells but absent on CD5+ mantle cell lymphoma B cells.45,46Bcl-1 and bcl-2 oncogenes are frequently rearranged in mantle cell and follicular center cell lymphomas,32-34,40 respectively, but not in CLLs.20 Our Southern blot analysis showed no alterations of bcl-1 and bcl-2 genes in the five isotype-switched CLLs, suggesting that rearrangements of these oncogenes do not play a role in the pathogenesis of IgA and/or IgG CLL. Using Southern blot analysis, a bcl-1 breakpoint can be detected in approximately 50% of mantle cell lymphomas.47 The absence of cyclin D1 expression of these cells further suggests that the bcl-1 gene is not associated with the emergence of isotype-switched CLLs. The p53 tumor suppressor gene is mutated in 10% of CLLs, including those clinically aggressive cases and CLLs that undergo transformation to high-grade lymphoma known as Richter's syndrome.22,23 p53 Mutation also has been shown in the progression of follicular lymphoma to diffuse lymphoma, suggesting that the transforming process is associated with p53 gene mutation.48 49 The absence of p53 suppressor gene mutation in IgA and/or IgG CLLs suggests that isotype-switched CLLs do not represent the clinical progression of transformed B-cell elements.
The Cμ exons were deleted in the rearranged genomic DNAs of all isotype-switched CLLs, suggesting that these IgA- and/or IgG-expressing clones underwent DNA switch recombination. In the CLL cells expressing both IgA and IgG, the same cDNA VH-D-JH sequence was joined with a Cα or a Cγ gene, suggesting that a “physiological” alternative RNA splicing underlied the double-isotype expression. Ig class switch possibly entails a transient stage of dual-Ig expression, as shown by the identification of B cells producing both IgM and IgE, or IgM and IgG, or IgM and IgA isotypes.50-52 In these cells, Cμ and Cε, or Cμ and Cγ, or Cμ and Cα mRNA segments are alternatively spliced, in each case, with the same VH-D-JH gene sequences. A comparable dual Ig CH chain expression also occurs during sequential switch from IgM to IgG to IgA in human B cells.53 Using PCR analysis, we did not find any evidence that VH-D-JH sequences of leukemic cells joined to Cμ gene in the PB or BM of all five IgA and/or IgG CLLs, suggesting that the neoplastic IgA and/or IgG CLLs are transformants of an isotype-switched B cell rather than isotype-switched subclones of a CLL B cell originally expressing IgM. Thus, isotype-switched CLL B cells would represent the neoplastic equivalents of B cells at later ontogenic stages than those that give rise to IgM-expressing CLLs.
All but one IgA and/or IgG CLL expressed mutated VH genes. In one IgA CLL (KA) and in the IgA/IgG CLL (TE), the expressed Ig VH genes displayed a clustering of R mutations in the CDRs that were highly consistent with positive selection of these mutations by Ag, as suggested by the probability value derived from the binomial distribution model.39 Similar findings have been obtained in lymphomas of various histological types, including follicular lymphoma,54,55 multiple myeloma,56 and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome–related Burkitt's lymphoma.57,58 In the present two isotype-switched CLLs, the nature of the putative selecting Ag is unknown. Self Ags could be potential candidates in light of the well-documented anti-self reactivity of many CLL Igs.59 In one IgA (GR) and one IgG (SC) CLL, the Ig VH gene R mutations were inconsistent in nature and distribution with Ag selection. The VH gene (VH251 or V5-51) expressed by an IgA CLL (KA) was unmutated, further suggesting that isotype switching and somatic hypermutation are discrete and independent events in the natural history of a B cell, and that switch progression to IgA can occur in the absence of somatic diversification. The apparent absence of intraclonal diversification in these IgA and/or IgG CLLs suggests a lack of ongoing somatic mutation in the neoplastic clones, and led us to speculate that the detected somatic mutations might have been present in the B cells before malignant transformation. Somatic hypermutation concomitant with and/or subsequent to malignant transformation should result in a relatively high degree of intraclonal diversification, as suggested by the step-wise accumulation of intraclonal somatic mutations in possibly Ag-selected follicular lymphoma B cells.54 55
The different patterns of somatic hypermutation in isotype-switched CLL and follicular lymphoma B cells may result from the application of antigenic stimulation at different stages of the natural history of the B-cell clone, ie, before malignant transformation in CLL; simultaneous and/or malignant transformation in follicular lymphoma. Definition of the temporal relationship between the beginning of Ig V gene somatic hypermutation and B-cell transformation may be important to understand the events underlying lymphomagenesis. Thus, the Ig VH gene configuration and the high degree of intraclonal conservation of IgA and/or IgG CLL B cells analyzed here suggest that isotype-switched CLL B cells may represent malignant transformants of mature B cells at different stages of ontogeny. The impact of malignant transformation at different B-cell ontogenic stages on the clinical course of CLL remains to be determined.
Supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grants No. EY-06337 to D.M.K. and AR-40908 and CA-68541 to P.C., and by MKM 338/96 Grant to A.M.
Address reprint requests to Daniel M. Knowles, MD, Department of Pathology, The New York Hospital-Cornell Medical Center, 525 E 68th St, New York, NY 10021.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal