Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)–infected patients develop a spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders ranging from nonneoplastic lymphadenopathies to B-cell lymphomas. Although evidence suggests that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) might be involved, its molecular profile and expression pattern in HIV-1–related lymphoproliferations remain to be defined. Using polymerase chain reaction–based techniques, we studied EBV types and variants in 28 lymphadenopathy lesions and in 20 lymphomas (15 large cell and 5 Burkitt-like). EBV was detected in 89% of lymphadenopathies and in 80% of lymphomas; viral DNA content was significantly higher in the latter. EBNA2 and LMP1 gene analysis indicated that half of the EBV+ lymphadenopathies were coinfected with both EBV type 1 and 2 strains and/or multiple type 1 variants. Conversely, all but one lymphoma carried a single viral variant, consistently type 1 in large cell lymphomas, and type 2 in Burkitt-like tumors. Most lymphomas, but no lymphadenopathies, showed monoclonal Ig heavy-chain rearrangement. Analysis of 5 large cell lymphomas and 9 lymphadenopathies for EBV transcripts identified LMP1 mRNA in most samples, and the EBNA2 transcript in all tumors. These findings provide evidence of a heterogeneous EBV population in lymphadenopathy lesions, strengthen the notion that lymphomas arise from clonal expansion of EBV+ cells, and suggest different roles for EBV types 1 and 2 in HIV-1–related lymphoproliferations.
PATIENTS INFECTED with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) develop a wide spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders, ranging from nonneoplastic lymphadenopathy to high-grade B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL).1 Two main histologic types of NHL are recognized, Burkitt-like lymphoma and large cell lymphoma.2 Although lymphadenopathy usually appears as an early manifestation of HIV-1 infection, lymphomas arise at a relatively late stage of infection, and the onset of large cell lymphoma is invariably associated with a low CD4+ cell count and an immunocompromised patient status.3 The finding that a significant proportion of HIV-1–infected subjects with lymphoma have a previous history of lymphadenopathy,4 together with the presence of monoclonal or oligoclonal Ig gene rearrangements in some of these lesions,5 6 suggests that lymphadenopathy might represent a lymphomatous lesion precursor.
Although the pathogenesis of HIV-1–related lymphoproliferative disorders is far from being fully elucidated, there is evidence that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) may be involved. EBV sequences and/or gene products are detectable in up to 80% of large cell lymphomas, and in about 40% of Burkitt-like lymphomas.7 Moreover, the presence of EBV in lymphadenopathy lesions correlates with a higher risk of developing lymphoma over time,4 thus suggesting that EBV might constitute an early promoter in HIV-1–related lymphomagenesis.
EBV is a ubiquitous human herpesvirus that is able to immortalize B cells in vitro and is associated with a variety of human malignancies.8 EBV isolates can be distinguished into two types by major sequence divergence in the genes coding for the EBV nuclear antigens (EBNA 2, 3A, 3B, 3C), and into distinct strains by specific nucleotide sequence variability within the EBNA2 and latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) genes.9-11 Furthermore, distinct EBV variants can be distinguished on the basis of the length and number of repeat sequences in the third exon of the LMP1 gene.10,12 The observation that EBV type 1 transforms B cells in vitro more efficiently than EBV type 213 suggests type-specific differences in oncogenic activity in vivo. Although healthy white subjects usually harbor a single EBV strain, usually of type 1, HIV-1–infected subjects may be infected with either type 1 or type 2; moreover, either type 1 or 2 has been found in HIV-1–related lymphomas,14,15 thus suggesting that both types may play an oncogenic role in the context of a weakened immune system. Furthermore, coinfection with EBV types 1 and 2 has been reported in HIV-1–infected subjects,16-18 but very little information is currently available on the genomic heterogeneity of EBV in HIV-1–related lymphadenopathies.4 19
Although in vitro EBV-immortalized B cells express all the latent proteins of EBV, including the six nuclear antigens (EBNA1, 2, 3A, 3B, 3C, LP) and the three latent membrane proteins (LMP1, 2A, 2B), different patterns of EBV latent protein expression have been described in EBV-related malignancies in vivo. Whereas the selective expression of EBNA1 protein is usually found in Burkitt lymphoma cells, expression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2A and/or LMP2B is frequently detected in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and Hodgkin's disease, and all EBNA and LMP proteins have been detected in posttransplant lymphomas.8 The question of EBV expression in HIV-1–related lymphomas has yet to be fully resolved. Although selective expression of the EBNA 1 has been consistently reported in EBV+ Burkitt-like lymphoma, heterogeneous expression of EBV latent proteins has been described in large cell lymphoma.7,15,20 Moreover, little information concerning EBV gene expression in lymphadenopathy lesions is available; to date the only study in this field was conducted by immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-fixed biopsy samples and it failed to detect EBNA2 and/or LMP1 expression.19
PCR Primers and Probes Used for EBV Detection and Expression Analysis
| Primers/Probes . | B95.8 Coordinates . | Sequence (bp) . | Annealing Temperature (°C) . | MgCl2 Concentration (mmol/L) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | (5′-3′ ) . | . | . | . |
| DNA-PCR: | ||||
| EBNA2 5′ | 48162-48181 | 5′-AGGCTGCCCACCCTGAGGAT-3′ | 62 | 1.5 |
| EBNA2 3′ | 48330-48311 | 5′-GCCACCTGGCAGCCCTAAAG-3′ | ||
| EBNA2-type 1/2 probe | 48253-48271 | 5′-GTTGCCGCCAGGTGGCAGC-3′ | ||
| EBNA3C 5′ | 99939-99958 | 5′-AGAAGGGGAGCGTGTGTTGT-3′ | 58 | 1.5 |
| EBNA3C 3′ | 100091-100072 | 5′-GGCTCGTTTTTGACGTCGGC-3′ | ||
| EBNA3C-type 1 probe | 100002-100021 | 5′-GAAGATTCATCGTCAGTGTC-3′ | ||
| EBNA3C-type 2 probe | 5′-CCGTGATTTCTACCGGGAGT-3′ | |||
| RT-PCR: | ||||
| EBNA2 5′ | 47940-47959 | 5′-GCGCCAATCTGTCTACATAG-3′ | 50 | 0.5 |
| EBNA2 3′ | 48534-48515 | 5′-CCCCATGTAACGCAAGATAG-3′ | ||
| EBNA2 probe | 48473-48454 | 5′-CGGGTGCTTAGAAGGTTGTT-3′ | ||
| LMP1 5′ | 168813-168833 | 5′-CAACCAATAGAGTCCACCAGT-3′ | 50 | 0.75 |
| LMP1 3′ | 169263-169243 | 5′-TCTTCAGAAGAGACCTTCTCT-3′ | ||
| LMP1 probe | 168888-168908 | 5′-GGAAGAAGGCCAAAAGCTGCC-3′ | ||
| LMP2A 5′ | 166820-166840 | 5′-GATTGCAACACGACGGGAATG-3′ | 50 | 1.0 |
| LMP2B 5′ | 169819-169839 | 5′-CAGTGTAATCTGCACAAAGAG-3′ | 50 | 0.5 |
| LMP2A/LMP2B 3′ | 271-251 | 5′-AAGTGACAACCGCAGTAAGCA-3′ | ||
| LMP2A/LMP2B probe | 229-249 | 5′-AAACTGCTGACACCGGTGACA-3′ | ||
| BZLF 5′ | 102478-102498 | 5′-GCCACCCGATTCTTGTATCGC-3′ | 55 | 1.5 |
| BZLF 3′ | 103063-103042 | 5′-AGTCTATCAGGACCTGGGAGGG-3′ | ||
| BZLF probe | 102853-102873 | 5′-TTCCCAGTCTCCGACATAACC-3′ |
| Primers/Probes . | B95.8 Coordinates . | Sequence (bp) . | Annealing Temperature (°C) . | MgCl2 Concentration (mmol/L) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | (5′-3′ ) . | . | . | . |
| DNA-PCR: | ||||
| EBNA2 5′ | 48162-48181 | 5′-AGGCTGCCCACCCTGAGGAT-3′ | 62 | 1.5 |
| EBNA2 3′ | 48330-48311 | 5′-GCCACCTGGCAGCCCTAAAG-3′ | ||
| EBNA2-type 1/2 probe | 48253-48271 | 5′-GTTGCCGCCAGGTGGCAGC-3′ | ||
| EBNA3C 5′ | 99939-99958 | 5′-AGAAGGGGAGCGTGTGTTGT-3′ | 58 | 1.5 |
| EBNA3C 3′ | 100091-100072 | 5′-GGCTCGTTTTTGACGTCGGC-3′ | ||
| EBNA3C-type 1 probe | 100002-100021 | 5′-GAAGATTCATCGTCAGTGTC-3′ | ||
| EBNA3C-type 2 probe | 5′-CCGTGATTTCTACCGGGAGT-3′ | |||
| RT-PCR: | ||||
| EBNA2 5′ | 47940-47959 | 5′-GCGCCAATCTGTCTACATAG-3′ | 50 | 0.5 |
| EBNA2 3′ | 48534-48515 | 5′-CCCCATGTAACGCAAGATAG-3′ | ||
| EBNA2 probe | 48473-48454 | 5′-CGGGTGCTTAGAAGGTTGTT-3′ | ||
| LMP1 5′ | 168813-168833 | 5′-CAACCAATAGAGTCCACCAGT-3′ | 50 | 0.75 |
| LMP1 3′ | 169263-169243 | 5′-TCTTCAGAAGAGACCTTCTCT-3′ | ||
| LMP1 probe | 168888-168908 | 5′-GGAAGAAGGCCAAAAGCTGCC-3′ | ||
| LMP2A 5′ | 166820-166840 | 5′-GATTGCAACACGACGGGAATG-3′ | 50 | 1.0 |
| LMP2B 5′ | 169819-169839 | 5′-CAGTGTAATCTGCACAAAGAG-3′ | 50 | 0.5 |
| LMP2A/LMP2B 3′ | 271-251 | 5′-AAGTGACAACCGCAGTAAGCA-3′ | ||
| LMP2A/LMP2B probe | 229-249 | 5′-AAACTGCTGACACCGGTGACA-3′ | ||
| BZLF 5′ | 102478-102498 | 5′-GCCACCCGATTCTTGTATCGC-3′ | 55 | 1.5 |
| BZLF 3′ | 103063-103042 | 5′-AGTCTATCAGGACCTGGGAGGG-3′ | ||
| BZLF probe | 102853-102873 | 5′-TTCCCAGTCTCCGACATAACC-3′ |
In this study we have applied polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based methods to analyze EBV types and variants and EBV gene expression in lymphadenopathies and lymphomas from HIV-1–infected patients. Results showed that lymphadenopathies and lymphomas differ with respect to genomic heterogeneity of EBV and mRNA expression patterns.
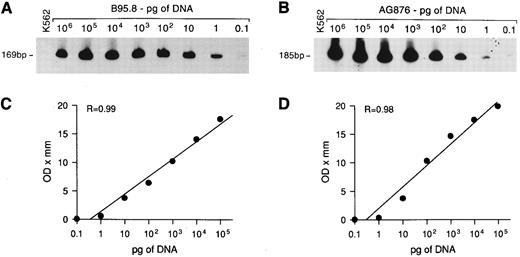
Sensitivity of DNA-PCR for EBNA2 gene detection. Tenfold serial dilutions of DNA from EBV+ B95.8 or AG876 cells were mixed with 1 μg of DNA from EBV− K562 cells and PCR amplified with EBNA2 primers. The amplified products, of 169 bp and 185 bp for EBV types 1 and 2, respectively, were visualized with a radiolabeled probe that detects EBV type 1 (A) and type 2 (B). Regression curves (C and D) were obtained as described in Materials and Methods.
Sensitivity of DNA-PCR for EBNA2 gene detection. Tenfold serial dilutions of DNA from EBV+ B95.8 or AG876 cells were mixed with 1 μg of DNA from EBV− K562 cells and PCR amplified with EBNA2 primers. The amplified products, of 169 bp and 185 bp for EBV types 1 and 2, respectively, were visualized with a radiolabeled probe that detects EBV type 1 (A) and type 2 (B). Regression curves (C and D) were obtained as described in Materials and Methods.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Pathologic samples.Lymph node or extralymphatic mass biopsy samples were collected from 28 patients with lymphadenopathy lesions and 20 patients with lymphomas, all with documented HIV-1 infection. Tumors were diagnosed and classified according to the International Working Formulation21 and grouped as Burkitt-like (5 cases) or large cell lymphoma (15 cases). The fraction of malignant cells in the tumor specimens was greater than 80% in most cases as determined by immunohistochemical analysis of cell surface markers. Biopsy samples were stored at −80°C until DNA and RNA extraction.
DNA extraction and Southern blot analysis.High-molecular-weight DNA was prepared by cell lysis, proteinase-K digestion, extraction with phenol-chloroform, and ethanol precipitation. Low-molecular-weight DNA was extracted using a standard procedure22 from 5- to 10-μm–thick sections of paraffin-embedded biopsy speciments. Southern blot analyses for EBV and for IgH gene rearrangements were performed on high-molecular-weight DNA (10 μg) after digestion with appropriate restriction endonucleases, as previously reported.23
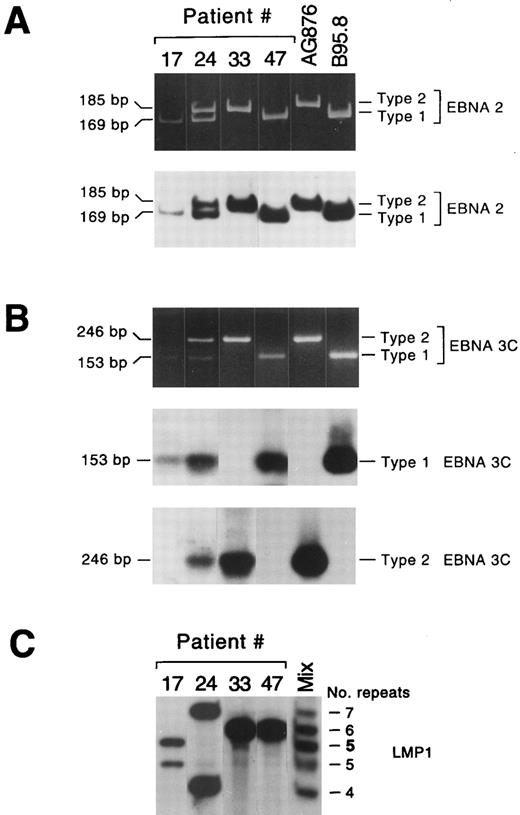
EBV types and variants in lymphadenopathy lesions and lymphomas. Representative lymphadenopathy lesions harboring EBV type 1 (no. 17) or EBV types 1 and 2 (no. 24), and lymphoma lesions harboring EBV type 2 (no. 33) or EBV type 1 (no. 47) are shown in (A) and (B). The amplified EBNA2 products were visualized in ethidium bromide–stained acrylamide gels and detected with a radiolabeled probe that detects EBV types 1 and 2 (A); the amplified EBNA 3C products from the same samples were visualized in ethidium bromide–stained gels and detected using two different radiolabeled probes specific for EBV types 1 and 2, respectively (B). (C) LMP1 variant analysis of the same lesions. Two different LMP1 variants were detected in each lymphadenopathy lesion, while a single LMP1 variant was detected in lymphoma samples. Lane “mix” contained a mixture of five amplified LMP1 products, containing 4, 5, 6, or 7 repeats, or 5 repeats (5) with the 15-bp insertion.
EBV types and variants in lymphadenopathy lesions and lymphomas. Representative lymphadenopathy lesions harboring EBV type 1 (no. 17) or EBV types 1 and 2 (no. 24), and lymphoma lesions harboring EBV type 2 (no. 33) or EBV type 1 (no. 47) are shown in (A) and (B). The amplified EBNA2 products were visualized in ethidium bromide–stained acrylamide gels and detected with a radiolabeled probe that detects EBV types 1 and 2 (A); the amplified EBNA 3C products from the same samples were visualized in ethidium bromide–stained gels and detected using two different radiolabeled probes specific for EBV types 1 and 2, respectively (B). (C) LMP1 variant analysis of the same lesions. Two different LMP1 variants were detected in each lymphadenopathy lesion, while a single LMP1 variant was detected in lymphoma samples. Lane “mix” contained a mixture of five amplified LMP1 products, containing 4, 5, 6, or 7 repeats, or 5 repeats (5) with the 15-bp insertion.
PCR analysis.EBV DNA was detected and typed by PCR using primers specific for the EBNA2 and EBNA3C genes as previously reported,24 by using 1 μg of sample DNA and 50 pmol of each primer (listed in Table 1); 35 amplification cycles, each of 40 seconds at 94°C, 1 minute at 62°C for EBNA2 primers and 58°C for EBNA3C primers, and 1 minute at 72°C, were performed in a DNA thermal cycler (Gene Amp PCR system 9600; Perkin Elmer, Foster City, CA). EBNA3C amplified products (30 μL) were electrophoresed in agarose gels and transferred to Nytran filters by Southern blotting; EBNA2 amplified products (20 μL) were electrophoresed in acrylamide gels and transferred to Nytran filters by electroblotting. Filters were hybridized with 5′ end 32P-labeled specific probes (Table 1) and exposed to x-ray film. To control the quality of samples, parallel reactions were run using the primers specific for a 110-bp sequence of the β-globin gene.25
To assess the sensitivity of the PCR technique and to estimate the relative amount of EBV DNA in the samples, a reference curve was prepared by PCR amplifying DNA extracted from EBV+ B95.8 cells or AG876 cells serially diluted in 1 μg of DNA from EBV− K562 cells. A PCR signal was obtained starting with 0.1 pg of B95.8 or AG876 DNA using the EBNA2-specific primers (Fig 1A and B) and with 1 pg using the EBNA3C-specific primers (not shown). As the B95.8 cell line contains about 200 EBV genomes/cell,26 PCR would detect as few as 2 and as many as 20 EBV genomes/1 μg DNA, using the EBNA2 and EBNA 3C primers, respectively. Autoradiographs of the EBNA2-amplified products were evaluated by densitometry (Ultrascan XL, LKB; Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden) and the optical density (OD) values were plotted against the dilutions of DNA; a linear correlation between the OD value and the amount of target DNA was observed over a range of 0.1 pg to 100 ng (Fig 1C and D). The relative amount of EBV DNA in the samples was calculated by comparing the OD values of their EBNA2-amplified products to the OD values of the standard controls; EBV DNA content was then expressed on a scale from 1+ (OD values included among those obtained from 0.1 to 1 pg control DNA) to 6+ (OD values included among those obtained from 10 to 100 ng control DNA).
Detection of EBV Types and Variants in HIV-1–Related Lymphadenopathies and Lymphomas
| Pathology . | No. EBV+/No. Tested . | EBV Type 1 . | EBV Type 2 . | EBV Types 1/2 . | Multiple LMP1 Variants . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphadenopathy | 25/28* | 17 | 1 | 6 | 10 |
| Burkitt-like lymphoma | 4/5 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Large-cell lymphoma | 12/15 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Pathology . | No. EBV+/No. Tested . | EBV Type 1 . | EBV Type 2 . | EBV Types 1/2 . | Multiple LMP1 Variants . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lymphadenopathy | 25/28* | 17 | 1 | 6 | 10 |
| Burkitt-like lymphoma | 4/5 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Large-cell lymphoma | 12/15 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
One case was not typable (see text).
To investigate EBV variants, 1 μg of sample DNA was amplified by PCR as previously described12 using a set of primers (5′-3′ GGCGCACCTGGAGGTGGTCC; TTTCCAGCAGAGTCGCTAGG) that immediately flank a portion of the 33-bp tandem repeats in the LMP1 gene.26 The PCR products were electrophoresed through 6% polyacrylamide/7 mol/L urea/Tris-borate gels, transferred electrophoretically to Hybond-N Plus membranes (Amersham, Buckinghamshire, UK), and hybridized with the internal oligonucleotide probe 5′-3′ TGACAATGGCCCACAGGACCCTG.27 Repeat number was assessed by comparison with a marker containing a mixture of five sequenced amplified products.12
Seminested PCR for the detection of IgH gene rearrangements was performed as previously described.24
Semiquantitative reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR.Frozen specimens were homogenized (Ultraturrax; IKA Werk, Staufen, Germany) and total RNA was extracted using RNAzolB (Biotecx Laboratories, Inc, Houston, TX). First-strand cDNA was made from 16 μg of total RNA in a 160-μL reaction mixture containing 50 mmol/L KCl, 10 mmol/L Tris- HCl pH 8.3, 50 pmol dT oligomer, 1 mmol/L of each dNTP, 50 U of Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus (MuLV) RT, 20 U of RNase inhibitor, and 5 mmol/L MgCl2 . RNA samples were preheated for 10 minutes at 65°C, incubated in the reaction mixture for 60 minutes at 42°C, and then incubated for 10 minutes at 99°C. Twenty microliters of the reverse-transcribed mixture was coamplified with primers specific for each of the viral genes listed in Table 1, and for the β-actin cellular gene. PCR was performed in a final volume of 100 μL containing 50 pmol of each primer specific for the viral gene, 12.5 pmol of primer specific for the β-actin gene, 200 μmol/L of each dNTP, 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl pH 8.3, 50 mmol/L KCl, 0.5 to 1.5 mmol/L MgCl2 , and 2.5 U of Taq DNA polymerase. Forty amplification cycles were performed using the annealing temperature reported in Table 1; 30 μL of each amplified sample was electrophoresed in agarose gels and transferred to Nytran filters by Southern blotting. Filters were hybridized with 5′ end 32P-labeled specific probes (Table 1) and exposed to x-ray films. Autoradiographs of the amplified products were analyzed by densitometry, and the relative amount of viral RNA was calculated as the ratio between the OD value of the amplified viral gene and the OD value of the amplified β-actin gene.
In situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry.Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from lymph nodes and tumor samples were hybridized overnight at 37°C with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled RNA probes specific for EBER-1/2 EBV transcripts (Dako, Golstrup, Denmark). Colorimetric detection was performed by using anti-FITC antibody followed by alkaline phosphatase-conjugated antimouse antibody and nitroblue tetrazolium as substrate. Adjacent sections were incubated with the monoclonal antibody CS1-4 (Dako), which recognizes the LMP1 protein. Detection was performed with the ABC kit (Vectastain; Vector, Burlingame, CA) and diaminobenzidine as substrate.
Molecular Profile of EBV in HIV-1–Related Lymphadenopathies
| Patient Code . | Ig (SB) . | Ig (PCR) . | EBV (SB) . | EBV Type (PCR) . | EBV DNA Amount (PCR)3-150 . | LMP . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | . | . | . | No. Variants . | No. Repeats3-151 . |
| 1 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 2 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 1+/1+ | 2 | 4, 3 |
| 3 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 3+ | 1 | 5 |
| 4 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 1+/2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 5 | G | Polyclonal | − | − | − | − | − |
| 6 | G | Polyclonal | − | NT | 2+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 7 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 8 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 9 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 10 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 3 | 4, 5, 6 |
| 11 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 3 |
| 12 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 13 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 1+/1+ | 2 | 4, 3 |
| 14 | G | Polyclonal | − | − | − | − | − |
| 15 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | − | − | − | − |
| 16 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 17 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 2 | 5, 5 |
| 18 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 2 | 7, 5 |
| 19 | G | ND | − | 1/2 | 1+/1+ | 2 | 4, 7 |
| 20 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 21 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 22 | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1+ | ND | ND |
| 23 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 2+/1+ | 1 | 4 |
| 24 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 3+/3+ | 2 | 4, 7 |
| 25 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 2 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 26 | G | Polyclonal | — | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 4 |
| 27 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 5 |
| 28 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| Patient Code . | Ig (SB) . | Ig (PCR) . | EBV (SB) . | EBV Type (PCR) . | EBV DNA Amount (PCR)3-150 . | LMP . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | . | . | . | No. Variants . | No. Repeats3-151 . |
| 1 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 2 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 1+/1+ | 2 | 4, 3 |
| 3 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 3+ | 1 | 5 |
| 4 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 1+/2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 5 | G | Polyclonal | − | − | − | − | − |
| 6 | G | Polyclonal | − | NT | 2+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 7 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 8 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 9 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 10 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 3 | 4, 5, 6 |
| 11 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 3 |
| 12 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 13 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 1+/1+ | 2 | 4, 3 |
| 14 | G | Polyclonal | − | − | − | − | − |
| 15 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | − | − | − | − |
| 16 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 17 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 2 | 5, 5 |
| 18 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 2 | 7, 5 |
| 19 | G | ND | − | 1/2 | 1+/1+ | 2 | 4, 7 |
| 20 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 2+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 21 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1 | 1+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 22 | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1+ | ND | ND |
| 23 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 2+/1+ | 1 | 4 |
| 24 | G | Polyclonal | − | 1/2 | 3+/3+ | 2 | 4, 7 |
| 25 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 2 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
| 26 | G | Polyclonal | — | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 4 |
| 27 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 5 |
| 28 | NA | Polyclonal | NA | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 5 |
Abbreviations: ND, not done; NA, not applicable because only low-molecular-weight DNA was available; NT, not typable.
The relative amount of EBV DNA was estimated by comparing OD values of amplified products to those obtained by amplification of 10-fold serial dilutions of B95.8 or AG876 DNA: 1+ (0.1-1 pg), 2+ (1-10 pg), 3+ (10-100 pg).
In boldface are reported LMP1 variants containing the 15-bp insertion in the third repeat element.
RESULTS
Detection of EBV types and variants.Detection and typing of EBV in 28 lymphadenopathy and 20 lymphoma specimens was performed by PCR using primer pairs specific for EBNA2 and EBNA3C sequences (Fig 2A and B). EBV DNA was detected in 25 of the 28 lymphadenopathy samples (89%), in 12 of the 15 large cell lymphomas (80%), and in 4 of the 5 Burkitt-like lymphomas (Table 2). The frequency of EBV type 1 was higher than type 2 in both the lymphadenopathy lesions (17 of 25) and the large cell lymphoma samples (11 of 12). Conversely, type 2 infection was found in 3 of 4 Burkitt-like lymphomas, but in only 1 lymphadenopathy, and was not detected in any of the large cell lymphomas. Coinfection with EBV types 1 and 2 was detected in 6 lymphadenopathies and in 1 large cell lymphoma (Table 2). In all of these cases EBV type 1 and 2 sequences were detected with primer pairs for both EBNA2 and EBNA3C. Only one lymphadenopathy case (no. 6, Table 3) could not be typed, as only EBV type 1 sequences were detected using EBNA2 primers, and only type 2 sequences were evidenced using EBNA3C primers.
Viral variants were distinguished by PCR amplification of the portion of the LMP1 gene containing the 33-bp repeats. This region contains from 3 to 7 repeats; an insertion of 15 bp is also present in one internal repeat in the B95.8 virus prototype and in several other isolates.10,12 Both the number and type of repeat sequences in the samples were assessed by comparison with a marker containing a mixture of five sequenced amplified products (Fig 2C). Multiple LMP1 variants were detected in 10 lymphadenopathy cases, but only in 1 lymphoma sample (Table 2). It has been shown that LMP1 divergence does not correlate with the distinction between types 1 and 2 based on EBNA gene diversity, and different EBV types may have nearly identical LMP1 sequences.10 Accordingly, in 2 of 6 coinfected lymphadenopathy samples, we found a single variant, whereas we detected 2 or 3 LMP1 variants in 6 samples despite the presence of a single EBV type (Table 3). The single lymphoma sample showing multiple LMP1 variants was the only tumor coinfected with both EBV type 1 and type 2 (no. 42, Table 4).
Molecular Profile of EBV in HIV-1–Related NHLs
| Patient Code . | Site . | Pathology . | Ig (SB) . | Ig (PCR) . | EBV (SB)4-150 . | EBER (ISH)4-151 . | EBV Type (PCR) . | EBV DNA Amount (PCR)‡ . | LMP . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | No. Variants . | No. Repeatsρ . |
| 29 | Lymph node | SNCCL | R | Clonal | + | ND | 2 | 5+ | 1 | 4 |
| 30 | Lymph node | SNCCL | R | Clonal | + | 20% | 1 | 6+ | 1 | 5 |
| 31 | Bone marrow | SNCCL | ND | ND | − | ND | − | − | − | − |
| 32 | Stomach | SNCCL | NA | Clonal | NA | 10% | 2 | 4+ | 1 | 3 |
| 33 | Ascites | SNCCL | R | Clonal | + | ND | 2 | 5+ | 1 | 6 |
| 34 | Brain | CNS-LCL | R | Clonal | + | ND | 1 | 5+ | 1 | 6 |
| 35 | Brain | CNS-LCL | NA | Clonal | NA | ND | − | − | − | − |
| 36 | Brain | CNS-LCL | NA | Clonal | NA | 15% | 1 | 4+ | ND | ND |
| 37 | Lymph node | LCL-IB | R | Clonal | − | ND | 1 | 3+ | 1 | 4 |
| 38 | Stomach | LCL-IB | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1+ | ND | ND |
| 39 | Lymph node | LCL-IBP | G | Polyclonal | − | ND | − | − | − | − |
| 40 | Skin | LNCCL | NA | Clonal | NA | 30% | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 4 |
| 41 | Skin | LCL-IBP | NA | Clonal | NA | − | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 42 | Bladder wall | LNCCL | NA | Polyclonal | NA | − | 1/2 | 1+/2+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 43 | Lymph node | LNCCL | R | Clonal | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 44 | Lymph node | LCL-IBP | R | Clonal | + | 45% | 1 | 4+ | 1 | 4 |
| 45 | Lymph node | LNCCL | R | Clonal | + | 20% | 1 | 5+ | 1 | 5 |
| 46 | Stomach | LCL-IB | R | Clonal | + | 45% | 1 | 5+ | 1 | 5 |
| 47 | Nasopharynx | LCL-IB | ND | Clonal | + | ND | 1 | 4+ | 1 | 6 |
| 48 | Pleural effusion | LCL-IB | R | Clonal | − | − | 1 | 3+ | 1 | 4 |
| Patient Code . | Site . | Pathology . | Ig (SB) . | Ig (PCR) . | EBV (SB)4-150 . | EBER (ISH)4-151 . | EBV Type (PCR) . | EBV DNA Amount (PCR)‡ . | LMP . | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | No. Variants . | No. Repeatsρ . |
| 29 | Lymph node | SNCCL | R | Clonal | + | ND | 2 | 5+ | 1 | 4 |
| 30 | Lymph node | SNCCL | R | Clonal | + | 20% | 1 | 6+ | 1 | 5 |
| 31 | Bone marrow | SNCCL | ND | ND | − | ND | − | − | − | − |
| 32 | Stomach | SNCCL | NA | Clonal | NA | 10% | 2 | 4+ | 1 | 3 |
| 33 | Ascites | SNCCL | R | Clonal | + | ND | 2 | 5+ | 1 | 6 |
| 34 | Brain | CNS-LCL | R | Clonal | + | ND | 1 | 5+ | 1 | 6 |
| 35 | Brain | CNS-LCL | NA | Clonal | NA | ND | − | − | − | − |
| 36 | Brain | CNS-LCL | NA | Clonal | NA | 15% | 1 | 4+ | ND | ND |
| 37 | Lymph node | LCL-IB | R | Clonal | − | ND | 1 | 3+ | 1 | 4 |
| 38 | Stomach | LCL-IB | ND | ND | ND | ND | 1 | 1+ | ND | ND |
| 39 | Lymph node | LCL-IBP | G | Polyclonal | − | ND | − | − | − | − |
| 40 | Skin | LNCCL | NA | Clonal | NA | 30% | 1 | 1+ | 1 | 4 |
| 41 | Skin | LCL-IBP | NA | Clonal | NA | − | 1 | 2+ | 1 | 4 |
| 42 | Bladder wall | LNCCL | NA | Polyclonal | NA | − | 1/2 | 1+/2+ | 2 | 4, 5 |
| 43 | Lymph node | LNCCL | R | Clonal | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| 44 | Lymph node | LCL-IBP | R | Clonal | + | 45% | 1 | 4+ | 1 | 4 |
| 45 | Lymph node | LNCCL | R | Clonal | + | 20% | 1 | 5+ | 1 | 5 |
| 46 | Stomach | LCL-IB | R | Clonal | + | 45% | 1 | 5+ | 1 | 5 |
| 47 | Nasopharynx | LCL-IB | ND | Clonal | + | ND | 1 | 4+ | 1 | 6 |
| 48 | Pleural effusion | LCL-IB | R | Clonal | − | − | 1 | 3+ | 1 | 4 |
Abbreviations: SNCCL, small noncleaved cell Burkitt-like lymphoma; CNS-LCL, central nervous system-large cell lymphoma; LCL-IB, large cell immunoblastic lymphoma; LCL-IBP, large cell immunoblastic lymphoma with plasmacytoid differentiation; ND, not done; NA, not applicable because only low-molecular-weight DNA was available.
Single genome dominance.
% of positive cells.
The relative amount of EBV DNA was estimated by comparing OD values of amplified products to those obtained by amplification of 10-fold serial dilutions of B95.8 or AG876 DNA: 1+ (0.1-1 pg), 2+ (1-10 pg), 3+ (10-100 pg), 4+ (100 pg-1 ng), 5+ (1-10 ng), 6+ (10-100 ng).
ρ In boldface are reported LMP1 variants containing the 15-bp insertion in the third repeat element.
The relative amount of EBV DNA in the EBV+ samples was estimated by comparing the OD values of their amplified EBNA2 products to the OD values obtained using standard reference samples, as detailed in Materials and Methods. As shown in Table 3, most of the EBV+ lymphadenopathy samples had very low levels of EBV DNA (ie, scored either 1+ or 2+) and accordingly, none of the analyzed lymphadenopathy specimens was found to be EBV+ by Southern blot analysis. Three cases were analyzed by in situ hybridization with EBER probes; 1 (no. 20) showed viral sequences in 2% to 3% of cells (Fig 3), and 2 (nos. 21 and 23) were negative. Interestingly, in 4 of 6 coinfected lymphadenopathy cases, the amounts of type 1 and type 2 EBV DNA were equivalent, while either type 1 or 2 predominated in the 2 remaining cases (Table 3).
In situ hybridization with EBER probes. In a representative lymphadenopathy case (no. 20), rare EBER+ cells are seen, mainly in the interfollicular areas (A and B). In a representative lymphoma case (no. 46) nearly half of the cells are EBER+ (C and D). Original magnification: ×130 (A and C) and ×260 (B and D).
In situ hybridization with EBER probes. In a representative lymphadenopathy case (no. 20), rare EBER+ cells are seen, mainly in the interfollicular areas (A and B). In a representative lymphoma case (no. 46) nearly half of the cells are EBER+ (C and D). Original magnification: ×130 (A and C) and ×260 (B and D).
Twelve of the 16 EBV+ lymphoma samples scored from 3+ to 6+ for EBV DNA content (ie, 102- to 105-fold higher than that found in the majority of the lymphadenopathy samples), and most were also positive by Southern blot analysis (Table 4). Seven of 11 tested samples were also positive for viral sequences by in situ hybridization with EBER probes (Table 4). Although the high content of EBV in these tumors strongly indicated that they arose from the proliferation of EBV+ cells, 4 large cell lymphomas contained consistently low levels of EBV DNA, a finding that might reflect either a dilution effect by nonneoplastic EBV− cells in the analyzed samples, or the presence of few infiltrating reactive EBV+ B cells.
Detection of B-cell clonal expansion.B-cell clonal expansion in lymphadenopathy and lymphoma biopsies was investigated by PCR amplification of the IgH VDJ region. All lymphadenopathy specimens analyzed disclosed a ladder of multiple bands indicative of reactive polyclonal B-cell proliferation (Table 3). In contrast, 16 of the 18 lymphoma samples studied showed a monoclonal rearrangement of the Ig heavy chain, suggesting a clonal B-cell expansion (Table 4). Interestingly, the only polyclonal tumor among the EBV+ lymphoma samples was case 42, which was positive for both EBV types (Table 4). Southern blot analysis of IgH gene rearrangements invariably confirmed the PCR results, as reported in Tables 3 and 4.
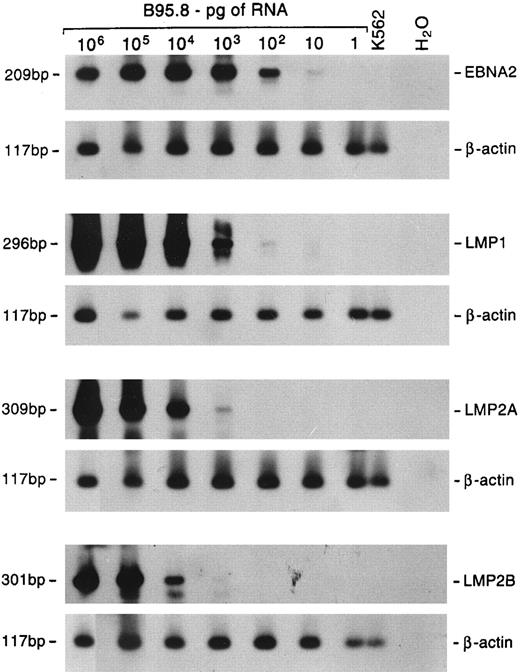
EBV gene expression.The profile of EBV gene expression was studied by RT-PCR in 5 large cell lymphomas and 9 lymphadenopathy cases for which cryopreserved material for RNA extraction was available. To detect and quantify the relative amount of viral RNA in the samples, the cDNAs were coamplified with a primer pair specific for a viral gene along with a primer pair specific for the β-actin cellular gene. The sensitivity of the assay with the different primer pairs was assessed using serial dilutions of RNA extracted from EBV+ B95.8 cells. The sensitivity was such that a positive signal was obtained starting from 10 pg of RNA using EBNA2-specific primers, 100 pg using the LMP1-specific primers, and 1 ng using LMP2A- and LMP2B-specific primers (Fig 4).
Sensitivity of semiquantitative RT-PCR. Tenfold dilutions of B95.8 RNA were mixed with 1 μg of RNA from EBV− K562 cells. Multiplex RT-PCR was performed using primer pairs specific for the β-actin cellular gene and either EBNA2, LMP1, LMP2A, or LMP2B gene. Hybridization was performed with radiolabeled probes specific for each gene. The lengths of the amplified products are shown on the left.
Sensitivity of semiquantitative RT-PCR. Tenfold dilutions of B95.8 RNA were mixed with 1 μg of RNA from EBV− K562 cells. Multiplex RT-PCR was performed using primer pairs specific for the β-actin cellular gene and either EBNA2, LMP1, LMP2A, or LMP2B gene. Hybridization was performed with radiolabeled probes specific for each gene. The lengths of the amplified products are shown on the left.
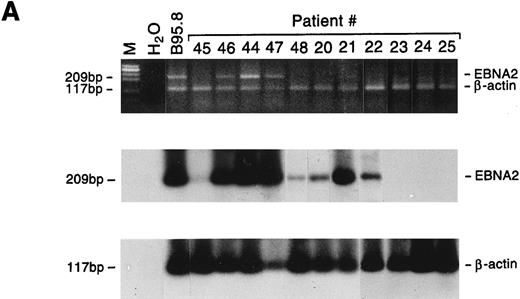
All 5 large cell lymphoma samples expressed the EBNA2 gene, and in 4 of 5 cases LMP1 mRNA was also detected. Both the EBNA2 and LMP1 mRNAs were also detected in 3 of 9 lymphadenopathy samples, whereas 2 additional cases showed positivity only for LMP1 (Fig 5). The relative amounts of EBNA2 and LMP1 mRNAs varied as assessed by comparison with the cellular β-actin transcript, but were consistently higher in lymphomas than in lymphadenopathy samples (Table 5). The detection of LMP1 protein in only 2 specimens (Table 5) may reflect the lower sensitivity of the immunohistochemical analysis, or that the LMP1 mRNA is not always translated, as reported for nasopharyngeal carcinomas.28 Interestingly, LMP2A and LMP2B gene expression was detected only in lymphoma samples. Because the promoters of the LMP2A and LMP2B genes contain the EBNA2-responsive element, their expression may partially reflect differences in EBNA2 expression. Although the LMP2A and LMP2B genes apparently play a nonessential role in in vitro EBV transformation, LMP2A has been suggested to interfere with B-cell signal transduction,29 and LMP2B mRNA was found to be expressed in rare EBV+ peripheral T-cell lymphomas.30
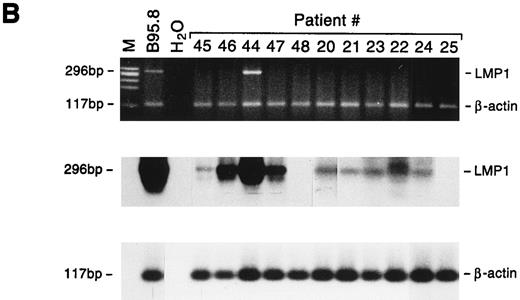
Detection of EBNA2 and LMP1 transcripts in lymphadenopathy lesions and lymphomas. Multiplex-PCR was performed using primers specific for the β-actin gene and either EBNA2 (A) or LMP1 gene (B); the amplified products of 117 bp, 209 bp, and 296 bp, respectively, were stained with ethidium bromide and hybridized with probes specific for EBNA2 or LMP1 and β-actin genes. M, molecular-weight marker φx 174/HaeIII.
Detection of EBNA2 and LMP1 transcripts in lymphadenopathy lesions and lymphomas. Multiplex-PCR was performed using primers specific for the β-actin gene and either EBNA2 (A) or LMP1 gene (B); the amplified products of 117 bp, 209 bp, and 296 bp, respectively, were stained with ethidium bromide and hybridized with probes specific for EBNA2 or LMP1 and β-actin genes. M, molecular-weight marker φx 174/HaeIII.
EBV Gene Expression in HIV-1–Related NHLs and Lymphadenopathies
| Patient Code . | EBV-RNA5-150 . | ICH LMP-1 . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | EBNA2 . | LMP1 . | LMP2A . | LMP2B . | BZLF . | . |
| Large cell lymphoma | ||||||
| 44 | 5.040 | 3.851 | 3.200 | 2.246 | 0.160 | 10% |
| 45 | <0.05 | 0.108 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | — |
| 46 | 1.010 | 2.081 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 5.865 | — |
| 47 | 2.390 | 1.000 | — | — | <0.05 | — |
| 48 | <0.05 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Lymphadenopathy | ||||||
| 20 | <0.05 | <0.05 | — | — | 0.075 | — |
| 21 | 1.880 | <0.05 | — | — | — | 1-2% |
| 22 | <0.05 | <0.05 | — | — | ND | ND |
| 23 | — | <0.05 | — | — | — | — |
| 24 | — | <0.05 | — | — | 0.209 | ND |
| 25 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
| 26 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
| 27 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
| 28 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
| Patient Code . | EBV-RNA5-150 . | ICH LMP-1 . | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | EBNA2 . | LMP1 . | LMP2A . | LMP2B . | BZLF . | . |
| Large cell lymphoma | ||||||
| 44 | 5.040 | 3.851 | 3.200 | 2.246 | 0.160 | 10% |
| 45 | <0.05 | 0.108 | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.05 | — |
| 46 | 1.010 | 2.081 | <0.05 | <0.05 | 5.865 | — |
| 47 | 2.390 | 1.000 | — | — | <0.05 | — |
| 48 | <0.05 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Lymphadenopathy | ||||||
| 20 | <0.05 | <0.05 | — | — | 0.075 | — |
| 21 | 1.880 | <0.05 | — | — | — | 1-2% |
| 22 | <0.05 | <0.05 | — | — | ND | ND |
| 23 | — | <0.05 | — | — | — | — |
| 24 | — | <0.05 | — | — | 0.209 | ND |
| 25 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
| 26 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
| 27 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
| 28 | — | — | — | — | — | ND |
Abbreviation: ND, not done.
The amount of viral RNA was calculated as the ratio between OD values obtained for the specific EBV amplification product and that of the β-actin amplification product.
BZLF mRNA was detected in both lymphadenopathy and lymphoma specimens (Table 5). Not surprisingly, expression of the BZLF gene, a transactivator of EBV lytic genes, did not correlate with EBV latent gene expression. The detection of BZLF1 mRNA in our cases is in agreement with the finding of antibodies to the BZLF1-encoded protein ZEBRA in about 30% of HIV-1 seropositive subjects31 and the presence of ZEBRA protein in a small proportion of neoplastic cells in NHLs arising in HIV-1–infected subjects.32
DISCUSSION
Our analysis of HIV-1–associated lymphadenopathy and lymphoma cases showed that 89% of the lymphadenopathy lesions and 80% of lymphomas tested harbored EBV. Analyses of EBNA2 and LMP1 genes in the EBV+ samples disclosed that all but one lymphoma harbored a single EBV variant, whereas 12 of 25 lymphadenopathy lesions evidenced coinfection with multiple EBV variants. These findings confirm and extend previous data concerning the association of EBV with lymphoproliferative disorders in HIV-1+ subjects,4,7,14 15 and for the first time document the presence of multiple EBV strains and variants differing in EBNA2 and LMP1 genes in a single lymphadenopathy lesion.
Although the detection of both EBV types 1 and 2 in the lymphadenopathies is highly suggestive of exogenous reinfection by different strains, LMP1 variants differing in the number of 33-bp repeats could alternatively be generated by intrastrain homologous recombination during viral replication.10 However, in three cases we found coinfection with two LMP1 variants that differed both in the number of repeats and for the presence or absence of the 15-bp insertion; one of these cases also gave discordant results upon EBNA2 and EBNA3C gene analysis, suggesting that these variants arose from interstrain recombination. Interstrain and intrastrain EBV recombinants were recently documented in EBV+ oral hairy leukoplakia lesions, leading to the proposal that recombination might lead to the generation of more pathogenic variants.33 Intertypic EBV recombinants have also been isolated from blood of HIV-1–infected subjects34; thus, a functional role of the heterogeneous EBV population in the pathogenesis of lymphadenopathy lesions might be proposed as well.
Unlike some reports,5,6 but in agreement with others19 and consistent with the detection of multiple EBV variants, all the lymphadenopathy lesions showed a polyclonal rearrangement of the Ig heavy chain genes. Conversely, all but one EBV+ lymphoma harbored a single EBV variant, thus implying a selective expansion of a single EBV+ cell clone. Indeed, in agreement with other studies,15 35 analysis of Ig heavy chain gene rearrangements confirmed a monoclonal proliferation in most of the lymphomas we studied; moreover, Southern blot detection of only a single episomal form of EBV in these cases strongly indicated that EBV infection preceded transformation.
Although type 2 variants were detected in approximately one third of the EBV+ lymphadenopathies (7 of 25) and mostly in association with EBV type 1 variants, it is noteworthy that 3 of 4 EBV+ Burkitt-like lymphomas, but none of the large cell lymphomas, carried a single EBV type 2 variant. This finding disagrees with previous reports of either type 1 or type 2 in both types of neoplastic lesions.14,15 Given that EBV type 2 transforms B lymphocytes less efficiently than type 1,13 36 it has been proposed that an immunodeficient status in the host might improve its oncogenic potential. Although possible differences in the study groups might explain this variance, it is noteworthy that all of our patients with large cell lymphoma had less than 200 CD4+ cells/μL.
It is generally agreed that Burkitt-like lymphomas express only EBNA1 protein4,7,15,20 (and our unpublished observations, 1996). In contrast, the data regarding EBV expression in large cell lymphomas are discordant. Although some workers reported LMP1 but not EBNA2 expression,19,37 we found both LMP1 and EBNA2 transcripts, in agreement with others.7 EBNA2 constitutes the principal determinant of the biologic difference that enables type 1 strains to transform B cells in vitro more efficiently than type 2 strains.38 Therefore, the different distribution of EBV types in the Burkitt-like and large cell lymphomas, combined with the detection of EBNA2 expression in the neoplastic samples mostly infected by EBV type 1, strongly suggests that the two EBV types play different roles in HIV-1–related malignancies, and that EBNA2 expression contributes to the oncogenic process in large cell lymphomas.
Although LMP1 protein is not significantly different in the two EBV types, it is thought to play a central role in B-cell transformation. The LMP1 gene product promotes B-cell proliferation39 and protects B cells from apoptosis.40 We detected LMP1 gene expression not only in large cell lymphomas, but also in half of the lymphadenopathy cases, albeit at lower levels, with or without coexpression of the EBNA2 gene. Because the detection and amounts of the mRNAs did not correlate with the amount of EBV DNA, the different patterns of EBV expression in these lesions probably represent a selective rather than a merely quantitative process. The inability to detect EBNA2 and LMP1 proteins in lymphadenopathies by immunohistochemical analysis19 had brought into question the role of EBV in these lesions and as a risk factor for the subsequent development of lymphoma. HIV-1 is known to actively and persistently infect lymph nodes, and it has been advanced that chronic antigenic stimulation by the virus might drive development of lymphadenopathy syndrome.41 The detection of EBV transcripts in half of the lymphadenopathies that we tested suggests that EBV also plays an important role in the polyclonal proliferations that characterize lymphadenopathy lesions, either directly, by promoting B-cell survival and proliferation, or indirectly, by inducing EBV-mediated antigenic stimulation. Overall, our findings not only strengthen the notion that lymphomas arise from a clonal expansion of EBV+ cells, but also suggest different roles for EBV types 1 and 2 in HIV-1–related lymphoproliferative disorders.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Sandra Cargnin, Monica Quaggio, and Daniela Zullato for technical assistance, Pierantonio Gallo for artwork, and Patricia Segato and Donna D'Agostino for help in preparing the manuscript.
Supported by grants from AIRC (1995 and 1996), and by grants from Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Progetto AIDS (1995 and 1996). The Oncology Section participated in the Human Capital and Mobility Research Network (ERBCHRXCT940651).
Address reprint requests to Anita De Rossi, PhD, Department of Oncology and Surgical Sciences, Oncology Section, University of Padova, Via Gattamelata 64, 35128 Padova, Italy.





This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal